Podcast
Questions and Answers
During a proximal paravertebral block, at which of the following locations is the injection site when using the landmark technique?
During a proximal paravertebral block, at which of the following locations is the injection site when using the landmark technique?
- Midpoint of the vertebral body
- Cranial aspect of the transverse process (correct)
- Caudal aspect of the transverse process
- Distal aspect of the spinous process
What is the intended effect of scoliosis, which can occur as a result of a proximal paravertebral block, during flank anesthesia?
What is the intended effect of scoliosis, which can occur as a result of a proximal paravertebral block, during flank anesthesia?
- To reduce the amount of lidocaine needed
- To widen the surgical field, enhancing access (correct)
- To stabilize the animal during surgery
- To narrow the surgical field for precision
During a proximal paravertebral block, which nerves are targeted for blocking to achieve effective flank anesthesia?
During a proximal paravertebral block, which nerves are targeted for blocking to achieve effective flank anesthesia?
- T13, L1, and L2 (correct)
- L3, L4, and S1
- T12, L2, and L3
- T11, L3, and L4
Why might performing a proximal paravertebral block inadvertently lead to an epidural?
Why might performing a proximal paravertebral block inadvertently lead to an epidural?
What is the primary advantage of using Xylazine alone in a caudal epidural at a specific dilution of 0.02-0.04 mg/kg diluted in 1cc per 100lbs of saline?
What is the primary advantage of using Xylazine alone in a caudal epidural at a specific dilution of 0.02-0.04 mg/kg diluted in 1cc per 100lbs of saline?
If a practitioner administers too much local anesthetic during a caudal epidural (e.g., 8-10 ml in a 1000-pound cow), what is most likely to occur?
If a practitioner administers too much local anesthetic during a caudal epidural (e.g., 8-10 ml in a 1000-pound cow), what is most likely to occur?
Which of the following is a potential complication associated with lumbo-sacral epidural anesthesia?
Which of the following is a potential complication associated with lumbo-sacral epidural anesthesia?
When performing a pudendal nerve block, what anatomical structures are used as landmarks during the rectal examination to guide the injection?
When performing a pudendal nerve block, what anatomical structures are used as landmarks during the rectal examination to guide the injection?
Why is a pudendal nerve block performed to anesthetize the retraction of the penis and control rectal/vaginal tone?
Why is a pudendal nerve block performed to anesthetize the retraction of the penis and control rectal/vaginal tone?
Following the initial injection during a pudendal nerve block, where should the needle be repositioned to target the caudal rectal and pelvic splanchnic nerves?
Following the initial injection during a pudendal nerve block, where should the needle be repositioned to target the caudal rectal and pelvic splanchnic nerves?
What volume of 2% lidocaine is recommended for intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) in cattle when using the dorsal digital vein?
What volume of 2% lidocaine is recommended for intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) in cattle when using the dorsal digital vein?
What is the primary goal of performing intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) when localizing lameness in cattle?
What is the primary goal of performing intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) when localizing lameness in cattle?
During the Peterson eye block is the auriculopalpebral nerve targeted and blocked?
During the Peterson eye block is the auriculopalpebral nerve targeted and blocked?
What are the key palpable landmarks to identify when performing a Peterson eye block in cattle?
What are the key palpable landmarks to identify when performing a Peterson eye block in cattle?
What is the approach when performing cornual anesthesia in cattle?
What is the approach when performing cornual anesthesia in cattle?
What is a significant consideration regarding lidocaine toxicity when performing cornual anesthesia in goats, especially compared to cattle?
What is a significant consideration regarding lidocaine toxicity when performing cornual anesthesia in goats, especially compared to cattle?
Which of the following procedures is LEAST likely to be performed under flank anesthesia?
Which of the following procedures is LEAST likely to be performed under flank anesthesia?
What is a key consideration when using an Inverted L block for flank anesthesia?
What is a key consideration when using an Inverted L block for flank anesthesia?
In a distal paravertebral block, which anatomical landmark is NOT typically used to guide needle placement?
In a distal paravertebral block, which anatomical landmark is NOT typically used to guide needle placement?
How does the effect of heat and sensation differ between proximal and distal paravertebral blocks when determining if the block was effective?
How does the effect of heat and sensation differ between proximal and distal paravertebral blocks when determining if the block was effective?
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of proximal paravertebral blocks?
Which of the following is NOT a benefit of proximal paravertebral blocks?
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be a consideration when selecting between a proximal and distal paravertebral block technique for flank anesthesia in cattle?
Which of the following is LEAST likely to be a consideration when selecting between a proximal and distal paravertebral block technique for flank anesthesia in cattle?
What is the primary disadvantage of using an Inverted L block for flank anesthesia in large animals compared to a proximal paravertebral block?
What is the primary disadvantage of using an Inverted L block for flank anesthesia in large animals compared to a proximal paravertebral block?
Which of the following best describes why heat is assessed following a flank anesthesia procedure?
Which of the following best describes why heat is assessed following a flank anesthesia procedure?
Which lumbar vertebrae are followed to locate landmarks for a proximal paravertebral block?
Which lumbar vertebrae are followed to locate landmarks for a proximal paravertebral block?
What gauge needle is recommended when performing a distal paravertebral block?
What gauge needle is recommended when performing a distal paravertebral block?
What is the recommended volume of lidocaine to deposit dorsal and ventral to the transverse process when performing a distal paravertebral block?
What is the recommended volume of lidocaine to deposit dorsal and ventral to the transverse process when performing a distal paravertebral block?
Why is it important to apply hobbles and good traction after administering a caudal epidural?
Why is it important to apply hobbles and good traction after administering a caudal epidural?
What is the maximum volume of 2% Lidocaine that can be administered to a standing 600lb pig during a Lumbo-Sacral Epidural?
What is the maximum volume of 2% Lidocaine that can be administered to a standing 600lb pig during a Lumbo-Sacral Epidural?
During an IVRA, which vessel should be used to administer an anesthetic?
During an IVRA, which vessel should be used to administer an anesthetic?
Which statement is correct regarding local anesthesia of the eye?
Which statement is correct regarding local anesthesia of the eye?
A guide needle with what gauge should be used as part of a Peterson eye block?
A guide needle with what gauge should be used as part of a Peterson eye block?
What is the most likely cause of pain after a cornual nerve block has been performed?
What is the most likely cause of pain after a cornual nerve block has been performed?
Which statement is correct regarding caudal epidurals?
Which statement is correct regarding caudal epidurals?
Which landmark best represents the needle insertion location for a caudal epidural injection?
Which landmark best represents the needle insertion location for a caudal epidural injection?
If a cow does not show signs of flaccid tail about 1 minute after administration of a caudal epidural, what is the most appropriate next step?
If a cow does not show signs of flaccid tail about 1 minute after administration of a caudal epidural, what is the most appropriate next step?
What is the consequence of accidentally performing an epidural during a proximal paravertebral block?
What is the consequence of accidentally performing an epidural during a proximal paravertebral block?
Why does xylazine alone, at a dilution of 0.02-0.04 mg/kg in 1cc per 100lbs of saline, provide flank anesthesia without motor blockade when administered as a caudal epidural?
Why does xylazine alone, at a dilution of 0.02-0.04 mg/kg in 1cc per 100lbs of saline, provide flank anesthesia without motor blockade when administered as a caudal epidural?
What are the key anatomical considerations when performing a pudendal nerve block, especially concerning potential complications?
What are the key anatomical considerations when performing a pudendal nerve block, especially concerning potential complications?
When performing intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) in cattle, why is it essential to ensure the tourniquet is functioning correctly throughout the procedure?
When performing intravenous regional anesthesia (IVRA) in cattle, why is it essential to ensure the tourniquet is functioning correctly throughout the procedure?
Several cranial nerves are blocked when performing a Peterson eye block in cattle; however, the block of the auriculopalpebral nerve is essential for what?
Several cranial nerves are blocked when performing a Peterson eye block in cattle; however, the block of the auriculopalpebral nerve is essential for what?
When performing cornual anesthesia in goats, why is it critical to block both branches of the cornual nerve?
When performing cornual anesthesia in goats, why is it critical to block both branches of the cornual nerve?
Why is the Inverted L block technique for flank anesthesia more prone to systemic toxicity of lidocaine?
Why is the Inverted L block technique for flank anesthesia more prone to systemic toxicity of lidocaine?
What is the method used to determine anesthetic success when using a distal paravertebral block?
What is the method used to determine anesthetic success when using a distal paravertebral block?
Which is a downfall to using proximal paravertebral blocks?
Which is a downfall to using proximal paravertebral blocks?
When performing a Segmental Thoracolumbar block, what should be considered to avoid potential problems?
When performing a Segmental Thoracolumbar block, what should be considered to avoid potential problems?
Flashcards
Paralumbar Fossa Block
Paralumbar Fossa Block
Anesthesia technique targeting the paralumbar fossa for flank procedures.
Epidural Anesthesia
Epidural Anesthesia
Anesthetic procedure involving injection into the epidural space.
Pudendal Nerve Block
Pudendal Nerve Block
Anesthesia targeting the pudendal nerve.
Bier Block
Bier Block
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anesthesia of the Eye
Anesthesia of the Eye
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cornual Anesthesia
Cornual Anesthesia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbar Nerves Location
Lumbar Nerves Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Paravertebral Block
Proximal Paravertebral Block
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal landmark ID
Proximal landmark ID
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Technique
Proximal Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Block Assessment
Block Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Pros and Cons
Proximal Pros and Cons
Signup and view all the flashcards
Segmental Thoracolumbar Block
Segmental Thoracolumbar Block
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Technique
Distal Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Block Assessment
Distal Block Assessment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inverted L risk
Inverted L risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudal Epidural Uses
Caudal Epidural Uses
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudal Epidural Drugs
Caudal Epidural Drugs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudal Epidural Technique
Caudal Epidural Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Caudal effect of shot
Caudal effect of shot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbo-Sacral Epidural
Lumbo-Sacral Epidural
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbo-Sacral Dose
Lumbo-Sacral Dose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lumbo-Sacral risk
Lumbo-Sacral risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pudendal Nerves Blocked
Pudendal Nerves Blocked
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pudendal Landmarks
Pudendal Landmarks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pudendal technique
Pudendal technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Limb Anesthesia Methods
Limb Anesthesia Methods
Signup and view all the flashcards
IV drug choice
IV drug choice
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eye Block
Eye Block
Signup and view all the flashcards
Local Infilatrate
Local Infilatrate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peterson Technique
Peterson Technique
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peterson Landmarks
Peterson Landmarks
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cornual block-Cattle
Cornual block-Cattle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goat Toxicity
Goat Toxicity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Clinical Anesthesia-Nerve Blocks is covered in VCS 878-Junior Surgery by Dr. Miesner.
Nerve Block Procedures
- Paralumbar fossa (Flank) anesthesia includes several methods.
- Epidurals include Caudal and Lumbosacral.
- Other nerve blocks are Pudendal Nerve block, Baer Block for Limb anesthesia, Anesthesia of the eye and orbit, and Cornual Anesthesia.
Flank Anesthesia - Laparotomy
- Procedures include Cesarean Section, GI-Surgery, and Exploratory
- Techniques include Proximal Paravertebral, Distal Paravertebral, Thoraco-Lumbar, Inverted L, and Line.
Proximal Paravertebral Block
- Landmarks are the 13th rib, L-1, L-2, L-3, and occasionally L-4.
- Nerves blocked are T-13, L-1, and L-2.
Proximal Paravertebral Procedure
- Palpable landmarks determine the location of the needle to nerve location.
- Find landmarks, L-5 is the most posterior palpable transverse process.
- Find the apex of L-1 process by following the last rib up.
- Blocking nerves requires a guide needle and a long spinal needle.
- 5 ml of Lidocaine is used per dorsal and ventral branch (10ml/per nerve).
Proximal Paravertebral Efficacy
- Scoliosis, heat, and sensation can be monitored to check if it worked.
Proximal Paravertebral Pros and Cons
- Benefits include that a small amount of lidocaine is used, scoliosis widens the surgical field, and that there is no lidocaine directly in surgical incision.
- Downfalls include scoliosis makes the animal a little unstable for a few hours, and that it can be difficult to palpate transverse processes in fat cattle.
Segmental Thoracolumbar Block
- Epidural deposition of 2% lidocaine occurs at a rate of 1ml/500lb.
- Spinal needle is used with a hanging drop technique.
- Potentially, it can be performed accidentally during Proximal Paravertebral block (note the small volume above).
Distal Paravertebral Block
- Landmarks: L-1, L-2 and L-4
- Nerves blocked are the same as proximal block
Distal Paravertebral Procedure
- Find the "apex” of transverse process.
- Deposit 10-15 ml of lidocaine dorsal and ventral to process, using an 18 gauge 1 ½ inch needle and fat cattle may require 3 inch.
Distal Paravertebral Efficacy
- Check for minimal Scoliosis, Heat and Sensation for efficacy.
Inverted L
- Involves a Large volume of lidocaine (toxic dose?..10mg/kg).
Epidural Anesthesia
- Used for posterior procedures.
Caudal Epidurals "Tail Block"
- Used for Dystocia, perineal surgery, castration, etc
- Lidocaine (2%) is dosed at 1cc per 200 pounds bw.
- Lidocaine + Xylazine dose is 0.02mg/kg.
- Xylazine alone dose is 0.02-0.04 mg/kg diluted in 1cc per 100lbs of saline, and provides flank anesthesia without motor blockade.
- Use an 18 ga to 20 ga 1" to 1½" needle
- Administer at the Sacro-coccygeal space or Cx 1-Cx2 space using “Hanging Drop” technique.
Caudal Epidural Efficacy
- A flaccid tail occurs within 1 minute.
- Decreased sensation to vulva is within 5 minutes.
- Too much dosage (ie 8 to 10 ml to 1000 pound cow) causes the animal to start to go down in about 5 minutes.
- Remember that the block does not completely wear off immediately, so, apply hobbles and good traction to prevent slipping.
Lumbo-Sacral Epidural Anesthesia "Rostral epidural"
- Used for anesthesia of the caudal half of the animal
- Restraint
- Cesarean (pigs, Sm. Ruminants, midline in cattle) Udder amputation, etc.
Lumbo-Sacral Epidural Anesthesia Dose
- Dose: 2% Lidocaine: Muir et al, pp 71
- Small Ruminants: 1ml/10lbs of bw and if subarachnoid injection * 0.5 ml/10lbs.
- Pigs: Standing 4ml/200lb, 6ml/400lb, 8ml/600lb or Recumbency (cesarean) 10ml/200lb, 15ml/400lb, 20ml/600lb.
Lumbo-Sacral Epidural Anesthesia Complications
- Complications include overdose, rapid administration, and subarachnoid injection.
- Other complications are loss of consciousness, convulsions, respiratory paralysis, hypotension, and hypothermia.
Pudendal Nerve Block
- Nerves blocked include (internal pudendal-fibers of S3 & S4), Caudal rectal (S4 & S5), and pelvic Splanchnic nn.
- It anesthetizes the retractor penis muscle, and rectal vaginal tone.
Pudendal Block Procedure
- Rectal exam and locate sacrosciatic ligament at lesser sciatic foramen, internal pudendal artery.
- Insert needle peri-rectal and advance.
- Inject 10-15ml 2% lidocaine ( internal pudendal nerve).
- Reposition ~ 2-3 cm caudal dorsally and inject another 10ml (caudal rectal and pelvic splanchnic nerves).
- Repeat procedure on other side.
Anesthesia of the Limb
- Three methods are available.
- Intravenous Regional Anesthesia, "Bier"
- Selective Regional Anesthesia
Selective Regional Anesthesia
- See: Greenough, et al; Lameness in Cattle
IV Regional Anesthesia/"Bier"
- See images provided.
I.V. Regional Anesthesia
- Use 20-25 ml of 2% Lidocaine IV to the Dorsal digital vein.
IV Regional Anesthesia-Localizing Lameness
- See image
Anesthesia of the Eye
- Methods include Local "Four Point" Infiltration and Peterson Eye Block.
Local Anesthesia
- 60-80 ml of 2% lidocaine.
- Use a 3 ½ inch needle.
- Retrobulbar, SQ, and auriculopalpebral.
Peterson Eye Block
- Supplies:
- Use a 14ga. 1 ½ in. guide needle and an 18ga 4 ½ in. needle.
- 20 ml of Lidocaine, 10ml to the foramen and 10ml to the auriculopalpebral nerve.
- Requires good restraint.
Peterson Eye Block Landmarks
- The "Notch is made by the zygomatic and temporal processes.
- Target the Coronoid process of the mandible.
Peterson Eye Block Blocking the Nerve
- Block auriculopalpebral nerve
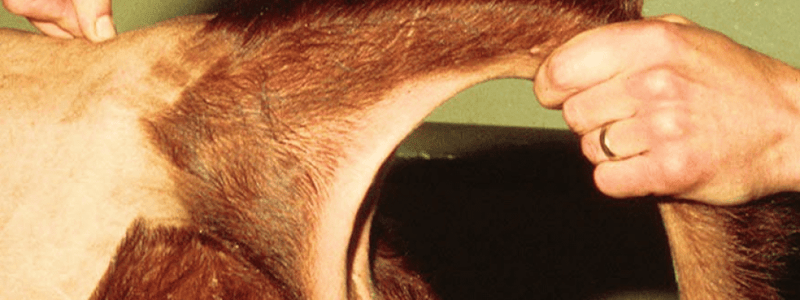
Cornual Block - Cattle
- See image
Cornual Anesthesia (Goats)
- Goats have: 2 branches, cattle 1 primary also some braches of cervical nerves to posterior horn (ring block for cosmetic).
- Goats: Lidocaine toxicity occurs at >5mg/kg.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.