Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary structural difference between a nerve and a neuron?
What is the primary structural difference between a nerve and a neuron?
- Nerves are bundles of axons while neurons are individual cells. (correct)
- Nerves are exclusively found in the CNS.
- Nerves do not transmit any impulses.
- Nerves consist only of myelinated axons.
Where are bundles of neurons known as tracts located?
Where are bundles of neurons known as tracts located?
- Only in the brain.
- Both peripheral and central nervous systems.
- In the peripheral nervous system.
- In the central nervous system. (correct)
Which type of neuron is responsible for carrying signals towards the central nervous system?
Which type of neuron is responsible for carrying signals towards the central nervous system?
- Interneurons
- Efferent neurons
- Motor neurons
- Sensory neurons (correct)
Which type of neuron is primarily responsible for transmitting signals within the central nervous system?
Which type of neuron is primarily responsible for transmitting signals within the central nervous system?
Which hemisphere of the brain primarily controls writing for right-handers?
Which hemisphere of the brain primarily controls writing for right-handers?
What is the function of Schwann cells in the nervous system?
What is the function of Schwann cells in the nervous system?
What is the main role of motor neurons in the nervous system?
What is the main role of motor neurons in the nervous system?
What is the diameter of the spinal cord?
What is the diameter of the spinal cord?
Which function is primarily associated with the left hemisphere of the brain?
Which function is primarily associated with the left hemisphere of the brain?
Which % of the nervous system is formed by interneurons?
Which % of the nervous system is formed by interneurons?
Which area of the brain is activated when left-handers imagine writing?
Which area of the brain is activated when left-handers imagine writing?
What do we call the segment of the nervous system dedicated to voluntary muscle movement?
What do we call the segment of the nervous system dedicated to voluntary muscle movement?
What is one of the functions of the spinal cord?
What is one of the functions of the spinal cord?
Which of the following skills is primarily controlled by the right hemisphere?
Which of the following skills is primarily controlled by the right hemisphere?
What type of reflex bypasses the brain?
What type of reflex bypasses the brain?
What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
What is the primary function of the cerebellum?
Which structure connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord?
Which structure connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord?
Which side of the brain activates for left-handers when performing tasks?
Which side of the brain activates for left-handers when performing tasks?
What role does the occipital lobe primarily serve?
What role does the occipital lobe primarily serve?
How is the cerebrum organized?
How is the cerebrum organized?
Which function is NOT associated with the brainstem?
Which function is NOT associated with the brainstem?
What might happen if a stroke occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain?
What might happen if a stroke occurs in the right hemisphere of the brain?
What is the main role of the frontal lobe?
What is the main role of the frontal lobe?
Which lobe is primarily involved in interpreting touch and pain?
Which lobe is primarily involved in interpreting touch and pain?
What is the primary role of the spinal cord in reflex actions?
What is the primary role of the spinal cord in reflex actions?
What characterizes the structure of the spinal cord?
What characterizes the structure of the spinal cord?
What symptom may indicate damage to the central nervous system (CNS) in relation to reflexes?
What symptom may indicate damage to the central nervous system (CNS) in relation to reflexes?
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for transmitting impulses to and from the periphery of the body?
Which part of the nervous system is responsible for transmitting impulses to and from the periphery of the body?
What occurs as a result of spinal cord injuries?
What occurs as a result of spinal cord injuries?
How does the knee-jerk reflex operate?
How does the knee-jerk reflex operate?
What is the central canal of the spinal cord primarily filled with?
What is the central canal of the spinal cord primarily filled with?
What happens to the reflex pathway during a knee-jerk reaction?
What happens to the reflex pathway during a knee-jerk reaction?
What is the primary function of glial cells in the nervous system?
What is the primary function of glial cells in the nervous system?
Which type of glial cell is responsible for forming the myelin sheath in the central nervous system?
Which type of glial cell is responsible for forming the myelin sheath in the central nervous system?
What distinguishes neurons from glial cells in the nervous system?
What distinguishes neurons from glial cells in the nervous system?
What is the role of ependymal cells in the nervous system?
What is the role of ependymal cells in the nervous system?
Which statement about neuron structure is correct?
Which statement about neuron structure is correct?
Which type of neuron is specialized for transmitting signals related to light?
Which type of neuron is specialized for transmitting signals related to light?
What percentage of cells in the brain are neurons?
What percentage of cells in the brain are neurons?
Which of the following is a function of microglial cells?
Which of the following is a function of microglial cells?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
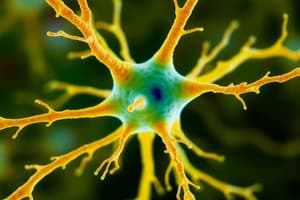
Neuron Structure and Function
- A neuron, also called a nerve cell, is the fundamental unit of the nervous system responsible for transmitting information
- Nerves are bundles of axons found in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- In the Central Nervous System (CNS), bundles of neurons are called tracts
- Axons are the long, slender projections of neurons that transmit electrical signals.
- Myelin is a fatty substance that insulates axons, increasing the speed of signal transmission
- Myelinated axons are covered in myelin, while unmyelinated axons lack this coating.
- Schwann cells create myelin in the PNS.
- Oligodendrocytes create myelin in the CNS.
Types of Neurons
- Sensory Neurons: Carry signals from the body to the CNS (brain and spinal cord). Also called afferent neurons.
- Interneurons: Connect neurons within the CNS. They are the most common type of neuron, making up about 99% of all neurons.
- Motor Neurons: Carry signals from the CNS to muscles and glands. Also called efferent neurons.
Reflex Arc
- In a reflex arc, sensory neurons transmit signals to interneurons in the spinal cord, which then activate motor neurons, resulting in a reflex action.
- Some reflexes bypass the brain, resulting in a quicker response.
Major Structures of the Brain
- Cerebrum: The largest part of the brain responsible for higher cognitive functions like language, memory, reasoning, and voluntary movement.
- Frontal Lobe: Controls personality, behavior, emotions, judgment, planning, problem-solving, speech, body movement, intelligence, concentration, and self-awareness.
- Parietal Lobe: Interprets language, sense of touch, pain, temperature, signals from vision, hearing, motor, sensory, and memory, spatial and visual perception.
- Occipital Lobe: Interprets vision, including color, light, and movement.
- Temporal Lobe: Involved in understanding language, memory, hearing, sequencing, and organization.
- Cerebellum: Located under the cerebrum, responsible for coordinating muscle movements, maintaining posture, and balance.
- Brainstem: Acts as a relay center between the cerebrum and cerebellum, connecting them to the spinal cord. Controls automatic functions like breathing, heart rate, body temperature, wake/sleep cycles, digestion, sneezing, coughing, vomiting, and swallowing.
- The two hemispheres of the cerebrum are interconnected by the corpus callosum, which transmits messages between them.
Brain Function
- The brain hemispheres specialize in different functions.
- Left Hemisphere: Generally controls speech, comprehension, arithmetic, and writing.
- Right Hemisphere: Generally controls creativity, spatial ability, artistic skills, and musical skills.
The Spinal Cord
- Part of the CNS, extending from the brainstem down the spine.
- It is crucial for transmitting nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body.
- It contains a central canal filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
- It has gray matter (centrally located) and white matter (surrounding the gray matter).
- The spinal cord facilitates reflexes, some of which bypass the brain for faster response.
- Injury to the spinal cord can disrupt signal transmission, leading to paralysis.
The Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
- The PNS consists of all the nerves branching out of the brain and spinal cord.
- It acts as the "connecting road" between the CNS and the body's periphery.
Cells of the Nervous System
-
Neurons: Nerve cells, responsible for transmitting nerve impulses.
-
Glial Cells: Support and protect neurons, forming the "glue" of the nervous system.
- Microglia act as macrophages in the CNS.
- Oligodendrocytes create myelin in the CNS.
- Ependymal Cells line the fluid-filled spaces of the brain and spinal cord and secrete CSF
- Astrocytes provide nutrients to neurons and form the blood-brain barrier.
-
The brain is composed of 10% neurons and 90% glial cells.
Neuron Structure
- Neurons have a cell body containing the nucleus and organelles.
- Dendrites: Receive electrical signals from other neurons.
- Axon: Transmits the signal to other neurons or effector cells.
4 Main Classes of Glial Cells
- Microglia: CNS resident macrophages.
- Oligodendrocytes: Form myelin sheath in the CNS.
- Ependymal cells: Line the fluid-filled spaces of the brain and spinal cord and secrete CSF.
- Astrocytes: Provide nutrients to neurons and form the blood-brain barrier.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.