Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of cilia and mucus-producing cells in the bronchi and bronchioles?
What is the primary role of cilia and mucus-producing cells in the bronchi and bronchioles?
- To capture foreign particles and facilitate their removal (correct)
- To enhance the elasticity of the lungs
- To assist in gas exchange
- To support the structure with cartilaginous rings
How do the lungs adhere to the thoracic cavity?
How do the lungs adhere to the thoracic cavity?
- Via the connection of the alveolar walls to the blood vessels
- By the pressure created in the pleural space (correct)
- Through muscle contractions of the diaphragm
- With the help of cartilaginous rings in the bronchi
Which structure primarily controls the air pressure in the lungs?
Which structure primarily controls the air pressure in the lungs?
- Alveoli
- Bronchioles
- Diaphragm (correct)
- The trachea
Which statement about alveoli is true?
Which statement about alveoli is true?
How many lobes does the right lung have?
How many lobes does the right lung have?
What percentage of oxygen exchange occurs via facilitated diffusion?
What percentage of oxygen exchange occurs via facilitated diffusion?
Which molecule predominantly carries oxygen in the blood?
Which molecule predominantly carries oxygen in the blood?
What is the primary role of the Medulla Oblongata in respiration?
What is the primary role of the Medulla Oblongata in respiration?
What type of infection is most commonly associated with tonsillitis?
What type of infection is most commonly associated with tonsillitis?
What is a major concern about the removal of tonsils?
What is a major concern about the removal of tonsils?
What is the primary treatment for chronic bronchitis?
What is the primary treatment for chronic bronchitis?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of laryngitis?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of laryngitis?
What bacterium is most commonly associated with lobular pneumonia?
What bacterium is most commonly associated with lobular pneumonia?
What constitutes the majority of carbon dioxide transport in the blood?
What constitutes the majority of carbon dioxide transport in the blood?
What type of pneumonia is generally considered less severe?
What type of pneumonia is generally considered less severe?
Which condition is characterized by the breakdown of alveolar walls, leading to permanent changes in lung function?
Which condition is characterized by the breakdown of alveolar walls, leading to permanent changes in lung function?
What is a common cause of pleurisy?
What is a common cause of pleurisy?
Which of the following treatments is commonly required for individuals with cystic fibrosis?
Which of the following treatments is commonly required for individuals with cystic fibrosis?
What role does smoking play in emphysema?
What role does smoking play in emphysema?
Which of the following is a characteristic symptom of asthma?
Which of the following is a characteristic symptom of asthma?
What is a common treatment option for individuals suffering from oxygen shortage due to emphysema?
What is a common treatment option for individuals suffering from oxygen shortage due to emphysema?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
What is the primary function of the respiratory system?
Which of the following accurately describes the stages of respiration?
Which of the following accurately describes the stages of respiration?
What is the role of the ciliated cells in the nasal passages?
What is the role of the ciliated cells in the nasal passages?
What function does the epiglottis serve during swallowing?
What function does the epiglottis serve during swallowing?
Which part of the respiratory system is primarily responsible for phonation?
Which part of the respiratory system is primarily responsible for phonation?
What is the role of turbinate bones in the nasal cavity?
What is the role of turbinate bones in the nasal cavity?
What ensures that respiration meets the body's needs effectively?
What ensures that respiration meets the body's needs effectively?
During internal respiration, which of the following occurs?
During internal respiration, which of the following occurs?
What is a leading cause of lung cancer?
What is a leading cause of lung cancer?
What is the purpose of a peak flow meter in asthma management?
What is the purpose of a peak flow meter in asthma management?
What does metastasis refer to in the context of lung cancer?
What does metastasis refer to in the context of lung cancer?
Which type of scan is primarily used for detecting lung cancer?
Which type of scan is primarily used for detecting lung cancer?
Why are helical low-dose CT scans more effective than previous CT scans?
Why are helical low-dose CT scans more effective than previous CT scans?
What harmful effect can tumors have on lung function?
What harmful effect can tumors have on lung function?
What do researchers aim to improve in lung cancer diagnosis?
What do researchers aim to improve in lung cancer diagnosis?
Which of the following substances is classified as a carcinogen found in tobacco smoke?
Which of the following substances is classified as a carcinogen found in tobacco smoke?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Overview of the Respiratory System
- Responsible for oxygen delivery to cells and removal of carbon dioxide.
- Efficient gas exchange requires adequate surface area and a moist environment.
Stages of Respiration
- Breathing involves:
- Inspiration: Breathing in.
- Expiration: Breathing out.
- External Respiration: Gas exchange between air and blood.
- Internal Respiration: Gas exchange between tissues and blood.
- Cellular Respiration: Utilization of oxygen to release energy and produce carbon dioxide.
Upper Respiratory Tract Components
- Nostrils and nasal passages:
- Lined with ciliated cells for air filtration, warming, and moisturizing.
- Turbinate bones increase surface area, aiding in air purification.
- Pharynx (throat): Passageway for air and food.
- Epiglottis: Flap preventing food from entering airways during swallowing.
- Larynx (voice box): Contains vocal cords; length determines pitch of sound.
- Trachea (windpipe): C-shaped cartilaginous structures provide support.
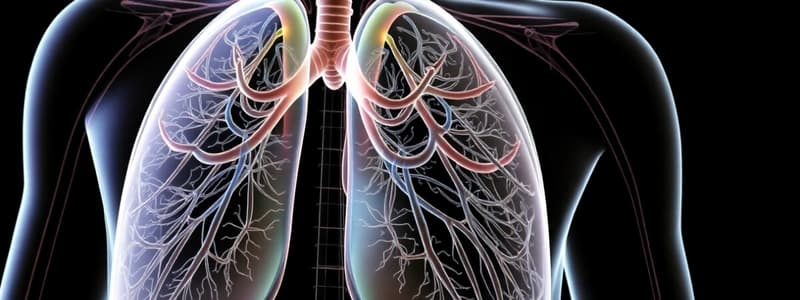
Lower Respiratory Tract Components
- Bronchi: Main passageways dividing from the trachea, having C-shaped rings for support.
- Bronchioles: Smaller branches without cartilaginous rings; lined with cilia and mucus cells.
- Lungs:
- Three lobes on the right, two on the left.
- Surrounded by pleural membrane creating a vacuum that aids lung function.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs where gas exchange occurs; one-cell thick walls promote efficient exchange with capillaries.
Mechanics of Breathing
- Controlled by diaphragm and intercostal muscles, influencing lung air pressure.
- Facilitated Diffusion: About 30% gas exchange enhanced by proteins in alveolar membranes.
- Oxygen (99%) transported primarily by hemoglobin; CO2 transported in varied forms (23% hemoglobin, 7% plasma, 70% as bicarbonate).
Regulation of Breathing
- Medulla Oblongata monitors blood CO2 levels and adjusts respiration rate accordingly.
Upper Respiratory Tract Infections
- Tonsillitis: Viral infection of tonsils; tonsils prevent pathogen entry but can lead to increased life infections post-removal.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the larynx due to viral infection causing sore throat and hoarseness.
Lower Respiratory Tract Disorders
- Bronchitis: Inflamed bronchi filled with mucus; acute (bacterial) treatable with antibiotics; chronic (often due to smoking) lacks cure.
- Pneumonia: Inflamed alveoli filled with liquids; can be lobular or bronchial, caused by bacteria or viruses.
- Pleurisy: Inflammation of pleura due to infections or other factors, causing sharp localized chest pain.
- Emphysema: Permanent breakdown of alveolar walls, reducing gas exchange surface area; commonly caused by smoking.
Genetic and Chronic Respiratory Disorders
- Cystic Fibrosis: Genetic disorder causing thick mucus in lungs; leads to infections and reduced function; treated with mucus-thinning medications.
- Asthma: Chronic condition causing bronchi constriction and excess mucus; managed with inhalers but not curable.
- Lung Cancer: Uncontrolled growth of abnormal lung cells; primary causes include smoking, radon exposure, and asbestos.
Technology and Lung Cancer Detection
- Lung cancer typically diagnosed at advanced stages using CT scans.
- Research focuses on early detection strategies, including DNA analysis for potential cancerous cells.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.