Podcast
Questions and Answers
In the Slocum test I, the MT stabilizes the foot and draws the tibia anteriorly and 30 degrees of ______ rotation.
In the Slocum test I, the MT stabilizes the foot and draws the tibia anteriorly and 30 degrees of ______ rotation.
medial
In the Slocum test II, the tibia is drawn anteriorly with 15 degrees of ______ rotation.
In the Slocum test II, the tibia is drawn anteriorly with 15 degrees of ______ rotation.
lateral
The lateral pivot shift test assesses anterolateral ______ or ACL injuries.
The lateral pivot shift test assesses anterolateral ______ or ACL injuries.
instability
During the lateral pivot shift test, the patient is positioned supine with hip flexed and abducted at ______ degrees.
During the lateral pivot shift test, the patient is positioned supine with hip flexed and abducted at ______ degrees.
The patient experiences hypermobility or pain in the ______ knee during the Slocum test I.
The patient experiences hypermobility or pain in the ______ knee during the Slocum test I.
MT ______ medically rotates tibia and extends the knee.
MT ______ medically rotates tibia and extends the knee.
Clarks sign is used to assess patella femoral ______ or chondromalacia.
Clarks sign is used to assess patella femoral ______ or chondromalacia.
In the brush/ stroke/ bulge test, a wave of fluid passes to the ______ side.
In the brush/ stroke/ bulge test, a wave of fluid passes to the ______ side.
McConnell's test determines if pain is lessened with ______ pressure during isometric quad contraction.
McConnell's test determines if pain is lessened with ______ pressure during isometric quad contraction.
During Helfet's test, the patient is seated with the knee ______ while the therapist extends the knee.
During Helfet's test, the patient is seated with the knee ______ while the therapist extends the knee.
The Valgus/Abduction stress test checks for ______ instability.
The Valgus/Abduction stress test checks for ______ instability.
The Varus abduction test evaluates ______ instability.
The Varus abduction test evaluates ______ instability.
In the anterior drawer test, the patient is positioned supine with the knee flexed at ______ degrees.
In the anterior drawer test, the patient is positioned supine with the knee flexed at ______ degrees.
Lachman's test is used to detect an ______ injury.
Lachman's test is used to detect an ______ injury.
The posterior drawer/sag sign test is performed with the knee flexed at ______ degrees.
The posterior drawer/sag sign test is performed with the knee flexed at ______ degrees.
A positive sign in the anterior drawer test indicates ______ mobility.
A positive sign in the anterior drawer test indicates ______ mobility.
During the Valgus test, a valgus force is applied to the knee when it is not ______.
During the Valgus test, a valgus force is applied to the knee when it is not ______.
In the Lachman's test, a soft mushy end feel indicates ______ mobility.
In the Lachman's test, a soft mushy end feel indicates ______ mobility.
MT holds distal tibia and posteriorly to the head of the ______ and great anterior/medial rotary force at the knee.
MT holds distal tibia and posteriorly to the head of the ______ and great anterior/medial rotary force at the knee.
Hughson's posterior medial rotation involves the ______ and PCL.
Hughson's posterior medial rotation involves the ______ and PCL.
The medial and lateral drawer test assesses the ______ and PCL.
The medial and lateral drawer test assesses the ______ and PCL.
Alley's compression test is used to diagnose ______ injury.
Alley's compression test is used to diagnose ______ injury.
Bounce home test checks for ______ injury or foreign body within the joint.
Bounce home test checks for ______ injury or foreign body within the joint.
McMurray's test is specifically designed to evaluate ______ injury.
McMurray's test is specifically designed to evaluate ______ injury.
Pain on distraction during Alley's compression test indicates ______ injury.
Pain on distraction during Alley's compression test indicates ______ injury.
A clicking or popping sound during McMurray's test may indicate a ______ injury.
A clicking or popping sound during McMurray's test may indicate a ______ injury.
If pain is felt while pushing the patella medially, it may indicate ______ dysfunction.
If pain is felt while pushing the patella medially, it may indicate ______ dysfunction.
During a squat, if the therapist tracks the knee, pain or ______ may suggest tracking dysfunction.
During a squat, if the therapist tracks the knee, pain or ______ may suggest tracking dysfunction.
In Kliegers test, medial or lateral ankle pain can indicate a deltoid ligament tear or ______ tear.
In Kliegers test, medial or lateral ankle pain can indicate a deltoid ligament tear or ______ tear.
During the Talar Tilt test, excessive movement on adduction suggests an issue with the ______ ligament.
During the Talar Tilt test, excessive movement on adduction suggests an issue with the ______ ligament.
The Fiess Line test assesses instability of the medial arch and evaluates the ______ tuberosity position.
The Fiess Line test assesses instability of the medial arch and evaluates the ______ tuberosity position.
In Homans test, pain during dorsiflexion with the knee extended may indicate ______.
In Homans test, pain during dorsiflexion with the knee extended may indicate ______.
The Thompson test is used to assess for an Achilles ______ by noticing the absence of plantar flexion.
The Thompson test is used to assess for an Achilles ______ by noticing the absence of plantar flexion.
Morton's test involves squeezing at the ______ to check for pain indicative of neuroma or stress fracture.
Morton's test involves squeezing at the ______ to check for pain indicative of neuroma or stress fracture.
Flashcards
Valgus Stress Test
Valgus Stress Test
Checks for medial collateral ligament (MCL) instability in the knee.
Varus Stress Test
Varus Stress Test
Assess for lateral collateral ligament (LCL) instability in the knee.
Anterior Drawer Test
Anterior Drawer Test
Examines the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) for instability, checking translation of the tibia.
Lachman's Test
Lachman's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Drawer Test
Posterior Drawer Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
MCL Instability
MCL Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
ACL Instability
ACL Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCL Instability
PCL Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slocum Test I
Slocum Test I
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slocum Test II
Slocum Test II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Pivot Shift
Lateral Pivot Shift
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Tibial Translation
Posterior Tibial Translation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee Instability
Knee Instability
Signup and view all the flashcards
MT test
MT test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Helfet test
Helfet test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brush/stroke/bulge signs
Brush/stroke/bulge signs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clark's sign
Clark's sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
McConnell's test
McConnell's test
Signup and view all the flashcards
MT Hold Test
MT Hold Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hughston's Posterior Drawer Test
Hughston's Posterior Drawer Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aley's Compression Test
Aley's Compression Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bounce Home Test
Bounce Home Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
McMurray's Test
McMurray's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
MCL
MCL
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCL
PCL
Signup and view all the flashcards
LCL
LCL
Signup and view all the flashcards
Waldron's test
Waldron's test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Klieger's test
Klieger's test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talar Tilt test
Talar Tilt test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fiess Line test
Fiess Line test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homans' test
Homans' test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thompson's test
Thompson's test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morton's test
Morton's test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patellofemoral dysfunction
Patellofemoral dysfunction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Knee Instability Tests
-
Valgus/ Abduction Stress Test: Tests for medial instability (MCL). Patient is supine with the knee in extension. The examiner applies a valgus force to the knee. A positive sign is hypermobility.
-
Varus Abduction Test: Assesses lateral instability (LCL). The patient is supine, and the examiner applies a varus force to the knee. A positive sign is hypermobility.
-
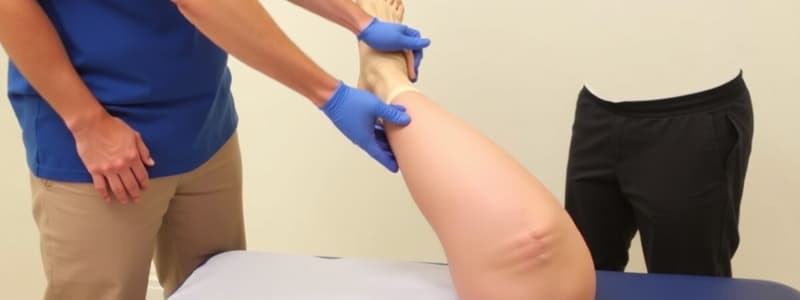
Anterior Drawer Test: Evaluates ACL instability. The patient is supine with the knee flexed to 90 degrees. The examiner stabilizes the foot and pulls the tibia anteriorly. A positive sign is hypermobility (more than 6 mm anterior translation).
-
Lachman's Test: Assesses ACL injury. Similar to the anterior drawer test; the patient is supine with the knee flexed at 30 degrees. The examiner pulls the tibia anteriorly while pushing the femur posteriorly. A positive sign is soft end-feel and hypermobility.
-
Posterior Drawer/ Sag Sign: Tests PCL instability. The patient is supine, knee flexed at 90 degrees. The examiner stabilizes the foot and pushes the tibia posteriorly. A positive sag sign indicates PCL instability. Pain and hypermobility are positive signs.
-
Slocum Test I: Examines anterolateral instability (ACL, LCL, ITB). The patient is supine with the knee flexed at 90 degrees, the hip at 45 degrees. The examiner stabilizes the foot. The examiner draws the tibia anteriorly. A positive sign includes hypermobility and pain in the lateral knee.
-
Slocum Test II: Assesses MCL/ACL instability, with the patient in the same position as Slocum test I but with 15 degrees of medial rotation. Positive findings indicate hypermobility and pain in the medial knee.
Other Knee Tests
-
Lateral Pivot Shift: Tests anterolateral instability. A positive sign is instability, potentially due to an ACL or IT band injury where the knee gives way during rotation.
-
Hughson's Posterior Drawer/ Lateral Drawer: For posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), medial collateral ligament (MCL) and lateral collateral ligament (LCL) damage.
-
Apley's Compression Test: Examines for injury of the meniscus and ligaments. A positive reaction is pain on distraction, and compression.
-
Bounce Home Test: Assesses meniscus injury and for foreign bodies within the knee joint.
-
McMurray's Test: Diagnoses a meniscal tear by causing pain.
-
Helfet's Test: Tests for impaired quadriceps.
-
Brushstroke/ Bulge Test: Identifies presence of fluid in the knee joint. A positive result is a wave of fluid.
-
Clark Sign: Tests for meniscus injury or patellofemoral problems.
-
McConnell's Test: Analyzes patellofemoral problems and pain associated with chondromalacia.
-
Walrond's Test: Identifies patellofemoral problems and pain.
-
Klieger's Lateral Rotation: Evaluates deltoid ligament and other ligament tears.
-
Talar Tilt: Checks for calcaneofibular ligament and deltoid ligament injury.
-
Fess Line Test: Checks for the instability of the medial arch.
-
Homans Test: Checks for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in the legs.
-
Thompson Test: Assesses Achilles tendon rupture. The patient is prone and the examiner squeezes the calf.
-
Morton's Test: Analyzes metatarsal stress fracture and Morton's neuroma. The patient is supine and the examiner squeezes at the metatarsal.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.