Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does the Slocum test I assess?
What does the Slocum test I assess?
- Patellar instability
- Medial collateral ligament injury
- Anterolateral instability (correct)
- Posteromedial instability
What position is the patient in during the Slocum test II?
What position is the patient in during the Slocum test II?
- Prone with extended knees
- Side-lying with abducted hips
- Supine with knees flexed at 90 degrees (correct)
- Supine with knees extended
What is indicated if a patient experiences hypermobility during the Slocum test I?
What is indicated if a patient experiences hypermobility during the Slocum test I?
- Anterolateral instability (correct)
- Patellar dislocation
- Injury to the ITB
- Lateral meniscus tear
In the lateral pivot shift test, what sensation may the patient experience?
In the lateral pivot shift test, what sensation may the patient experience?
What specific rotation is applied during Slocum test II?
What specific rotation is applied during Slocum test II?
What is the purpose of the Hughsons posterior drawer test?
What is the purpose of the Hughsons posterior drawer test?
During the Alleys compression test, what does pain on distraction indicate?
During the Alleys compression test, what does pain on distraction indicate?
What does a rubbery end feel during the Bounce Home test suggest?
What does a rubbery end feel during the Bounce Home test suggest?
What is assessed by McMurray's test?
What is assessed by McMurray's test?
In the Hughsons posterior drawer test, the position of the tibia is tested for what sign?
In the Hughsons posterior drawer test, the position of the tibia is tested for what sign?
What does pain on compression during the Alleys compression test indicate?
What does pain on compression during the Alleys compression test indicate?
During McMurray's test, which symptom is often observed due to meniscal tears?
During McMurray's test, which symptom is often observed due to meniscal tears?
What knee position is used during the Alleys compression test?
What knee position is used during the Alleys compression test?
What does the MT snapping technique primarily do?
What does the MT snapping technique primarily do?
What indicates a meniscus tear during the Helfet test?
What indicates a meniscus tear during the Helfet test?
What does the brush/stroke/bulge test assess?
What does the brush/stroke/bulge test assess?
During Clarke's sign, what is the expected result if there is patellofemoral dysfunction?
During Clarke's sign, what is the expected result if there is patellofemoral dysfunction?
What is assessed in McConnell's test?
What is assessed in McConnell's test?
What does the Valgus/Abduction stress test assess?
What does the Valgus/Abduction stress test assess?
Which test is conducted with the patient supine and the knee flexed at 90 degrees?
Which test is conducted with the patient supine and the knee flexed at 90 degrees?
What is the positive sign associated with the Lachman's test?
What is the positive sign associated with the Lachman's test?
What condition does the posterior drawer / sag sign test evaluate?
What condition does the posterior drawer / sag sign test evaluate?
Which of the following tests requires the therapist to apply a varus force?
Which of the following tests requires the therapist to apply a varus force?
What position is the patient in for both the anterior drawer and posterior drawer tests?
What position is the patient in for both the anterior drawer and posterior drawer tests?
What is indicated when there is hypermobility greater than 6 mm anterior translation during the anterior drawer test?
What is indicated when there is hypermobility greater than 6 mm anterior translation during the anterior drawer test?
What is the reported sign during the Varus abduction test?
What is the reported sign during the Varus abduction test?
What is indicated if a patient experiences pain while performing a squat and the therapist tracks the knee?
What is indicated if a patient experiences pain while performing a squat and the therapist tracks the knee?
During the Kliegers test, what indicates a deltoid ligament tear?
During the Kliegers test, what indicates a deltoid ligament tear?
What is assessed by the Talar Tilt test?
What is assessed by the Talar Tilt test?
In the Fiess Line test, what does it indicate if the navicular tuberosity drops to touch the floor?
In the Fiess Line test, what does it indicate if the navicular tuberosity drops to touch the floor?
What is being assessed with Homans test?
What is being assessed with Homans test?
What outcome indicates an Achilles rupture during the Thompson test?
What outcome indicates an Achilles rupture during the Thompson test?
What symptom is associated with Morton's test?
What symptom is associated with Morton's test?
What does excessive movement on abduction during the Talar Tilt test indicate?
What does excessive movement on abduction during the Talar Tilt test indicate?
Flashcards
Valgus stress test
Valgus stress test
Tests for medial collateral ligament (MCL) instability. A valgus force is applied to the knee.
Varus stress test
Varus stress test
Evaluates lateral collateral ligament (LCL) stability. A varus force (outward push) on the knee is used.
Anterior drawer test
Anterior drawer test
Checks for anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) instability. The tibia is pulled forward while the femur is pushed back.
Lachman’s test
Lachman’s test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior sag sign
Posterior sag sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Drawer Test
Posterior Drawer Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
MCL
MCL
Signup and view all the flashcards
ACL
ACL
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slocum Test I
Slocum Test I
Signup and view all the flashcards
Slocum Test II
Slocum Test II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Pivot Shift Test
Lateral Pivot Shift Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does a 'sag' indicate?
What does a 'sag' indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does 'hypermobility' during Slocum tests suggest?
What does 'hypermobility' during Slocum tests suggest?
Signup and view all the flashcards
MT Hold
MT Hold
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hughston's Posterior Drawer Test
Hughston's Posterior Drawer Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Alleys Compression Test
Alleys Compression Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bounce Home Test
Bounce Home Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
McMurray's Test
McMurray's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Rotation
Medial Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Rotation
Lateral Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sag Sign
Sag Sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
MT Snapping
MT Snapping
Signup and view all the flashcards
Helfet's Test
Helfet's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brush Test
Brush Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clarke's Sign
Clarke's Sign
Signup and view all the flashcards
McConnell's Test
McConnell's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Waldron's Test
Waldron's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Klieger's Test / Lateral Rotation
Klieger's Test / Lateral Rotation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Talar Tilt Test
Talar Tilt Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fiess Line Test
Fiess Line Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Homans Test
Homans Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thompson Test
Thompson Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morton's Test
Morton's Test
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does excessive movement during a Talar Tilt test indicate?
What does excessive movement during a Talar Tilt test indicate?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Knee Examination Tests
-
Valgus/ Abduction Stress Test: Evaluates medial instability (MCL). Performed with the patient supine, applying valgus force to the knee in extension (or when not locked). A positive test shows excessive mobility, indicating possible MCL injury.
-
Varus Abduction Test: Assesses lateral instability (LCL). Performed with the patient supine, a varus force is applied to the knee, and excessive mobility suggests LCL injury.
-
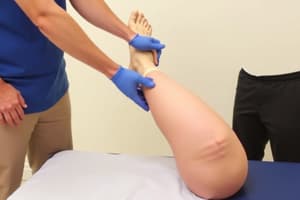
Anterior Drawer Test: Evaluates ACL instability. The patient is supine with the knee flexed at 90 degrees and the hip at 45 degrees; the examiner stabilizes the foot and pulls the tibia anteriorly. Excessive mobility indicates possible ACL injury.
-
Lachman's Test: Used to evaluate ACL injuries. In this test, the patient is supine, the knee is flexed to 30 degrees, and the examiner pulls the tibia anteriorly while pushing the femur posteriorly. A soft mushy end feel or hyper mobility indicates a positive test and possible injury.
-
Posterior Drawer/ Sag Sign: Assesses PCL instability. The patient is supine, and the knee is flexed at 90 degrees. The examiner stabilizes the foot and pushes the tibia posteriorly while looking for a sag sign (posterior movement of the tibia). Hypermobility or pain indicated possible injury.
-
Slocum Test I: Evaluates combined anterolateral instability (ACL, LCL, ITB). The patient is in a supine position, knee flexed at 90, hip at 45; examiner stabilizes the foot and draws the tibia anteriorly. Pain in the lateral knee with hypermobility indicates a positive test.
-
Slocum Test II: Assesses medial instability (MCL and ACL) through the application of medial rotation of the tibia. The patient is supine, knee flexed at 90, and a positive test shows hypermobility and pain in the medial knee.
Additional Tests
-
Lateral Pivot Shift: Evaluates anterolateral instability (ACL or ITB injury) in a specific manner. The patient is supine, hip flexed, abducted, and slight medial knee rotation. The examiner tries to put the knee into distraction and reduction to look for the giving away feeling with reduction at 20-40 degrees flexion.
-
Hughston's Posterior Medial and Lateral Drawer Test: Assesses Posterior/Lateral instability of PCL and LCL. The patient is supine or sitting position, knee flexed at 90 degrees; MT look for sag sign or apply posterior force. Hyper mobility indicates injury
-
Alleys Compression Test: Used to evaluate any type of ligament or meniscus injuries. The patient is prone, knee bent at 90, examiner applying distraction, rotating, and compression to the knee to look for specific pain.
-
Bounce Home Test: Used to diagnose meniscus injury or foreign body within the joint. The examiner pushes the knee back and forth to determine whether the joint returns to its original place.
-
McMurray's Test: A test for meniscus tears, the examiner puts the knee into some stress, twisting the knee whilst pushing in a specific direction to assess pain and sounds produced.
-
Helfet Test: Used to examine possible meniscus tears. In this test, the patient is seated with the knee flexed and the examiner slowly extends the knee while checking the alignment.
-
Other Tests: The document describes various other tests, such as Clarke's sign, Mcconnells test, Waldron's test, Kliegers and Lateral Rot, Talar Tilt, and Fiss line test, with specific methods and potential findings. Important information about the tests is detailed for each one.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.