Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is a primary safety consideration in MRI due to the strong magnetic field it generates?
Which of the following is a primary safety consideration in MRI due to the strong magnetic field it generates?
- The risk of acoustic trauma due to the loud noises produced during scanning.
- The movement of ferromagnetic objects at high speeds, posing a projectile risk. (correct)
- The potential for radiofrequency burns from the RF coil.
- The possibility of inducing seizures in individuals with photosensitive epilepsy.
Why might researchers choose to use fTCDS over other neuroimaging techniques when investigating cerebral dominance?
Why might researchers choose to use fTCDS over other neuroimaging techniques when investigating cerebral dominance?
- fTCDS provides higher spatial resolution, allowing for precise localization of brain activity.
- fTCDS is more effective at measuring activity in deep brain structures compared to cortical regions.
- fTCDS is less susceptible to individual differences in brain structure and skull density.
- fTCDS is resistant to movement artifacts, making it suitable for use with individuals who cannot remain still. (correct)
In the context of Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), what does fractional anisotropy (FA) primarily reflect?
In the context of Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), what does fractional anisotropy (FA) primarily reflect?
- The overall volume of white matter in a specific brain region.
- The concentration of myelin along individual axons.
- The degree to which water diffusion is directionally oriented within white matter tracts. (correct)
- The metabolic activity levels within grey matter structures.
What is the primary reason T2-weighted MRI sequences are utilized in functional MRI (fMRI)?
What is the primary reason T2-weighted MRI sequences are utilized in functional MRI (fMRI)?
In the study by Van der Auwera et al. (2021) using DTI to investigate dyslexia, what was the key finding regarding fractional anisotropy (FA) in the arcuate fasciculus (AF) of children with dyslexia before reading instruction?
In the study by Van der Auwera et al. (2021) using DTI to investigate dyslexia, what was the key finding regarding fractional anisotropy (FA) in the arcuate fasciculus (AF) of children with dyslexia before reading instruction?
Which biophysical principle underlies Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography (fTCDS)?
Which biophysical principle underlies Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography (fTCDS)?
Which of the following best describes how structural MRI can be used to study the progression of Alzheimer's Disease (AD)?
Which of the following best describes how structural MRI can be used to study the progression of Alzheimer's Disease (AD)?
Which of the following factors is most critical when selecting a neuroimaging technique for a particular research question?
Which of the following factors is most critical when selecting a neuroimaging technique for a particular research question?
In functional MRI (fMRI), what is the Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) signal and what does it measure?
In functional MRI (fMRI), what is the Blood Oxygen Level Dependent (BOLD) signal and what does it measure?
Which of the following best explains why an individual with extensive metal implants might be excluded from participating in an MRI study?
Which of the following best explains why an individual with extensive metal implants might be excluded from participating in an MRI study?
Why is the choice of a neuroscientific technique driven by the research question?
Why is the choice of a neuroscientific technique driven by the research question?
According to the research spotlight on language laterality by Parker et al. (2022), how well do behavioral measures of language lateralization correlate with fTCD measures?
According to the research spotlight on language laterality by Parker et al. (2022), how well do behavioral measures of language lateralization correlate with fTCD measures?
In the context of DTI, how does the mean diffusivity (MD) relate to white matter integrity, and what does a high MD value often indicate?
In the context of DTI, how does the mean diffusivity (MD) relate to white matter integrity, and what does a high MD value often indicate?
Apart from spatial resolution and temporal resolution, what is another important consideration when evaluating neuroimaging techniques?
Apart from spatial resolution and temporal resolution, what is another important consideration when evaluating neuroimaging techniques?
How does fMRI compensate when a function is compensated for following an injury?
How does fMRI compensate when a function is compensated for following an injury?
Flashcards
Neuroimaging Importance
Neuroimaging Importance
Structural & functional neuroimaging techniques answer questions we couldn't answer otherwise like limits to behavioral testing, identifying key brain regions, evaluate treatment efficacy.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
A neuroimaging technique where hydrogen protons align with magnetic field, radio waves shift alignment, protons emit energy as radio waves. The density of atoms differs in grey matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid.
MRI: T1 vs T2
MRI: T1 vs T2
T1 measures how quickly protons realign with the main magnetic field, while T2 measures how quickly protons release energy and recover to equilibrium.
MRI Safety
MRI Safety
Signup and view all the flashcards
Structural MRI Usage
Structural MRI Usage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mean Diffusivity (MD)
Mean Diffusivity (MD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fractional Anisotropy Colors
Fractional Anisotropy Colors
Signup and view all the flashcards
DTI: Patient Studies
DTI: Patient Studies
Signup and view all the flashcards
fMRI Activation
fMRI Activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
fMRI Usefulness
fMRI Usefulness
Signup and view all the flashcards
BOLD Temporal Resolution
BOLD Temporal Resolution
Signup and view all the flashcards
fTCDS Benefits
fTCDS Benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Doppler effect
Doppler effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
fTCDS Limitations
fTCDS Limitations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Structural and functional neuroimaging techniques are useful in neuroscience and cognition studies.
Lecture 1: Techniques Covered
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is covered.
- Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) is covered.
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) is covered.
- Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography (fTCDS) is covered.
Lecture 2: Additional Topics
- Electroencephalography (EEG) and Event-Related Potentials (ERPs) are touched on in the second lecture.
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is also included in the second lecture.
Why Use Neuroscientific Techniques?
- These techniques help answer questions that behavioral testing alone cannot.
- They overcome limitations in behavioral testing, like examining implicit processing.
- Key brain regions are identified without animal models or lesion studies.
- These techniques help to evaluate treatment efficacy at a mechanistic level.
- They help with the potential identification of biomarkers.
- Each technique has pros and cons.
How to Choose a Technique
- The specific research question drives the selection of the neuroscientific technique.
- Practical constraints influence the choice of technique.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Protons in hydrogen molecules align with the magnetic field when a person is inside the MRI scanner.
- Applying a radio wave shifts the alignment of the protons.
- After radio waves are turned off, protons emit energy as radio waves.
- A coil of wire around the head detects radio waves, which are then are sent to a computer.
- Variations in hydrogen atom density in grey matter, white matter, and cerebrospinal fluid result in different signals.
- T1 measures the speed at which protons realign with the magnetic field.
- T2 measures proton energy release as they return to equilibrium.
MRI Safety
- MRI machines have powerful magnets that can make ferromagnetic objects dangerous.
- Participants cannot have metal in the body, including pacemakers, aneurysm clips or metal/cochlear implants
- Participants cannot have certain IUDs, dental work, or tattoos.
- Participants must remove jewelry, watches, piercings, coins, wallets, and glasses.
- The MRI is very loud and participants should use earplugs because the MRI is very loud.
- Claustrophobia and anxiety are a concern.
Structural MRI Applications
- Identifying brain damage areas and relating it to symptoms.
- Observing volumetric changes related to behavior or intervention.
- Understanding that the relationship isn't always clear-cut.
MRI: Pros and Cons
- MRI provides good spatial resolution.
- MRI is clinically and experimentally useful.
- MRI is relatively non-invasive.
- MRI is purely structural.
- Not everyone can be scanned due to metal implants or claustrophobia.
- Participants must remain very still and it is expensive.
Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI)
- DTI measures water molecule diffusion (freedom of movement from high to low concentration.
- DTI is a structural measure of white matter.
- DTI is also measured using an MRI machine.
- Mean Diffusivity (MD) measures a voxel's overall water diffusion.
- MD is insensitive to fiber orientation.
- MD is often used clinically.
- High MD often denotes poor white matter connections.
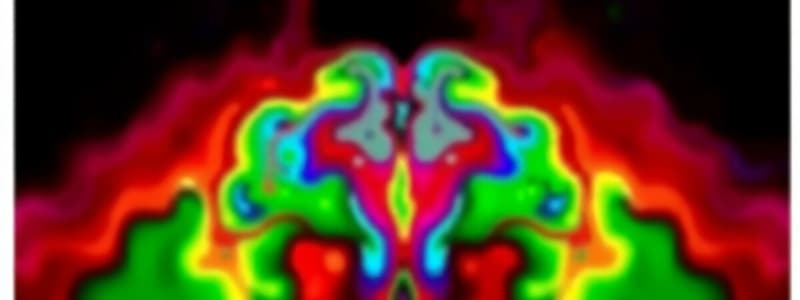
- Fractional Anisotropy notes red = left-right, green = anterior-posterior, blue = superior-inferior
- Maps display orientation, not direction.
- Microscopic and macroscopic factors can cause anisotropy.
DTI Applications
- Investigates white matter structural integrity in cases such as schizophrenia.
- Examines fractional anisotropy (FA) differences in specific structures, such as the arcuate fasciculus in dyslexia.
- Focuses on tracking changes in fractional anisotropy (FA) of specific tracts as they relate to particular experiences.
Van der Auwera et al. (2021) Research
- A three-time longitudinal investigation of the arcuate fasciculus with kids developing dyslexia.
- DTI was used to assess FA in arcuate fasciculus (AF).
- The study looked at typically developing children and those with dyslexia across different age ranges.
- Differences in fractional anisotropy were present between children with and without dyslexia before reading instruction began.
- There is a predictive link between AF FA and reading skills.
- Supports the idea that an AF deficit is core to poor reading ability.
DTI: Pros and Cons
- Good spatial resolution for white matter tracts.
- Has strong clinical and experimental utility.
- Relatively non-invasive.
- Purely structural.
- Some contraindications exist (eg. metal implants, claustrophobia).
- Participants have to remain completely still.
- Very expensive.
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI)
- Is a form of MRI.
- It is T2 weighted to get the functional component (EPI: echo-planer imaging).
- It's is usually overlaid on a T1 scan taken in the same session.
- BOLD (Blood Oxygen Level Dependent) technique measures brain activity by changes in oxygenated blood levels.
fMRI Applicaitons
- Relates structural and functional information.
- Useful for studying functional significance of brain areas.
- Reveals where compensation happens for functions after an injury.
Cummine et al Research (2015)
- Investigated the rapid automatized naming and reading relationship.
- Tasks included RAN letters, RAN numbers, rapid word reading, and rapid nonword reading.
- RAN and reading activate common brain regions.
- Correlation exists between RAN and reading in motor brain regions.
- Differences exist between RAN and reading in non-motor regions.
FMRI: Pros and Cons
- Has good spatial resolution.
- Measures where specific activity is occurring.
- Identifies key areas involved in different processes.
- Poor temporal resolution.
- The BOLD response takes approx. 4 seconds.
- It is an indirect measure of activity via blood flow.
- Issues arise in interpretation from statistical thresholds and the dead salmon paper.
Functional Transcranial Doppler Sonography (fTCDS)
- Uses ultrasound to measure blood flow based on the Doppler effect.
- The frequency of ultrasound waves corresponds to blood flow toward or away from the probe.
- Measures bilateral blood flow in the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory.
fTCDS Applications
- Measures hemispheric cerebral dominance.
- fTCDS is better than behavioural tests.
- Examines group/individual differences in cerebral asymmetries among patients.
- This is done in patients vs. controls.
- Lateralised functions include language, face processing, and object recognition.
COLA Consortium Research
- Studied the relationship between language lateralisation using fTCDs.
- Inconsistent language lateralization was tested using a behavioural test with lateralised cerebral blood flow.
- Parker et al., (2022) tested the dissociable language laterality hypothesis using behavior and lateralized cerebral blood flow.
- Language laterality is not a unitary trait.
fTCDS: Pros and Cons
- Validated measures of language dominance.
- Easy to administer and non-invasive.
- Participants can have cochlear implants, metal, or claustrophobia.
- Resistant to movement
- Poor spatial resolution.
- Only determines if activity is more left or right, but not where.
- Poor temporal resolution.
- Individual differences in MCA architecture or skull density mean a clean signal may not be possible.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.