Podcast
Questions and Answers
During which weeks of gestation does the development of the CNS typically begin?
During which weeks of gestation does the development of the CNS typically begin?
- 5th and 6th week
- 1st and 2nd week
- 3rd and 4th week (correct)
- 7th and 8th week
Which of the following is the correct order of neurulation?
Which of the following is the correct order of neurulation?
- Neural tube, neural groove, neural fold
- Neural groove, neural fold, neural tube
- Neural fold, neural tube, neural groove
- Neural fold, neural groove, neural tube (correct)
What two major structures does the forebrain (prosencephalon) differentiate into during secondary neurulation?
What two major structures does the forebrain (prosencephalon) differentiate into during secondary neurulation?
- Mesencephalon and Rhombencephalon
- Cerebrum and Cerebellum
- Metencephalon and Myelencephalon
- Telencephalon and Diencephalon (correct)
In the context of neural tube defects, what is the primary characteristic of spina bifida occulta?
In the context of neural tube defects, what is the primary characteristic of spina bifida occulta?
Which of the following is a known risk factor for neural tube defects?
Which of the following is a known risk factor for neural tube defects?
In myelomeningocele, what are the components contained within the cystic distension?
In myelomeningocele, what are the components contained within the cystic distension?
What is the primary distinction between diastematomyelia and diplomyelia?
What is the primary distinction between diastematomyelia and diplomyelia?
A child with Chiari II malformation is likely to experience which of the following?
A child with Chiari II malformation is likely to experience which of the following?
What is the initial assessment performed on a newborn with a suspected neural tube defect?
What is the initial assessment performed on a newborn with a suspected neural tube defect?
What is a key diagnostic tool used to visualize tethered cords, spinal lipomas, and the size of the spinal defect?
What is a key diagnostic tool used to visualize tethered cords, spinal lipomas, and the size of the spinal defect?
Why is it important to keep a patient flat postoperatively after neural tube defect surgery?
Why is it important to keep a patient flat postoperatively after neural tube defect surgery?
What percentage of infants with myelomeningocele are expected to survive with modern treatment?
What percentage of infants with myelomeningocele are expected to survive with modern treatment?
What is a common long-term complication associated with myelomeningocele?
What is a common long-term complication associated with myelomeningocele?
What is the primary characteristic of an encephalocele?
What is the primary characteristic of an encephalocele?
Typically, which location is the most common site for an encephalocele to occur?
Typically, which location is the most common site for an encephalocele to occur?
What is the primary goal of surgical intervention for an encephalocele?
What is the primary goal of surgical intervention for an encephalocele?
How does a tethered cord primarily cause issues in patients with neural tube defects?
How does a tethered cord primarily cause issues in patients with neural tube defects?
Which of the following cutaneous findings is commonly associated with a tethered cord?
Which of the following cutaneous findings is commonly associated with a tethered cord?
How soon is surgical intervention recommended to occur for neural tube defects without contraindication?
How soon is surgical intervention recommended to occur for neural tube defects without contraindication?
Which maternal factor can increase the risk of neural tube defects?
Which maternal factor can increase the risk of neural tube defects?
When is simultaneous shunt placement typically performed in the setting of myelomeningocele?
When is simultaneous shunt placement typically performed in the setting of myelomeningocele?
What is a characteristic of abnormalities of primary neurulation?
What is a characteristic of abnormalities of primary neurulation?
What position is the patient placed in pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
What position is the patient placed in pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
In the context of spinal lipoma, what is the significance of a 'low tethered cord'?
In the context of spinal lipoma, what is the significance of a 'low tethered cord'?
If the sac of a neural tube defect is ruptured, what immediate pre-operative management step is essential?
If the sac of a neural tube defect is ruptured, what immediate pre-operative management step is essential?
What are the main goals when addressing a tethered cord with surgical intervention?
What are the main goals when addressing a tethered cord with surgical intervention?
What is the significance of monitoring OccipitoFrontal Circumference (OFC) in the context of neural tube defects, specifically Chiari malformation?
What is the significance of monitoring OccipitoFrontal Circumference (OFC) in the context of neural tube defects, specifically Chiari malformation?
What is the purpose of performing a voiding cystourethrogram or urodynamic studies in a patient with a neural tube defect?
What is the purpose of performing a voiding cystourethrogram or urodynamic studies in a patient with a neural tube defect?
Which prenatal test can help assess the risk of neural tube defects by measuring a specific protein level?
Which prenatal test can help assess the risk of neural tube defects by measuring a specific protein level?
During which stage of brain and spinal cord development does the neural tube typically form?
During which stage of brain and spinal cord development does the neural tube typically form?
Which of the following statements accurately differentiates between diastematomyelia and diplomyelia?
Which of the following statements accurately differentiates between diastematomyelia and diplomyelia?
Why is Trendelenburg positioning utilized pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
Why is Trendelenburg positioning utilized pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
What is the rationale behind keeping a patient in a flat position postoperatively following neural tube defect surgery?
What is the rationale behind keeping a patient in a flat position postoperatively following neural tube defect surgery?
In the management of myelomeningocele, when is simultaneous shunt placement usually considered, and what specific condition warrants this approach?
In the management of myelomeningocele, when is simultaneous shunt placement usually considered, and what specific condition warrants this approach?
What is the primary surgical objective when addressing a tethered cord associated with a neural tube defect?
What is the primary surgical objective when addressing a tethered cord associated with a neural tube defect?
What is the most critical immediate pre-operative management step if the sac of a neural tube defect is ruptured?
What is the most critical immediate pre-operative management step if the sac of a neural tube defect is ruptured?
How does folic acid deficiency during pregnancy contribute to the development of neural tube defects?
How does folic acid deficiency during pregnancy contribute to the development of neural tube defects?
Which of the following best describes the implication of a 'low tethered cord' in the context of spinal lipoma?
Which of the following best describes the implication of a 'low tethered cord' in the context of spinal lipoma?
What is the significance of closely monitoring OccipitoFrontal Circumference (OFC) in infants with neural tube defects, particularly those with Chiari II malformation?
What is the significance of closely monitoring OccipitoFrontal Circumference (OFC) in infants with neural tube defects, particularly those with Chiari II malformation?
What is the primary rationale for performing voiding cystourethrograms or urodynamic studies on patients with neural tube defects?
What is the primary rationale for performing voiding cystourethrograms or urodynamic studies on patients with neural tube defects?
During secondary neurulation, what structures are formed, and what characterizes abnormalities in this process?
During secondary neurulation, what structures are formed, and what characterizes abnormalities in this process?
Which prenatal screening test is most effective for assessing the risk of neural tube defects during the second trimester?
Which prenatal screening test is most effective for assessing the risk of neural tube defects during the second trimester?
What percentage of infants with myelomeningocele are expected to have normal urinary continence with modern treatment?
What percentage of infants with myelomeningocele are expected to have normal urinary continence with modern treatment?
Which of the following postoperative monitoring parameters is MOST crucial in the immediate period following neural tube defect repair to prevent complications?
Which of the following postoperative monitoring parameters is MOST crucial in the immediate period following neural tube defect repair to prevent complications?
What is the primary distinction between spina bifida occulta and spina bifida manifesta?
What is the primary distinction between spina bifida occulta and spina bifida manifesta?
What is the likely underlying cause of late mortality in patients with myelomeningocele despite successful initial surgical repair?
What is the likely underlying cause of late mortality in patients with myelomeningocele despite successful initial surgical repair?
Which statement accurately describes the position the patient should be placed in pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
Which statement accurately describes the position the patient should be placed in pre-operatively for neural tube defect interventions?
What is the significance of simultaneous shunt placement during myelomeningocele repair concerning the development of hydrocephalus?
What is the significance of simultaneous shunt placement during myelomeningocele repair concerning the development of hydrocephalus?
Within what timeframe is surgical intervention recommended for neural tube defects, assuming no contraindications exist?
Within what timeframe is surgical intervention recommended for neural tube defects, assuming no contraindications exist?
What is a key characteristic related to the closure of the cranial and caudal neuropores during primary neurulation?
What is a key characteristic related to the closure of the cranial and caudal neuropores during primary neurulation?
Why is multiple layer closure advocated during surgical repair of myelomeningocele?
Why is multiple layer closure advocated during surgical repair of myelomeningocele?
Which long-term complication is most frequently associated with myelomeningocele, impacting daily life and requiring ongoing management?
Which long-term complication is most frequently associated with myelomeningocele, impacting daily life and requiring ongoing management?
Which of the following is a risk factor for neural tube defects associated with maternal health conditions?
Which of the following is a risk factor for neural tube defects associated with maternal health conditions?
Considering associated conditions, which of the following sensory or motor deficits would MOST likely be associated with lesion at the L4 nerve root?
Considering associated conditions, which of the following sensory or motor deficits would MOST likely be associated with lesion at the L4 nerve root?
What is the most likely cause of early mortality in infants who survive initial surgical repair of myelomeningocele?
What is the most likely cause of early mortality in infants who survive initial surgical repair of myelomeningocele?
How do medications like carbamazepine and phenytoin act as risk factors for neural tube defects?
How do medications like carbamazepine and phenytoin act as risk factors for neural tube defects?
What is the significance of a cutaneous finding such as a tuft of hair or subcutaneous lipoma observed on the lower back of a newborn?
What is the significance of a cutaneous finding such as a tuft of hair or subcutaneous lipoma observed on the lower back of a newborn?
Flashcards
Neurulation
Neurulation
A process of neural tube formation & stability of the brain and spinal cord.
Neurulation timing
Neurulation timing
The CNS development starts during the 3rd & 4th week of gestation.
Primary Neurulation
Primary Neurulation
The neural tube develops from folding of the neural plate, leading to fusion & closure in the midline.
Anencephaly
Anencephaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina bifida occulta
Spina bifida occulta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina bifida manifesta
Spina bifida manifesta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spina Bifida Occulta - Simple
Spina Bifida Occulta - Simple
Signup and view all the flashcards
Simple Spina Bifida Occulta Defect
Simple Spina Bifida Occulta Defect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Complex Spina Bifida Occulta
Complex Spina Bifida Occulta
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meningocele
Meningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myelomeningocele
Myelomeningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal lipoma
Spinal lipoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tethered cord
Tethered cord
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chiari II Malformations
Chiari II Malformations
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lesion assessment
Lesion assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurological assessment
Neurological assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
MRI spine
MRI spine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Acute complication of Myelomeningocele
Acute complication of Myelomeningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Site: Encephalocele
Site: Encephalocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
The 3 germ layers
The 3 germ layers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secondary Neurulation
Secondary Neurulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
The 3 primary brain vesicles
The 3 primary brain vesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Forebrain becomes...
Forebrain becomes...
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hindbrain becomes...
Hindbrain becomes...
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cause of anencephaly
Cause of anencephaly
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk factors for Myelomeningocele
Risk factors for Myelomeningocele
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal Lipoma Definition
Spinal Lipoma Definition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spinal lipoma presentation
Spinal lipoma presentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tethered cord treatment.
Tethered cord treatment.
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diastomyelia
Diastomyelia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Diplomyelia
Diplomyelia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Criteria for chiari malformation
Criteria for chiari malformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chiari malformation presentation
Chiari malformation presentation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assessment of Chiari malformation
Assessment of Chiari malformation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Assessment of spinal lesion
Assessment of spinal lesion
Signup and view all the flashcards
CT brain
CT brain
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurosurgery intervention
Neurosurgery intervention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orthopedic intervention
Orthopedic intervention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urological intervention
Urological intervention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy
Signup and view all the flashcards
If non-ruptured
If non-ruptured
Signup and view all the flashcards
US
US
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serum Alpha fetoprotein:
Serum Alpha fetoprotein:
Signup and view all the flashcards
Postoperative
Postoperative
Signup and view all the flashcards
Important step in the post operation
Important step in the post operation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Neural Tube Defects
- Neural tube defects relate to neurosurgery
- They occur because of complications during neurulation
- They are listed as costing 5 LE
Normal Development of CNS
- There are three germ layers
- Ectoderm germ layer
- Mesoderm germ layer
- Endoderm germ layer
- Stages of brain and spinal cord development & maturation:
- Primary neurulation
- Secondary neurulation
- Neuronal proliferation & histogenesis (Migration Maturation)
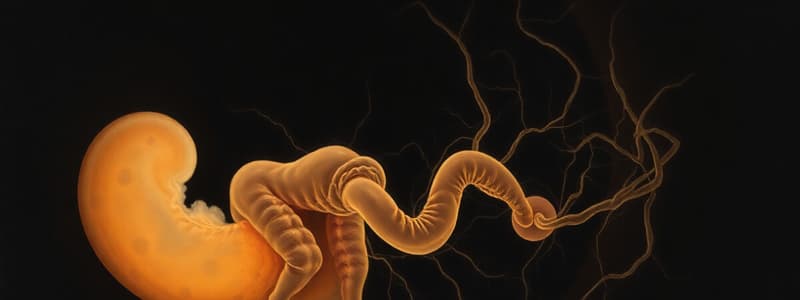
Neurulation
- Formation & stability of the brain and spinal cord
- Development of the CNS starts during the 3rd & 4th week of gestation
- Neurulation can be primary
- Neural fold becomes neural groove, and lastly neural tube
- Fusion of the neural tube occurs usually midline
- Any complication during neurulation results in a neural tube defect
Primary Neurulation
- It occurs during weeks 3-4
- Neural plate folds to close in the midline
- Neural fold fuses and then closes in the midline
- Neural tube formation occurs
- Cranial neuropore turns into the brain
- Caudal neuropore turns into the spinal cord
Secondary Neurulation
- It occurs during weeks 8-10
- After the cranial neuropore closes, the tube develops into 3 primary vesicles
- Forebrain = prosencephalon
- Midbrain = mesencephalon
- Hindbrain = rhombencephalon
- The primary vesicles develop into 5 secondary vesicles
- Forebrain becomes telencephalon & diencephalon
- Hindbrain becomes metencephalon & myelencephalon
Abnormalities of Primary Neurulation
- Failure of closure of cranial neuropore results in anencephaly
- Failure of closure of the caudal neuropore results in neural tube defect, or Spina Bifida
- Anencephaly results if the neural tube doesn't close at the cranial end, so the brain doesn't develop
- The condition is not compatible with life
- Results if The vertebral arch remain open and defect
- Spina bifida occulta involves closed skin over the defect, usually asymptomatic, or may be associated with other hidden types of spinal dysraphism
- Spina bifida manifesta presents with a sac over the defect filled either by CSF or spinal cord
Risk factors for neural tube defect
- Unclear causes account for over 60%
- 10% caused by Chromosomal abnormalities
- 10% caused by Environmental exposure
- General Stress and war times
- Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy
- Folic acid antagonist carbamazepine, phenytoin
- Prenatal infection or irradiation,
- Maternal factors:
- Medication use (antiepileptic drugs)
- Disease (diabetes)
Spina Bifida Classification
- Spina Bifida Occulta (Simple - Complex)
- Spina Bifida Manifesta (Meningocele - Myelomeningocele)
Spina Bifida Occulta
- Simple: Congenital absence of a spinal process with some missing lamina
- Complex:
- A defect in the spinal arch where the nerves and spinal cord are abnormal and other anomalies may be present
- A defect in the spinal arch
- Can be characterized by a small defect in the spinal arch with normal nerves and spinal cord and no other abnormalities
- No visible exposure of meninges or neural tissue
- Incidence occurs in 10-20% of cases
- Congenital absence of spinal process
- The neural tube defect is covered by skin
Spina Bifida Manifesta
- Meningocele: Congenital defect of the vertebral arch with some cystic distension of meninges.
- Myelomeningocele: Congenital defect of the vertebral arch with some cystic distension of meninges & Spinal cord
- The sac may be intact or ruptured
- Some infants may have no symptoms or only mild symptoms
- The cyst contains Meninges and CSF, but no abnormalities of the neural tissue
- Most severe & most common
- The cyst contains::
- Meninges
- CSF
- Nerves & spinal cord
- May not be covered by skin
Presentation
- Defect may be palpable
- May be overlying cutaneous manifestation:
- Dimple
- Nevus flaminous (red spot) or port wine
- Pad of subcutaneous fat
- Tuft of hair "Small hair growth"
- Often an incidental finding
- In which patient is usually intact neurologically
Risk factors
- Previous birth with MM
- Families where close relatives (siblings)
- War
- Economic disasters
Complication
- May or may not cause instability
- 1/3 have some neurologic deficit
- Structure & functional abnormality of the spinal cord or cauda equina
Spinal Dysraphism
- Associated conditions may include: Diastmatomyelia or diplomyelia., Tethered cord, Spinal lipoma, Dermoid tumors
Associated conditions
- Severe paralysis, bowel & urinary dysfunction
- Hydrocephalus with myelomeningocele is 80% of cases at the age of < 6 months
- Closure of the MM defect may convert a latent hydrocephalus to active hydrocephalus
- Chiari malformation type 2
Spinal Lipoma
- Subcutaneous lipoma passes through a midline defect in the lumbodorsal fascia vertebral arch & dura then emerges with a normally low tethered cord
- Back mass
- Presentation may consist of: Bladder problems, Foot deformities, Sensory loss, or cutaneous manifestations
- MRI lumbosacral in investigation
- A possible treatment is Release of Tethering or Reduce the buck of fatty tissue
Tethered Cord
- Abnormally low conus medullaris associated with short thickened filum terminalis
- Scoliosis (↑) or kyphosis
- Leg pain
- Increasing spasticity worsening gait
- Deterioration of urodynamic manifestations
- Cutaneous finding: tuft of hair, Subcutaneous lipoma
- Investigation: MRI lumbosacral spine low conus medullaris or with intradural lipoma
-
- Cutting of the filum (untethering) &/or
-
- Excision of lipoma if present
Diastmatomyelia & Diplomyelia
- Diastmatomyelia:
- 2 hemi- cords, each with its own central canal & with a separate Dural tube &
- Separated by rigid osseocartilaginous median septum
- Diplomyelia
- 2 hemicords within a single dural tube
- Separated by a non-rigid fibrous median septum
Chiari II Malformations
- A heterogeneous group of conditions with disruption of normal CSF flow through the foramen magnum
- Causally dislocated
- cervicomedullary junction
- pons
- 4th ventricles & medulla
- Cerebellar tonsils located at or below the foramen magnum
- Hydrocephalus is present in most cases
- Swallowing difficulties
- Stridor
- May be progress to quadriparesis
- Arm weakness
- Apneic spell
- Weak or absent cry
- Facial weakness
- Plain x-ray
- MRI
- Laryngoscopy
- V-P shunt for hydrocephalus
- Posterior fossa decompression for
- (Neurogenic dysphagia - stridor - Apneic spell)
- Chiari type I - Chiari III - Chiari 0 - Chiari 1.5
Evaluation & Assessment
- Lesion assessment: Measure size of defect and if the sac is ruptured or unruptured
- Neurological assessment:
- Assessment of spinal lesion:
- Spontaneous movement of the lower
- Lowest level of neurologic function in response to painful stimulus
- loss of anal corrugation
- Assessment of commonly associated Chiari malformation: 4. Measure OFC 5. Inspiratory stridor or apneic episodes
- Assessment of spinal lesion:
- Orthopedic assessment:
- For sever kyphotic or scoliotic spine deformities
- For hip & knee deformities
- Urological assessment:
- Frequent wetted
- Start patient on regular catheterization
- Nerve Roots:
- T12: Complete paralysis of all muscles of lower limbs
- L1: Inguinal region and hip flexors
- L2: Anterior mid thigh and hip flexors
- L3: Distal anterior thigh + Hip flexors & knee extensors
- L4: Medial lower leg and foot + Knee extensors & ankle dorsiflexors
- L5: Lateral leg and foot - Hallux extension & ankle plantar flexors
- S1: Lateral side of the foot - Ankle plantar Flexors & evertors
Investigation
- CT brain: associated hydrocephalus
- MRI spine: size, tethered cord, spinal lipoma
- Orthopedic & urological investigations
Management
- Team based therapy:
- Neurosurgery intervention: Surgical repair of the defect, Shunt surgery for hydrocephalus, Untethering of cord, Excision of the spinal lipoma, Reconstruction of the spinal canal
- Orthopedic intervention: Surgical treatment of congenital anomalie
- Urological intervention: Treatment of bladder complication + Catheterization for neurogenic bladder and anticholinergic drugs
- Physiotherapy: For neurological weakness
- Pre-operative
- If ruptured start antibiotic
- If non ruptured Cover the lesion with soaked sterile dressing with normal saline
- Position: "Trendelenburg"
Operative
- Within 36 hours unless there is a contraindication for surgery
- Multiple layer closure is advocate
- Avoid placing tension on the neural placode
- The filum terminalis should be divided if it can be located
- The skin is mobilized and closed
- Simultaneous shunt is not usually done except if overt hydrocephalus at birth
- Other operative varieties to myelomeningocele: 1.Shunt surgery for hydrocephalus
- Decompressive craniotomy for Chiari malformation
- Untethering of cord
- Excision of the spinal lipoma
- Reconstruction of the spinal canal
- Excision pf skin dimple
Postoperative
- Bladder catheterization regimen
- Daily OFC measurement
- Keep patient flat to reduce CSF pressure on incision
- 85% of cases occur in MM infants
Outcome with Modern Treatment
- 85% of MM infants survive
- The most common cause of early mortality is: complications from Chiari malformation respiratory arrest and aspiration
- Late mortality is usually due to shunt malfunction
- 80% will have normal IQ
- 40-85% are ambulatory with bracing
- 3-10% have normal urinary continence
Complications
- Acute complication:
- Hydrocephalus
- Neurogenic bladder
- Orthopedic deformity
- Long term complications:
- ADHD & learning disability
- Weight gain & Obesity
- Cardiovascular disease
- Spine deformity
- Fecal incontinence & constipation
- Sexual dysfunction
- Urinary tract hydroureter & hydronephrosis, UTI
- Lymphedema
- Intrauterine repair of myelomeningocele:
- Can be considered but the outcome is the same as repair of the defect postnatal
Encephalocele
- Protrusion of the meninges & brain substances through a defect in the skull
- Due to failure of closure of the cranial neuropore
- Occipital is common
- Parietal
- Frontal
- Basal
- Character can be associated with hydrocephalus
- May be ruptured or intact sac
- Surgical repair or closing the encephalocele.
- Children who have developed hydrocephalus will require a CSF shunt
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.