Podcast
Questions and Answers
Why are operations considered vitally important to any organization?
Why are operations considered vitally important to any organization?
- An organization is evaluated by the perception and not its operational performance.
- Operations are important for ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Operations are essential for marketing promotions and public relations.
- An organization is ultimately judged by its operational performance. (correct)
In the context of operations, what does the transformation process enable an organization to do?
In the context of operations, what does the transformation process enable an organization to do?
- Minimize energy consumption and reduce waste.
- Maximize short-term profits, regardless of long-term consequences.
- Transform a range of basic inputs into outputs for the end customer. (correct)
- Focus exclusively on the needs of internal stakeholders.
How do successful businesses approach value creation for their stakeholders?
How do successful businesses approach value creation for their stakeholders?
- Businesses focus on creating value primarily for shareholders.
- Businesses focus on maximizing short-term profits exclusively.
- Businesses aim to satisfy many stakeholders through comprehensive collaboration. (correct)
- Businesses create value by prioritizing the needs of the local communities.
What is a key aspect of the stakeholder theory?
What is a key aspect of the stakeholder theory?
How does the stakeholder theory view the role of business in society?
How does the stakeholder theory view the role of business in society?
Why might an organization design or redesign its structure?
Why might an organization design or redesign its structure?
What aspects of an organization does its structure define?
What aspects of an organization does its structure define?
On what does the most effective organizational structure depend?
On what does the most effective organizational structure depend?
Which statement accurately describes a vertical organizational structure?
Which statement accurately describes a vertical organizational structure?
What can be a disadvantage of a vertical organizational structure?
What can be a disadvantage of a vertical organizational structure?
How are project managers or team leaders structured in a horizontal organization?
How are project managers or team leaders structured in a horizontal organization?
How might employees in a horizontal organization feel about the company?
How might employees in a horizontal organization feel about the company?
What is a potential limitation of horizontal organizational structures?
What is a potential limitation of horizontal organizational structures?
According to Frank Ostroff, which structure has the ability to be more successful as the world globalizes?
According to Frank Ostroff, which structure has the ability to be more successful as the world globalizes?
When do most new companies and small businesses utilize horizontal organizational structures?
When do most new companies and small businesses utilize horizontal organizational structures?
What is associated with vertically integrated organizations?
What is associated with vertically integrated organizations?
What is a characteristic of a horizontally integrated organization?
What is a characteristic of a horizontally integrated organization?
What is the primary aim of streamlining an organization as an emerging trend?
What is the primary aim of streamlining an organization as an emerging trend?
How might self-directed work teams act as the basic production group as an emerging trend?
How might self-directed work teams act as the basic production group as an emerging trend?
Why is it important to restructure an organization?
Why is it important to restructure an organization?
What results from cutting costs?
What results from cutting costs?
What qualities define leadership?
What qualities define leadership?
What role does flexibility play in leadership?
What role does flexibility play in leadership?
What are the three key objectives that students should achieve after completing this chapter?
What are the three key objectives that students should achieve after completing this chapter?
According to this chapter, where do operations take place?
According to this chapter, where do operations take place?
How would you define the scope of operational responsibilities?
How would you define the scope of operational responsibilities?
What is the ultimate responsibility for senior-level managers within the firm?
What is the ultimate responsibility for senior-level managers within the firm?
What does effective value creation for businesses by levering resources involve?
What does effective value creation for businesses by levering resources involve?
What is the ultimate aim in creating competitive advantage?
What is the ultimate aim in creating competitive advantage?
What is meant by the definition of an organization?
What is meant by the definition of an organization?
What determines the best structures?
What determines the best structures?
What are some advantages of using vertical structure?
What are some advantages of using vertical structure?
What are emerging trends within a business?
What are emerging trends within a business?
According to lecture, why is it important to negotiate?
According to lecture, why is it important to negotiate?
Flashcards
Defining Operations
Defining Operations
Activities transforming inputs (materials, energy, customer requirements, etc.) into outputs for customers.
How is an organization judged?
How is an organization judged?
This is determined by how well the operations perform, not by its mission statement.
Outputs
Outputs
The final product/service offering for the customer, combining physical and psychological elements.
Transformation Inputs
Transformation Inputs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Operations Inputs
Operations Inputs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stakeholder Theory
Stakeholder Theory
Signup and view all the flashcards
Value Creation
Value Creation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Key Result Area of a CEO
Key Result Area of a CEO
Signup and view all the flashcards
Organization Design
Organization Design
Signup and view all the flashcards
The Best Structure depends on:
The Best Structure depends on:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vertical Structure
Vertical Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of Vertical Structures
Advantages of Vertical Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of Vertical Structures
Disadvantages of Vertical Structures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Horizontal Structure
Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Advantages of Horizontal Structure
Advantages of Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disadvantages of Horizontal Structure
Disadvantages of Horizontal Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emerging organizational trends
Emerging organizational trends
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why Restructure?
Why Restructure?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Characteristics of Leadership
Characteristics of Leadership
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Chapter Objectives
- Define operations
- Describe value leadership
- Define different organizational structures
- Explain the key elements in organizational design
- Explain the emerging trends in organizational structures
Understanding Operations
- Operations occur across all sectors, including manufacturing, services, private, and public
- Operations are critical for any organization because an organization's performance is judged by its operations
- The scope of operations is wide-ranging and involves various functions within an organization, not limited to a specific department
Defining Operations
- Operations involve activities that transform basic inputs (materials, energy, customer needs, information, skills, finance) into outputs for the customer
Basic Operations System
- Includes inputs, processes, outputs, and feedback
- Inputs undergo transformation to add value and become finished goods and services
- The final product/service provides tangible and intangible benefits to the customer, linking service and production operations
Leader/Stakeholder Theory and Value Creation
- Entrepreneurs/managers create value by capturing the joint interests of stakeholders
- Stakeholder interests may conflict but align over time
- Stakeholder Theory is an idea about how business works, by creating value for customers, suppliers, employees, communities, financiers, shareholders and banks.
- Social value satisfies stakeholders through collaboration
- An organization's value is what stakeholders seek in a relationship with it
- The process begins with creating goods valued by consumers, and meeting consumer needs more fully, especially given competitors, which is the key result area for a CEO
- It is important to make the best use of resources, to leverage these resources alone or with partners
- Senior-level managers have the ultimate responsibility within the firm ensuring stakeholders benefit and the organization competes and ideally gains competitive advantage
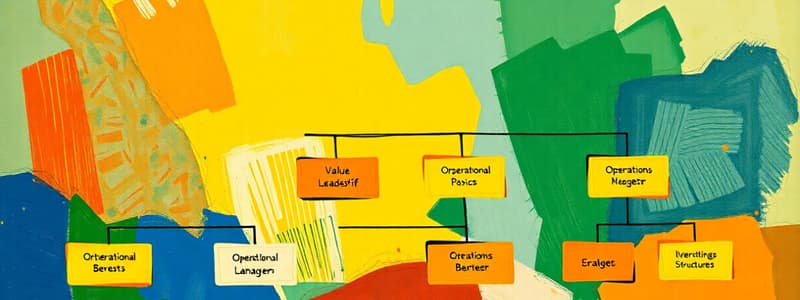
Why Design an Organization
- Organizational design arranges people and jobs to meet goals
- Organizational charts show this graphically
- Design defines responsibilities, accountability, communication, and relationships
- Design involves the organizational components and their relationships
- Design portrays authority and power, and provides a "home" and identity for employees
- Key questions to consider are: What positions exist and how are they grouped? What is the reporting sequence? and What is each person/unit responsible for?
Best Structures
- The best structures depend on: The type of work, the size of the workforce, revenue, geographic dispersion, and degree of diversification
- Two Types of Structures: Vertically (Tall) and Horizontal (flat)
Vertical Structure
- Has a chain of management with a CEO at the top that delegates downward
- Power flows from the top
- There is a well-defined chain of command
- Employees report to superiors in the organizational structure
- Each person has specific duties
Advantages of Vertical Structures
- Efficiency via quick decision-making
- Responsibility is held by those highest in the chain
- Employees have defined duties with specialized tasks
- Designating tasks is easier with well-defined responsibilities
- Generally easier to manage
Disadvantages of Vertical Structures
- Can be rigid with many rules
- Dependent on a strong leader
- Weak upper management can impede decision-making
- Transparency is lacking
- Employees may feel stifled
Horizontal Structure
- Less-defined chain of command where all employees have input
- Employees work in teams instead of having defined duties
- Employees may report to multiple supervisors
- There are almost no middle managers; high-level managers handle day-to-day tasks
- Costs less because there are fewer managers
Advantages of Horizontal Structures
- There are fewer rules
- There is more power in employee hands
- Employee satisfaction can increase
- Employees feel a stronger sense of belonging
Disadvantages of Horizontal Structures
- It is less efficient and requires more time to make decisions
- Workers need more skills, and can increase stress
- It is harder to implement than vertical structures, especially as the business grows
- The company needs a culture of teamwork
- Employees can be less sure of their roles
- Project managers lack authority
Horizontal or Vertical Structures
- Frank Ostroff (2013) notes that companies are becoming more horizontal as the world globalizes
- Organizations should implement the best aspects of both horizontal and vertical structures
- Most new and small businesses utilize a horizontal structure due to a limited amount of employees
- Management styles in these horizontal structures are more informal
- Small businesses may lack resources to hire middle management
Emerging Trends
- Interdependence of different departments
- Response to rapid changing environments
- Streamline the organization to improve communication and decision-making
- The rise of technology that has made virtual organizations boundary-less
- Self-directed work teams are the basic production group
- Motivation, expanding the scope of jobs, involving workers in problem solving and planning, and fostering open communications
Need to Restructure
- Designing Organizations to Create Value (2003) writes that "a poor design can lead to lost profits and even result in the failure of the institution.”
- There is a need to cut costs by removing layers of bureaucracy to drive competitiveness
- There is a need to respond to competition
- There is a response to Jit
Characteristics of Leadership
- Flexibility
- Tenaciousness
- Empathy
- Transparency
- Compassion
- Communication
- Decisiveness
- Conflict resolutions
- Clear vision
- Passion
- Protection
- Understanding
- Problem solving
- Negotiation
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.