Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of dendrites in a nerve cell?
What is the main function of dendrites in a nerve cell?
- Form a myelin sheath around the axon
- Contain the nucleus and control cell functioning
- Carry nerve impulses away from the cell body
- Carry nerve impulses into the cell body (correct)
Which part of a nerve cell is responsible for controlling the functioning of the cell?
Which part of a nerve cell is responsible for controlling the functioning of the cell?
- Nodes of Ranvier
- Cell body (correct)
- Dendrites
- Axon terminal
What is the function of the myelin sheath on axons?
What is the function of the myelin sheath on axons?
- Acts as an insulator
- Carries nerve impulses into the cell body
- Protects axon from damage (correct)
- Contains organelles and cytoplasm
In a nerve cell, what does the term 'neurilemma' refer to?
In a nerve cell, what does the term 'neurilemma' refer to?
Which cells are responsible for forming the myelin sheath outside the brain and spinal cord?
Which cells are responsible for forming the myelin sheath outside the brain and spinal cord?
What is the function of nodes of Ranvier in nerve cells?
What is the function of nodes of Ranvier in nerve cells?
What gives myelinated fibers their white color?
What gives myelinated fibers their white color?
Describe the structural components of a nerve cell.
Describe the structural components of a nerve cell.
Explain the role of dendrites in nerve cells.
Explain the role of dendrites in nerve cells.
What is the function of the myelin sheath on axons?
What is the function of the myelin sheath on axons?
Differentiate between myelinated and unmyelinated fibers.
Differentiate between myelinated and unmyelinated fibers.
Explain the significance of Schwann cells in the nervous system.
Explain the significance of Schwann cells in the nervous system.
What are the nodes of Ranvier and what is their function?
What are the nodes of Ranvier and what is their function?
Explain how the myelin sheath contributes to the color of myelinated fibers.
Explain how the myelin sheath contributes to the color of myelinated fibers.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
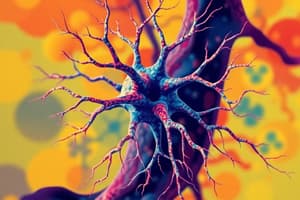
- Nerve cells are the basic structural and functional units of the nervous system, varying in size and shape but all containing a cell body, dendrites, and axon.
- Neurons can be classified based on function or structure, with the cell body containing the nucleus and controlling cell functioning, surrounded by cytoplasm that contains organelles.
- Dendrites are short extensions of the cell body's cytoplasm that carry nerve impulses into the cell body.
- The axon is a single, long extension of the cytoplasm that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body, branching into smaller branches at its end that terminate at the axon terminal.
- Most axons are covered by a myelin sheath, a fatty material that acts as an insulator, protects the axon, and speeds up the movement of nerve impulses. Schwann cells outside the brain and spinal cord form the myelin sheath, with gaps in the sheath called nodes of Ranvier.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.