Podcast
Questions and Answers
A nerve block involves temporary blocking of pathways for the passage of impulses by injecting a local __________.
A nerve block involves temporary blocking of pathways for the passage of impulses by injecting a local __________.
anaesthetic
The radial nerve is the largest nerve of the __________ plexus.
The radial nerve is the largest nerve of the __________ plexus.
brachial
Indications for a radial nerve block include reductions of __________ and surgery of the area.
Indications for a radial nerve block include reductions of __________ and surgery of the area.
fractures
The median nerve supplies the flexor carpi __________, superficial digital flexor, and deep digital flexor muscles.
The median nerve supplies the flexor carpi __________, superficial digital flexor, and deep digital flexor muscles.
The ulnar nerve lies relatively superficial between the flexor carpi ulnaris and __________ lateralis muscle.
The ulnar nerve lies relatively superficial between the flexor carpi ulnaris and __________ lateralis muscle.
The volar or metacarpal nerves are terminal branches of the __________ nerve.
The volar or metacarpal nerves are terminal branches of the __________ nerve.
The peroneal nerve supplies innervation to tibialis anterior, as well as __________ and lateral digital extensors.
The peroneal nerve supplies innervation to tibialis anterior, as well as __________ and lateral digital extensors.
For cattle, the peroneal nerve is blocked immediately behind the posterior edge of the lateral __________ of the tibia.
For cattle, the peroneal nerve is blocked immediately behind the posterior edge of the lateral __________ of the tibia.
The tibial nerve supplies innervation to the ______, superficial and deep digital flexors.
The tibial nerve supplies innervation to the ______, superficial and deep digital flexors.
For tibial nerve block in horses, the needle is inserted about 10 cm above the ______.
For tibial nerve block in horses, the needle is inserted about 10 cm above the ______.
Pudic nerve block is primarily indicated for surgical interference with the ______ and prepuce.
Pudic nerve block is primarily indicated for surgical interference with the ______ and prepuce.
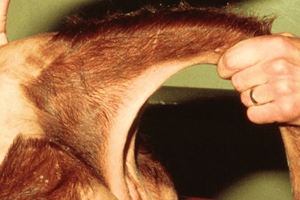
The ischiorectal fossa lies between the anal orifice and the ischial ______.
The ischiorectal fossa lies between the anal orifice and the ischial ______.
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is primarily produced by the ______ plexi within the ventricular system.
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is primarily produced by the ______ plexi within the ventricular system.
For liver biopsy in cattle, the usual site is the 12th ______ space on the right.
For liver biopsy in cattle, the usual site is the 12th ______ space on the right.
The gall bladder in cattle projects beyond the right border of the liver in the ______ part of the intercostal space.
The gall bladder in cattle projects beyond the right border of the liver in the ______ part of the intercostal space.
The artery for pudic nerve block is generally one inch below the ______.
The artery for pudic nerve block is generally one inch below the ______.
Flashcards
What muscles does the tibial nerve innervate?
What muscles does the tibial nerve innervate?
The tibial nerve supplies the gastrocnemius, superficial and deep digital flexors, popliteus, and tibialis posterior muscles, as well as the posteromedial and posterolateral aspects of the pes.
What is a tibial nerve block used for?
What is a tibial nerve block used for?
A tibial nerve block is used to diagnose lameness in the hindlimb and can also be used to perform a tibial neurectomy.
What does the pudic nerve innervate?
What does the pudic nerve innervate?
The pudic nerve supplies the muscles and skin of the external genitalia.
What is a pudic nerve block used for?
What is a pudic nerve block used for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is bone marrow typically collected in different species?
Where is bone marrow typically collected in different species?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and how is it collected?
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and how is it collected?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is a liver biopsy typically performed?
Where is a liver biopsy typically performed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where is a gall bladder biopsy typically performed?
Where is a gall bladder biopsy typically performed?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a nerve block?
What is a nerve block?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the indications for nerve blocks in animals?
What are the indications for nerve blocks in animals?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the radial nerve?
What is the radial nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is radial nerve block used?
Why is radial nerve block used?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the median nerve?
What is the median nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of median nerve block?
What is the purpose of median nerve block?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the ulnar nerve?
What is the ulnar nerve?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of an ulnar nerve block and neurectomy?
What is the purpose of an ulnar nerve block and neurectomy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nerve Blocks
- Nerve blocks temporarily interrupt nerve impulses.
- Local anesthetic solutions are injected to desensitize and temporarily paralyze the region controlled by the nerve.
- Indications include pain relief and improving animal function.
- Chronic conditions like splints, ringbone, navicular disease, and laminitis in horses are treated with nerve blocks.
Radial Nerve Block
- The radial nerve is the largest branch of the brachial plexus.
- Indications include fracture reduction, elbow joint dislocation, and surgical procedures.
- The site of the block is along the musculospiral groove of the humerus, between the triceps muscle heads.
Median Nerve Block
- The median nerve runs below the elbow, then down the forearm between the radius and flexor carpi radialis muscle.
- It supplies muscles involved in pronation and digital flexion.
- The block site is below the medial tuberosity of the radius, in the groove between the radius and flexor carpi radialis.
Ulnar Nerve Block and Neurectomy
- The ulnar nerve is relatively superficial in the lower third of the forearm.
- It lies between the flexor carpi ulnaris and the ulnaris lateralis muscle.
- It provides sensation and motor function to muscles related to the wrist and fingers.
- The block site is a few inches above the accessory carpal.
Volar Nerve Block and Neurectomy
- The volar/metacarpal nerves are branches of the median nerve.
- High volar block involves injecting 5-7 cm above the fetlock joint, in the depression between the suspensory ligament and deep flexor tendon.
- Low volar block is performed midway between the fetlock and coronet, between the deep and superficial digital flexors.
Peroneal Nerve Block
- The peroneal nerve innervates the tibialis anterior, long and lateral digital extensors, and peroneus muscles.
- Its block desensitizes the anterolateral part of the leg and foot, and the anteromedial part of the fetlock joint.
- Indications include lameness diagnosis.
- The site of the peroneal nerve block in cattle is immediately behind the lateral condyle of the tibia.
Tibial Nerve Block
- The tibial nerve innervates the gastrocnemius, superficial and deep digital flexors, popliteus, and tibialis posteromedial and posterolateral muscles of the pes.
- Indications include lameness diagnosis and tibial neurectomy.
- The block site in horses is approximately 10 cm above the hock, between the tendo-achilles and digital extensor muscles, on the medial aspect of the limb.
Pudic Nerve Block
- The pudic nerve branches from the sacral spinal nerves.
- It is crucial for procedures involving the penis and prepuce.
- The internal pudic artery is palpated rectally to locate the nerve.
- The nerve is situated just cranial to the lesser sciatic foramen.
- The block site is within the ischiorectal fossa (between the anal orifice and ischial tuberosities).
Site for Collection of Bone Marrow
- Indications for bone marrow collection include disease investigation.
- Collection sites vary by species:
- Cattle, horses, sheep, goats: ribs and tuber coxae
- Dogs, cats, pigs: iliac crest and proximal femur
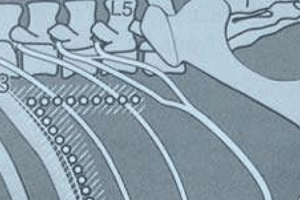
Site for Collection of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
- Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a plasma filtrate, surrounding the brain and spinal cord.
- CSF collection in horses involves puncturing the cisterna magna (suboccipital site).
- In cattle, sheep, and goats, a lumbar puncture is used.
Liver Biopsy
- The usual liver biopsy site in most animals is the 12th intercostal space on the right.
- This area is along a line running from the tuber coxae to the point of the shoulder.
- In cattle, the biopsy area is at the junction of the upper and middle thirds of the 10th or 11th intercostal space on the right side.
Gall Bladder Biopsy
- The gall bladder biopsy site is often at the ventral aspect of the 11th intercostal space on the right.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.