Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of sensory neurons?
What is the primary function of sensory neurons?
Sensory neurons detect changes in the internal or external environment and transmit that information to the central nervous system.
Describe the role of interneurons in the nervous system.
Describe the role of interneurons in the nervous system.
Interneurons are located entirely within the central nervous system and facilitate communication between sensory and motor neurons.
List and briefly describe the four main structures of a neuron.
List and briefly describe the four main structures of a neuron.
The four main structures are the soma (cell body), dendrites (receive signals), axon (transmits signals), and terminal buttons (release neurotransmitters).
What distinguishes local interneurons from relay interneurons?
What distinguishes local interneurons from relay interneurons?
How does the soma contribute to the life processes of a neuron?
How does the soma contribute to the life processes of a neuron?
What is the primary function of dendrites in a neuron?
What is the primary function of dendrites in a neuron?
Describe the role of the synapse in neuron communication.
Describe the role of the synapse in neuron communication.
What is the structure and function of an axon?
What is the structure and function of an axon?
What is an action potential and how does it travel along the axon?
What is an action potential and how does it travel along the axon?
Explain the significance of the myelin sheath.
Explain the significance of the myelin sheath.
What happens to the action potential when it reaches branching points in the axon?
What happens to the action potential when it reaches branching points in the axon?
How does the neurolemma contribute to the structure of neurons?
How does the neurolemma contribute to the structure of neurons?
What Greek word is the origin of the term 'dendrite' and how does it relate to its structure?
What Greek word is the origin of the term 'dendrite' and how does it relate to its structure?
What is the role of the neuron’s membrane in maintaining cellular function?
What is the role of the neuron’s membrane in maintaining cellular function?
How do mitochondria contribute to a neuron's energy management?
How do mitochondria contribute to a neuron's energy management?
What is the significance of proteins embedded in the neuron's membrane?
What is the significance of proteins embedded in the neuron's membrane?
What are chromosomes, and what role do they play in cellular function?
What are chromosomes, and what role do they play in cellular function?
Explain the function of genes within chromosomes.
Explain the function of genes within chromosomes.
What characteristic distinguishes multipolar neurons from bipolar and unipolar neurons?
What characteristic distinguishes multipolar neurons from bipolar and unipolar neurons?
Describe the primary function of sensory bipolar neurons.
Describe the primary function of sensory bipolar neurons.
Explain how unipolar neurons transmit sensory information.
Explain how unipolar neurons transmit sensory information.
What role do terminal buttons play in neuronal communication?
What role do terminal buttons play in neuronal communication?
What structures allow the CNS to communicate with the rest of the body?
What structures allow the CNS to communicate with the rest of the body?
How do the shapes of axons and dendrites differ among the three types of neurons?
How do the shapes of axons and dendrites differ among the three types of neurons?
What is the significance of the action potential in relation to terminal buttons?
What is the significance of the action potential in relation to terminal buttons?
In what way do the dendrites of unipolar neurons contribute to sensory detection?
In what way do the dendrites of unipolar neurons contribute to sensory detection?
What is the cytoskeleton and its significance in a neuron's shape?
What is the cytoskeleton and its significance in a neuron's shape?
How do enzymes contribute to cellular function within neurons?
How do enzymes contribute to cellular function within neurons?
Describe the role of microtubules in axoplasmic transport.
Describe the role of microtubules in axoplasmic transport.
What are the differences between anterograde and retrograde axoplasmic transport?
What are the differences between anterograde and retrograde axoplasmic transport?
What is the source of energy for axoplasmic transport in neurons?
What is the source of energy for axoplasmic transport in neurons?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Neuron Structure & Function
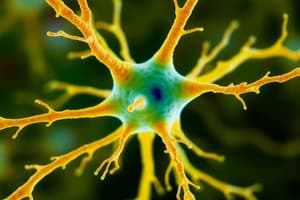
- The Neuron is the fundamental unit of the nervous system, responsible for information processing and transmission.
- Neurons come in diverse forms, adapting to their specialized roles.
- Key Neuron Structures:
- Soma (Cell Body): Contains the nucleus and vital cellular machinery for life processes.
- Dendrites: Treelike branches extending from the soma, receiving information from other neurons.
- Axon: Long, slender tube conveying information from the cell body to the terminal buttons.
- Terminal Buttons: Knob-like structures at the end of axons, releasing neurotransmitters to communicate with other neurons.
- Synapse: The junction between the terminal button of an axon and the dendrite/soma of another neuron, facilitating unidirectional communication.
Neuron Types
- Multipolar Neuron: The most common type, characterized by one axon and multiple dendrites extending from the soma.
- Bipolar Neuron: Possesses one axon and one dendrite positioned at opposite ends of the soma. Typically sensory neurons, detecting environmental changes.
- Unipolar Neuron: Characterized by one axon connected to the soma, branching to receive sensory information and send it to the CNS. Often involved in detecting touch, temperature, and other sensory events.
Internal Structure
- Membrane: The cell's boundary, composed of a lipid bilayer that houses various protein molecules with specific functions.
- Some proteins detect external substances (e.g., hormones) and communicate their presence within the cell.
- Others control access to the cell, selectively allowing substances to enter or exit.
- Transporters actively move specific molecules into or out of the cell.
- Cytoplasm: A jelly-like substance within the cell containing specialized structures, including:
- Mitochondria: Break down nutrients (e.g., glucose) and provide energy for cellular functions by producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Nucleus: Contains chromosomes composed of DNA strands that hold the "recipes" for protein synthesis.
- Genes: Sections of the chromosome directing the synthesis of specific proteins, crucial for cell function.
- Cytoskeleton: A protein matrix that provides structural support and shape to the neuron.
- Composed of various protein strands linked together to form a cohesive network.
- Axoplasmic Transport: An active process that transports substances efficiently along the axon, vital for delivering materials from the soma to the terminal buttons and vice versa.
- Anterograde Transport: From the soma to the terminal buttons.
- Retrograde Transport: From the terminal buttons to the soma.
- Both forms of transport rely on microtubules (protein strands) for their movement.
- Energy for these processes is provided by ATP produced by mitochondria.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.