Podcast
Questions and Answers
What structure surrounds the glomerulus in the nephron?
What structure surrounds the glomerulus in the nephron?
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Bowman's capsule (correct)
- Peritubular capillaries
- Distal convoluted tubule
Which part of the nephron is responsible for the majority of reabsorption?
Which part of the nephron is responsible for the majority of reabsorption?
- Proximal convoluted tubule (correct)
- Loop of Henle
- Collecting duct
- Distal convoluted tubule
Which process occurs in the glomerulus?
Which process occurs in the glomerulus?
- Reabsorption of nutrients
- Secretion of waste
- Glomerular filtration (correct)
- Formation of renal filtrate
What is the main purpose of the peritubular capillaries?
What is the main purpose of the peritubular capillaries?
What role do microvilli play in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What role do microvilli play in the proximal convoluted tubule?
What is one of the main functions of the kidneys?
What is one of the main functions of the kidneys?
Which structure carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
Which structure carries urine from the kidneys to the bladder?
What role do nephrons play in the kidneys?
What role do nephrons play in the kidneys?
Where are the kidneys located in the human body?
Where are the kidneys located in the human body?
What structure is responsible for the elimination of urine?
What structure is responsible for the elimination of urine?
What are renal pyramids part of in the kidney?
What are renal pyramids part of in the kidney?
Which layer of the kidney contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules?
Which layer of the kidney contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules?
What is the function of the renal fascia surrounding the kidneys?
What is the function of the renal fascia surrounding the kidneys?
What is the process of egg cell formation in females called?
What is the process of egg cell formation in females called?
Which hormone initiates the growth of ovarian follicles?
Which hormone initiates the growth of ovarian follicles?
What happens to the ruptured follicle after ovulation?
What happens to the ruptured follicle after ovulation?
During sexual stimulation, what causes the penis to become erect?
During sexual stimulation, what causes the penis to become erect?
What immediately follows ovulation in the female reproductive cycle?
What immediately follows ovulation in the female reproductive cycle?
What is the role of blood pressure in kidney filtration?
What is the role of blood pressure in kidney filtration?
What constitutes renal filtrate?
What constitutes renal filtrate?
Which factor primarily influences the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)?
Which factor primarily influences the Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)?
Where does the majority of reabsorption occur in the kidneys?
Where does the majority of reabsorption occur in the kidneys?
What is active transport in tubular reabsorption primarily used for?
What is active transport in tubular reabsorption primarily used for?
How much filtrate do the kidneys typically form in a 24-hour period?
How much filtrate do the kidneys typically form in a 24-hour period?
Which mechanism allows for passive reabsorption of negative ions?
Which mechanism allows for passive reabsorption of negative ions?
Which hormone increases sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion?
Which hormone increases sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion?
What is the primary purpose of meiosis in the reproductive system?
What is the primary purpose of meiosis in the reproductive system?
What are the three parts of a sperm cell?
What are the three parts of a sperm cell?
Where does sperm production take place in the male reproductive system?
Where does sperm production take place in the male reproductive system?
How does FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) influence sperm production?
How does FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) influence sperm production?
What is the average pH level of semen?
What is the average pH level of semen?
What triggers the process of urination in the body?
What triggers the process of urination in the body?
What is the primary composition of urine?
What is the primary composition of urine?
What is the normal specific gravity range for urine?
What is the normal specific gravity range for urine?
What is the primary function of the testes?
What is the primary function of the testes?
What role do sustentacular cells play in the male reproductive system?
What role do sustentacular cells play in the male reproductive system?
Which gland produces an alkaline secretion that neutralizes acidic urine in the urethra?
Which gland produces an alkaline secretion that neutralizes acidic urine in the urethra?
What is the purpose of the seminal vesicles' secretion?
What is the purpose of the seminal vesicles' secretion?
What structure surrounds the first inch of the urethra?
What structure surrounds the first inch of the urethra?
What developmental condition refers to the failure of the testes to descend?
What developmental condition refers to the failure of the testes to descend?
Which duct receives sperm from the ductus deferens and secretions from the seminal vesicles?
Which duct receives sperm from the ductus deferens and secretions from the seminal vesicles?
What is the function of the ductus deferens in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of the ductus deferens in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of aldosterone in urine formation?
What is the primary function of aldosterone in urine formation?
Which hormone contributes to decreased blood volume by reducing sodium reabsorption?
Which hormone contributes to decreased blood volume by reducing sodium reabsorption?
What is the role of pinocytosis in the kidneys?
What is the role of pinocytosis in the kidneys?
How do kidneys respond when blood pH is too acidic?
How do kidneys respond when blood pH is too acidic?
What initiates the secretion of renin in the kidneys?
What initiates the secretion of renin in the kidneys?
What happens to small proteins during the filtration process in the glomerulus?
What happens to small proteins during the filtration process in the glomerulus?
What is a function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in urine formation?
What is a function of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in urine formation?
What occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule regarding renal filtrate?
What occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule regarding renal filtrate?
What is the primary function of the fimbriae in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the fimbriae in the female reproductive system?
Where does fertilization of the ovum typically occur?
Where does fertilization of the ovum typically occur?
What are the two main layers of the endometrium?
What are the two main layers of the endometrium?
What is the length of the vagina?
What is the length of the vagina?
What happens to an ovum if it is not fertilized?
What happens to an ovum if it is not fertilized?
Which part of the uterus opens into the vagina?
Which part of the uterus opens into the vagina?
What is the function of the vaginal flora?
What is the function of the vaginal flora?
What occurs during an ectopic pregnancy?
What occurs during an ectopic pregnancy?
What is the primary role of erythropoietin in the urinary system?
What is the primary role of erythropoietin in the urinary system?
How does the renin-angiotensin system primarily affect blood pressure?
How does the renin-angiotensin system primarily affect blood pressure?
What is the main function of the urethra?
What is the main function of the urethra?
What structural feature allows the urinary bladder to expand without tearing?
What structural feature allows the urinary bladder to expand without tearing?
Where are the ureters located in relation to the peritoneum?
Where are the ureters located in relation to the peritoneum?
What is the trigone in the urinary bladder?
What is the trigone in the urinary bladder?
What function does the external urethral sphincter serve?
What function does the external urethral sphincter serve?
What triggers the micturition reflex?
What triggers the micturition reflex?
What is the primary function of the clitoris in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the clitoris in the female reproductive system?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the functional layer of the endometrium get lost?
During which phase of the menstrual cycle does the functional layer of the endometrium get lost?
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating milk release during lactation?
What hormone is primarily responsible for stimulating milk release during lactation?
What structure becomes the corpus luteum after ovulation?
What structure becomes the corpus luteum after ovulation?
Which glands are responsible for lubricating the vagina during sexual intercourse?
Which glands are responsible for lubricating the vagina during sexual intercourse?
Which hormone prepares mammary glands for milk production during pregnancy?
Which hormone prepares mammary glands for milk production during pregnancy?
What occurs at the end of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
What occurs at the end of the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle?
What role does relaxin play in the menstrual cycle?
What role does relaxin play in the menstrual cycle?
Flashcards
Kidney Function
Kidney Function
Kidneys filter blood, remove waste, and maintain the body's fluid and electrolyte balance.
Nephron
Nephron
Functional unit of the kidney, responsible for urine formation.
Renal Cortex
Renal Cortex
Outer layer of the kidney containing renal corpuscles and tubules.
Renal Medulla
Renal Medulla
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Corpuscle
Renal Corpuscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary System Components
Urinary System Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Location
Kidney Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureters
Ureters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Tubule Function
Renal Tubule Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peritubular Capillaries
Peritubular Capillaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renal Filtrate
Renal Filtrate
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Reabsorption
Tubular Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Active Transport (Reabsorption)
Active Transport (Reabsorption)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT)
Proximal Convoluted Tubules (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Threshold Level
Threshold Level
Signup and view all the flashcards
Filtration Mechanism
Filtration Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Size Exclusion (Filtration)
Size Exclusion (Filtration)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Renin-Angiotensin System
Renin-Angiotensin System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Erythropoietin
Erythropoietin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vitamin D Activation
Vitamin D Activation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ureter Function
Ureter Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urinary Bladder - Trigone
Urinary Bladder - Trigone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethral Sphincters
Urethral Sphincters
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urination Reflex
Urination Reflex
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aldosterone's Role
Aldosterone's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
ANH's Effect
ANH's Effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
ADH's Function
ADH's Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubular Secretion Purpose
Tubular Secretion Purpose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pinocytosis for Protein Reabsorption
Pinocytosis for Protein Reabsorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reabsorption in the PCT
Reabsorption in the PCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys and Acid-Base Balance
Kidneys and Acid-Base Balance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gametes
Gametes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Meiosis
Meiosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sperm Structure
Sperm Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen
Semen
Signup and view all the flashcards
FSH and Spermatogenesis
FSH and Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone and Spermatogenesis
Testosterone and Spermatogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inhibin and FSH
Inhibin and FSH
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glans Penis Structure
Glans Penis Structure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis Erection
Penis Erection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovarian Follicle Development
Ovarian Follicle Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Corpus Luteum
Corpus Luteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes Location
Testes Location
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis Function
Epididymis Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ductus Deferens Function
Ductus Deferens Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicle Secretion
Seminal Vesicle Secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Function
Prostate Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Gland Function
Bulbourethral Gland Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semen Flow
Semen Flow
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fallopian Tubes
Fallopian Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fimbriae
Fimbriae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peristalsis in Fallopian Tubes
Peristalsis in Fallopian Tubes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus Parts
Uterus Parts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Myometrium
Myometrium
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrium Layers
Endometrium Layers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagina Function
Vagina Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Normal Vaginal Flora
Normal Vaginal Flora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clitoris Function
Clitoris Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labia Majora & Minora
Labia Majora & Minora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mons Pubis
Mons Pubis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vestibule
Vestibule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bartholin's Glands
Bartholin's Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
What do mammary glands produce?
What do mammary glands produce?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormones in Milk Production
Hormones in Milk Production
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Phase Purpose
Menstrual Phase Purpose
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
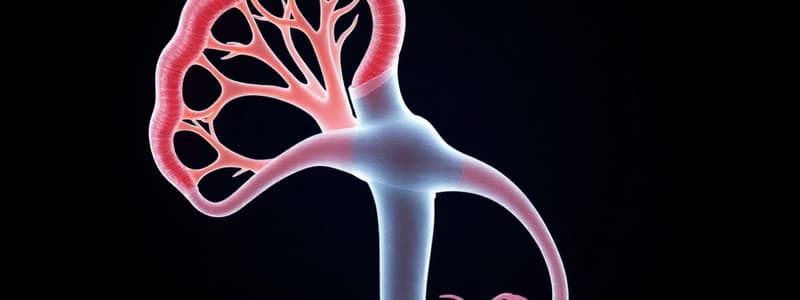
Glomerulus and Nephron Structures
- The glomerulus is surrounded by a structure called Bowman's capsule, which is part of the nephron.
- The proximal convoluted tubule is responsible for the majority of reabsorption in the nephron.
- Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, where blood pressure forces water and small solutes from the blood into Bowman's capsule.
- Peritubular capillaries are responsible for reabsorbing filtered substances back into the blood.
- Microvilli in the proximal convoluted tubule increase the surface area for absorption.
Kidney Functions and Anatomy
- One of the main functions of the kidneys is to regulate blood volume and composition.
- The ureters carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Nephrons are the functional units of the kidneys, responsible for filtration, reabsorption, and secretion.
- The kidneys are located in the retroperitoneal space, behind the peritoneum, on either side of the vertebral column.
- The urethra is responsible for the elimination of urine from the bladder.
- Renal pyramids are part of the renal medulla in the kidney.
- The renal cortex, the outermost layer of the kidney, contains renal corpuscles and convoluted tubules.
- Renal fascia surrounds the kidneys and helps to hold them in place.
Female Reproductive System
- Oogenesis is the process of egg cell formation in females.
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) initiates the growth of ovarian follicles.
- After ovulation, the ruptured follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone.
- During sexual stimulation, blood flow increases to the penis, causing it to become erect.
- The luteal phase immediately follows ovulation in the female reproductive cycle.
Kidney Filtration and Reabsorption
- Blood pressure is essential for kidney filtration.
- Renal filtrate is composed of water, small solutes (glucose, amino acids), and waste products.
- The Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) is primarily influenced by blood pressure.
- Most reabsorption occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule.
- Active transport in tubular reabsorption is primarily used for reabsorbing nutrients and electrolytes against their concentration gradient.
- The kidneys typically form about 180 liters of filtrate daily.
- Passive reabsorption of negative ions occurs through the electrochemical gradient.
- Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption and potassium excretion.
Male Reproductive System
- Meiosis, a type of cell division, is essential for producing sperm cells with half the number of chromosomes.
- The three parts of a sperm cell are the head (containing DNA), midpiece (with mitochondria), and tail (for movement).
- Sperm production occurs in the seminiferous tubules within the testes.
- FSH stimulates sperm production in seminiferous tubules.
- The average pH level of semen is slightly alkaline (7.2-7.8).
- The urge to urinate is triggered by the stretching of the bladder wall.
- Urine is primarily composed of water, urea, electrolytes, and other waste products.
- The normal specific gravity range for urine is between 1.005 and 1.030.
- Testes are responsible for producing sperm cells and testosterone.
- Sustentacular cells in the testes provide support and nourishment to developing sperm cells.
- The prostate gland produces an alkaline secretion that neutralizes acidic urine in the urethra.
- The seminal vesicles' secretion provides fructose for sperm energy and other substances.
- The prostatic urethra surrounds the first inch of the urethra.
- Cryptorchidism refers to the failure of the testes to descend into the scrotum.
- The ejaculatory duct receives sperm from the ductus deferens and secretions from the seminal vesicles.
- The ductus deferens transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory duct.
Hormonal Regulation of Urine Formation
- Aldosterone plays a significant role in urine formation by regulating sodium reabsorption.
- Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) contributes to decreased blood volume by reducing sodium reabsorption.
- Pinocytosis is a process where the kidneys absorb small proteins and other substances from the renal filtrate.
- When blood pH is too acidic, the kidneys excrete more hydrogen ions (H+) and reabsorb bicarbonate ions (HCO3-).
- Low blood pressure stimulates the secretion of renin in the kidneys.
- Small proteins are typically reabsorbed by pinocytosis during filtration in the glomerulus.
- Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) increases water reabsorption in the collecting ducts, resulting in concentrated urine.
- Reabsorption of filtered substances occurs in the proximal convoluted tubule.
Female Reproductive Anatomy and Functions
- Fimbriae are finger-like projections that sweep the ovum into the fallopian tube following ovulation.
- Fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla of the fallopian tube.
- The two main layers of the endometrium are the functional layer (shed during menstruation) and basal layer (forms new functional layer).
- The vagina is approximately 3-4 inches long.
- If an ovum is not fertilized, it disintegrates and is shed during menstruation.
- The cervix is the part of the uterus that opens into the vagina.
- Vaginal flora is a community of bacteria in the vagina that helps to maintain the acidic pH and protect against infections.
- Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, often in the fallopian tube.
Kidney Functions and Erythropoietin
- Erythropoietin is a hormone produced by the kidneys that stimulates the production of red blood cells.
- The renin-angiotensin system increases blood pressure by constricting blood vessels and stimulating the release of aldosterone.
Urinary System Anatomy and Functions
- The urethra carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body.
- The rugae, folds in the bladder wall, allow the bladder to expand without tearing.
- The ureters run alongside the peritoneum, entering the bladder at the posterior aspect.
- The trigone is a triangular region in the urinary bladder formed by the openings of the two ureters and the urethra.
- The external urethral sphincter, a muscle surrounding the urethra, allows for voluntary control of urination.
- The stretching of the bladder wall triggers the micturition reflex.
Female Reproductive System Functions
- The clitoris is a sensitive erectile tissue in the female reproductive system.
- The menstrual phase of the menstrual cycle is characterized by the shedding of the functional layer of the endometrium.
- Prolactin stimulates milk release during lactation.
- The corpus luteum is formed from the ruptured follicle after ovulation.
- Bartholin's glands are responsible for lubricating the vagina during sexual intercourse.
- Estrogen prepares mammary glands for milk production during pregnancy.
- The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle ends with ovulation.
- Relaxin, produced during pregnancy, relaxes ligaments and softens the cervix.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.