Podcast
Questions and Answers
What degree of flexion is required for the flexion-rotation drawer test?
What degree of flexion is required for the flexion-rotation drawer test?
- 10-15°
- 0-5°
- 15-20° (correct)
- 25-30°
What is the primary aim of the acute phase of treatment?
What is the primary aim of the acute phase of treatment?
- Strengthen quadriceps
- Control pain and swelling (correct)
- Establish normal gait mechanics
- Restore full flexion
What is the primary reason for using crutches in the acute phase?
What is the primary reason for using crutches in the acute phase?
- To accelerate strengthening
- To promote normal gait mechanics
- To reduce pain
- To minimize joint effusion and edema (correct)
What is the expected outcome for knee extension in the acute phase?
What is the expected outcome for knee extension in the acute phase?
What is the purpose of patella mobilization in the acute phase?
What is the purpose of patella mobilization in the acute phase?
What is the indicator for progression to full weight-bearing?
What is the indicator for progression to full weight-bearing?
What is a precaution that should be taken in the acute phase?
What is a precaution that should be taken in the acute phase?
What is the goal of quadriceps activation in the acute phase?
What is the goal of quadriceps activation in the acute phase?
What is the primary focus of Phase 1 in the provided rehabilitation program?
What is the primary focus of Phase 1 in the provided rehabilitation program?
What is added to the exercise routine in Phase 2?
What is added to the exercise routine in Phase 2?
When should the physician be alerted?
When should the physician be alerted?
What type of exercises are initiated in Phase 1?
What type of exercises are initiated in Phase 1?
What is the primary goal of Phase 1 (0-2 weeks) of the rehabilitation program?
What is the primary goal of Phase 1 (0-2 weeks) of the rehabilitation program?
What is the goal of strengthening exercises in Phase 2?
What is the goal of strengthening exercises in Phase 2?
What is the recommended treatment for the first week of Phase 1?
What is the recommended treatment for the first week of Phase 1?
What type of exercises are continued from Phase 1 in Phase 2?
What type of exercises are continued from Phase 1 in Phase 2?
What is emphasized in Phase 2 to minimize joint stress?
What is emphasized in Phase 2 to minimize joint stress?
What is the target range of motion for knee flexion during Phase 1?
What is the target range of motion for knee flexion during Phase 1?
What is the purpose of static quadriceps contractions?
What is the purpose of static quadriceps contractions?
What is added to the exercise routine to improve neuromuscular control?
What is added to the exercise routine to improve neuromuscular control?
How often should the quadriceps strengthening exercises be performed during Phase 1?
How often should the quadriceps strengthening exercises be performed during Phase 1?
What is the purpose of patellar mobilization?
What is the purpose of patellar mobilization?
What is the purpose of gait drills during Phase 1?
What is the purpose of gait drills during Phase 1?
What is the purpose of ankle pump exercises during Phase 1?
What is the purpose of ankle pump exercises during Phase 1?
What is the primary focus of Phase 3 in the rehabilitation program?
What is the primary focus of Phase 3 in the rehabilitation program?
What type of exercises are initiated in Phase 3 to improve neuromuscular control?
What type of exercises are initiated in Phase 3 to improve neuromuscular control?
What is a caution or contraindication in Phase 3?
What is a caution or contraindication in Phase 3?
What is the criteria for progressing to Phase 3?
What is the criteria for progressing to Phase 3?
What is a sign to alert the physician in Phase 3?
What is a sign to alert the physician in Phase 3?
What type of exercises are progressed in Phase 3?
What type of exercises are progressed in Phase 3?
What is the goal of maximizing strength in Phase 3?
What is the goal of maximizing strength in Phase 3?
What is the final goal of Phase 3?
What is the final goal of Phase 3?
What is the warning to the patient regarding the knee when sitting or laying down?
What is the warning to the patient regarding the knee when sitting or laying down?
What percentage of partial weight bearing with two crutches is allowed from the first postoperative day?
What percentage of partial weight bearing with two crutches is allowed from the first postoperative day?
How long must cryotherapy be performed after every exercise session?
How long must cryotherapy be performed after every exercise session?
What is added to the protocol if there is lack of extension?
What is added to the protocol if there is lack of extension?
How often should patellar mobilization be done?
How often should patellar mobilization be done?
What is the best way to check extension during the exercise?
What is the best way to check extension during the exercise?
What is the primary goal of Phase 2 of the rehabilitation protocol?
What is the primary goal of Phase 2 of the rehabilitation protocol?
What is the weight used for passive knee extension in prone position?
What is the weight used for passive knee extension in prone position?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
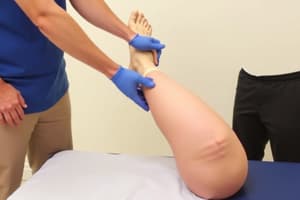
Flexion-Rotation Drawer Test
- The flexion-rotation drawer test is performed with the knee flexed 15-20° and the tibia in neutral rotation.
- The examiner grasps the leg at the ankle, and the weight of the thigh leads to posterior translation with lateral rotation of the femur and anterior translation of the tibia, resulting in anterolateral instability.
Rehabilitation Phases
Phase 1 (Acute Phase, 0-2 weeks)
- Aim: Control pain and swelling, restore pain-free ROM, and emphasize knee extension.
- Recommended treatment:
- Gait and weight-bearing exercises with crutches, progressing to full weight-bearing without crutches.
- ROM exercises, strengthening exercises, patella mobilization, and quadriceps/adductor sets.
- Partial range squats, standing terminal knee extension, standing or prone hamstring curls, and heel raises.
Phase 2 (Sub-Acute Phase, 2-12 weeks)
- Aim: Maintain full ROM and flexibility, progress strengthening exercises, and improve neuromuscular control.
- Recommended treatment:
- Continue Phase 1 exercises, adding bicycle/elliptical with increased resistance.
- Avoid patella femoral joint stress.
- Single leg balance exercises and proprioception exercises.
Phase 3 (Limited Return to Activity/Sport, 2-12 weeks)
- Aim: Maintain full ROM and flexibility, maximize strength, initiate single leg exercises, and maximize neuromuscular control.
- Recommended treatment:
- Straight ahead jogging, plyometrics, and treadmill with progressive resistance.
- Continue Phase 2 exercises, adding step-ups, single-limb balance, and static lunges.
- Avoid patella femoral joint stress, especially with plyometrics.
- Initiate return to sport/work activities with physician approval.
Exercise Program
Phase 1 (0-2 weeks)
- Gentle knee flexion exercises to achieve 100°-110° knee flexion.
- Extension ROM to 0°, quadriceps/VMO setting, supported calf raises, hip abduction and extension, and hamstring pulleys/rubbers.
- Static quadriceps contractions, ankle pump, and patellar mobilization.
Patient Education
- Keep the knee straight when sitting or laying down.
- Warning: Avoid placing supports under the knee to prevent loss of extension.
- Gait drills: partial weight bearing with two crutches, gradually increasing as tolerated.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.