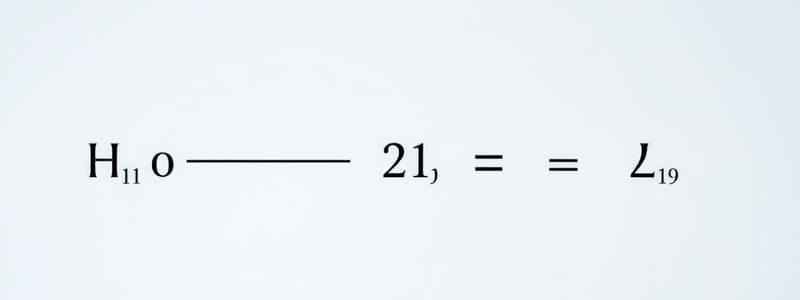Podcast
Questions and Answers
What term describes the phenomenon where a solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids?
What term describes the phenomenon where a solute distributes itself between two immiscible liquids?
- Decantation
- Sublimation
- Fractional distillation
- Partition (correct)
According to the Nernst Distribution Law, under what condition is the ratio of solute concentrations in two phases constant?
According to the Nernst Distribution Law, under what condition is the ratio of solute concentrations in two phases constant?
- Changing volumes
- Different solvents
- Constant temperature (correct)
- Variable pressure
Which of the following is the correct expression for the partition coefficient (K) of a solute between two solvents?
Which of the following is the correct expression for the partition coefficient (K) of a solute between two solvents?
- $K = \frac{[Solute]_{Solvent 2}}{[Solute]_{Solvent 1}}$ (correct)
- $K = [Solute]_{Solvent 2} - [Solute]_{Solvent 1}$
- $K = [Solute]_{Solvent 1} \times [Solute]_{Solvent 2}$
- $K = \frac{[Solute]_{Solvent 1}}{[Solute]_{Solvent 2}}$
In the context of the Nernst Distribution Law, what does a high partition coefficient (KD >> 1) indicate?
In the context of the Nernst Distribution Law, what does a high partition coefficient (KD >> 1) indicate?
For the Nernst Distribution Law to be valid, what condition must be met regarding the solute's molecular form in both solvents?
For the Nernst Distribution Law to be valid, what condition must be met regarding the solute's molecular form in both solvents?
What is the primary requirement for the solvents used in liquid-liquid extraction, as described by the Nernst Distribution Law?
What is the primary requirement for the solvents used in liquid-liquid extraction, as described by the Nernst Distribution Law?
In a scenario where iodine ($I_2$) is distributed between water and tetrachloromethane, and the $K_D$ is greater than 1, in which solvent is iodine more soluble?
In a scenario where iodine ($I_2$) is distributed between water and tetrachloromethane, and the $K_D$ is greater than 1, in which solvent is iodine more soluble?
What is the effect of increasing temperature on the partition coefficient ($K_D$) of a solute between two immiscible liquids, assuming all other conditions remain constant?
What is the effect of increasing temperature on the partition coefficient ($K_D$) of a solute between two immiscible liquids, assuming all other conditions remain constant?
A solute, X, has a partition coefficient of 4 between ether and water. If 10g of X is dissolved in 100 mL of water, how much X would be extracted by a single extraction with 100 mL of ether?
A solute, X, has a partition coefficient of 4 between ether and water. If 10g of X is dissolved in 100 mL of water, how much X would be extracted by a single extraction with 100 mL of ether?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of solvent extraction?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of solvent extraction?
What piece of laboratory equipment is typically used to perform solvent extraction?
What piece of laboratory equipment is typically used to perform solvent extraction?
In a separatory funnel, after adding two immiscible solvents, how is the layer with the higher density typically removed?
In a separatory funnel, after adding two immiscible solvents, how is the layer with the higher density typically removed?
Why is it more efficient to perform solvent extraction using several portions of extracting solvent rather than one large volume?
Why is it more efficient to perform solvent extraction using several portions of extracting solvent rather than one large volume?
After performing solvent extraction, what is the next typical step to recover the solute from the extracting solvent?
After performing solvent extraction, what is the next typical step to recover the solute from the extracting solvent?
A solution contains 5g of compound A in 50 mL of water. If the partition coefficient ($K_D$) of compound A between ether and water is 2, how much of compound A will remain in the water after extraction with 50 mL of ether?
A solution contains 5g of compound A in 50 mL of water. If the partition coefficient ($K_D$) of compound A between ether and water is 2, how much of compound A will remain in the water after extraction with 50 mL of ether?
What is the fundamental assumption underlying the application of the Nernst Distribution Law to solvent extraction processes?
What is the fundamental assumption underlying the application of the Nernst Distribution Law to solvent extraction processes?
Calculate the partition coefficient ($K_D$) given: [Solute in Solvent A] = 0.02 M, [Solute in Solvent B] = 0.08 M, where Solvent B is in the numerator.
Calculate the partition coefficient ($K_D$) given: [Solute in Solvent A] = 0.02 M, [Solute in Solvent B] = 0.08 M, where Solvent B is in the numerator.
A chemist performs an extraction and finds that the $K_D$ for compound Y is 0.1 between water and dichloromethane. What does that indicate?
A chemist performs an extraction and finds that the $K_D$ for compound Y is 0.1 between water and dichloromethane. What does that indicate?
Consider a scenario where a weak acid (HA) is being partitioned between water and ether. If the acid dissociates to a significant extent in water but not in ether, how would this affect the observed partition coefficient?
Consider a scenario where a weak acid (HA) is being partitioned between water and ether. If the acid dissociates to a significant extent in water but not in ether, how would this affect the observed partition coefficient?
In a liquid-liquid extraction, if an emulsion forms between the two phases, what is the best course of action to resolve it?
In a liquid-liquid extraction, if an emulsion forms between the two phases, what is the best course of action to resolve it?
In solvent extraction, which factor does NOT affect the efficiency of solute transfer?
In solvent extraction, which factor does NOT affect the efficiency of solute transfer?
Which statement is FALSE regarding the conditions for the Nernst Distribution Law?
Which statement is FALSE regarding the conditions for the Nernst Distribution Law?
A researcher finds that a solute dimerizes in the organic phase but remains monomeric in the aqueous phase. How does this affect the applicability of the Nernst Distribution Law?
A researcher finds that a solute dimerizes in the organic phase but remains monomeric in the aqueous phase. How does this affect the applicability of the Nernst Distribution Law?
If you perform three consecutive extractions, each with 25 mL of solvent, versus one extraction with 75 mL of solvent, and the $K_D$ is favorable, which method typically yields more solute extracted from the original solution?
If you perform three consecutive extractions, each with 25 mL of solvent, versus one extraction with 75 mL of solvent, and the $K_D$ is favorable, which method typically yields more solute extracted from the original solution?
In the context of solvent extraction, what does 'washing' a solution refer to?
In the context of solvent extraction, what does 'washing' a solution refer to?
In a scenario where a distribution coefficient (KD) is less than 1, how can the extraction efficiency be improved without changing the solvents or temperature?
In a scenario where a distribution coefficient (KD) is less than 1, how can the extraction efficiency be improved without changing the solvents or temperature?
Considering the partition coefficient (KD), if a substance has a KD of 0.01 between water and chloroform, which method would effectively increase its extraction into chloroform?
Considering the partition coefficient (KD), if a substance has a KD of 0.01 between water and chloroform, which method would effectively increase its extraction into chloroform?
A compound partitions between water and ethyl acetate with a distribution coefficient ($K_D$) of 5. Starting with 100 ml of an aqueous solution containing 1 gram of the compound, how many extractions with 100 ml ethyl acetate are required to remove at least 99% of the compound from the aqueous phase?
A compound partitions between water and ethyl acetate with a distribution coefficient ($K_D$) of 5. Starting with 100 ml of an aqueous solution containing 1 gram of the compound, how many extractions with 100 ml ethyl acetate are required to remove at least 99% of the compound from the aqueous phase?
What is the primary purpose of adding sodium chloride (NaCl) to the aqueous phase during a liquid-liquid extraction?
What is the primary purpose of adding sodium chloride (NaCl) to the aqueous phase during a liquid-liquid extraction?
A successful solvent extraction procedure relies on the formation of two distinct layers. What characteristic must be observed to ensure the formation of these layers?
A successful solvent extraction procedure relies on the formation of two distinct layers. What characteristic must be observed to ensure the formation of these layers?
A researcher is trying to extract a polar compound from a nonpolar solvent into water, but the partition coefficient is very low. Which modification to the extraction procedure would likely improve the yield of the polar compound in the water layer?
A researcher is trying to extract a polar compound from a nonpolar solvent into water, but the partition coefficient is very low. Which modification to the extraction procedure would likely improve the yield of the polar compound in the water layer?
In a liquid-liquid extraction using a separatory funnel, after shaking the funnel, it's important to vent it. Why?
In a liquid-liquid extraction using a separatory funnel, after shaking the funnel, it's important to vent it. Why?
Which strategy would be LEAST effective in improving the separation of two compounds with very similar distribution coefficients between two immiscible solvents?
Which strategy would be LEAST effective in improving the separation of two compounds with very similar distribution coefficients between two immiscible solvents?
A chemist is attempting to extract a carboxylic acid from an organic solvent into water. Knowing that the carboxylic acid is more soluble in its ionized form, what adjustment to the aqueous phase would likely improve the extraction efficiency?
A chemist is attempting to extract a carboxylic acid from an organic solvent into water. Knowing that the carboxylic acid is more soluble in its ionized form, what adjustment to the aqueous phase would likely improve the extraction efficiency?
Which method is used to determine the concentration of a substance in each phase with high accuracy during or after solvent extraction?
Which method is used to determine the concentration of a substance in each phase with high accuracy during or after solvent extraction?
How does the presence of impurities that strongly interact with the solute affect the determination of a partition coefficient?
How does the presence of impurities that strongly interact with the solute affect the determination of a partition coefficient?
When performing a liquid-liquid extraction, you notice that the two layers do not separate cleanly and a persistent emulsion forms. You have tried adding salt and gently swirling the mixture, but the emulsion persists. What is a less common, but potentially effective, method to resolve the emulsion?
When performing a liquid-liquid extraction, you notice that the two layers do not separate cleanly and a persistent emulsion forms. You have tried adding salt and gently swirling the mixture, but the emulsion persists. What is a less common, but potentially effective, method to resolve the emulsion?
In a scenario where you are trying to extract a metal cation from an aqueous solution into an organic solvent, what type of ligand would be most effective in facilitating this extraction?
In a scenario where you are trying to extract a metal cation from an aqueous solution into an organic solvent, what type of ligand would be most effective in facilitating this extraction?
Flashcards
Partition (in chemistry)
Partition (in chemistry)
The distribution of a solute between two immiscible liquids.
Partition Coefficient (K)
Partition Coefficient (K)
The ratio of a solute's concentration in two immiscible solvents at equilibrium. It indicates how a solute distributes itself.
Nernst Distribution Law
Nernst Distribution Law
The ratio of a solute's concentration in phase A to its concentration in phase B is constant at a given temperature.
Solvent Extraction
Solvent Extraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Separatory Funnel
Separatory Funnel
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is KD?
What is KD?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Partition describes when a solute distributes between two immiscible liquids.
- In such systems, the solute's concentration in each liquid maintains a constant ratio at a constant temperature.
Nernst Distribution Law
- Defines the equilibrium constant, or partition coefficient (K), for a solute distributed between two solvents
- K = [Asolvent 2] / [Asolvent 1]
- States that the ratio of a solute's concentration in phase A to its concentration in phase B is constant at a given temperature.
- KD (Distribution or partition coefficient) = (concentration of solute in phase B) / (concentration of solute in phase A)
- KD = [Asolv. 2] / [Asolv. 1]
- The value of KD depends on the solute and the two immiscible solvents.
- Temperature affects the coefficient which is applicable only when the solute has the same molecular formula in both solvents
- Solutions must be dilute.
- For iodine (I2) in water and tetrachloromethane: KD = [I2 in tetrachloromethane] / [I2 (aq)]
Calculating KD
- For bromine (Br2) partitioning between tribromomethane (CHBr3) and water at 25°C:
- Solvent 1 is water (H2O) and solvent 2 is tribromomethane (CHBr3), which is usually the organic solvent.
- KD = [Br2 in CHBr3] / [Br2 (aq)]
- If KD > 1 (when solvent 1 is water and solvent 2 is an organic solvent), the solute is more soluble in the organic phase than the aqueous phase.
- A larger KD indicates greater solubility in the organic phase.
- Example calculation determining if the Nernst Distribution Law is followed, resulting in KD values of 66.7, 66.7 and 68.1 showing that the law is being obeyed
Example Calculation
- 10 g of carboxylic acid in 100 mL of water shaken with 100 mL of ethoxyethane (ether), with 6.5 g of acid remaining in the aqueous solution
- Mass of acid extracted by ether = 3.5 g
- [Acid in ether] = 35 g L-1
- [Acid (aq)] = 65 g L-1
- KD = [Acid in ether] / [Acid (aq)] = 0.54
- A KD of 0.54 indicates the acid is more soluble in water than ether.
Solvent Extraction
- This is the process of removing a solute from one liquid/solvent (usually water) into another immiscible solvent
- A separatory funnel is used, where the more dense layer goes out of the bottom tap, and the less dense layer is poured from the top
- Using several portions of the extracting solvent makes it more efficient
- These portions are then combined, and the solvent is evaporated to yield the solute.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.