Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the percentage of the filtered load that is reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
What is the percentage of the filtered load that is reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)?
- 25%
- 5%
- 67% (correct)
- 3%
Where does tubuloglomerular feedback regulation occur in the nephron?
Where does tubuloglomerular feedback regulation occur in the nephron?
- Thick Ascending Loop of Henle
- Macula Densa (correct)
- Collecting Tubule
- Glomerulus
What happens to the majority of the filtered load if reabsorption does not occur?
What happens to the majority of the filtered load if reabsorption does not occur?
- The body would produce a large amount of urine (correct)
- It is completely reabsorbed
- Waste products would be reabsorbed
- It would be filtered into the capillaries
Which segment of the nephron reabsorbs 3% of the filtered load?
Which segment of the nephron reabsorbs 3% of the filtered load?
Which membrane faces the lumen in the tubular system?
Which membrane faces the lumen in the tubular system?
What is the main function of reabsorption in the nephron?
What is the main function of reabsorption in the nephron?
In which part of the nephron does the filtration process occur?
In which part of the nephron does the filtration process occur?
How much of the filtered load remains to be excreted as urine?
How much of the filtered load remains to be excreted as urine?
What is the primary role of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in sodium reabsorption?
What is the primary role of the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in sodium reabsorption?
Which segment of the nephron is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose?
Which segment of the nephron is primarily responsible for the reabsorption of glucose?
In which part of the nephron does the countercurrent system primarily operate?
In which part of the nephron does the countercurrent system primarily operate?
Which diuretic type inhibits the Na+-Cl- symporter?
Which diuretic type inhibits the Na+-Cl- symporter?
Which of the following substances is NOT typically reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule?
Which of the following substances is NOT typically reabsorbed in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule?
What drives the reabsorption of water in relation to sodium in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule?
What drives the reabsorption of water in relation to sodium in the Proximal Convoluted Tubule?
How much of the filtered sodium is typically reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle?
How much of the filtered sodium is typically reabsorbed in the Loop of Henle?
What role does chloride play in the functioning of the thick ascending Loop of Henle?
What role does chloride play in the functioning of the thick ascending Loop of Henle?
Which ion is reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule to regulate calcium excretion?
Which ion is reabsorbed in the distal convoluted tubule to regulate calcium excretion?
What is the effect of combining loop and thiazide diuretics?
What is the effect of combining loop and thiazide diuretics?
What primarily distinguishes the thick ascending limb from the descending limb of the Loop of Henle?
What primarily distinguishes the thick ascending limb from the descending limb of the Loop of Henle?
Which transport mechanism is involved in sodium reabsorption in the thick ascending Loop of Henle?
Which transport mechanism is involved in sodium reabsorption in the thick ascending Loop of Henle?
In the PCT, sodium reabsorption occurs primarily through which mechanism?
In the PCT, sodium reabsorption occurs primarily through which mechanism?
What is the primary function of tubuloglomerular feedback?
What is the primary function of tubuloglomerular feedback?
Which hormone is involved in increasing sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
Which hormone is involved in increasing sodium reabsorption in the collecting tubule?
Which structure is responsible for the production of renin in response to decreased GFR?
Which structure is responsible for the production of renin in response to decreased GFR?
What role does arginine vasopressin (AVP) play in the collecting tubule?
What role does arginine vasopressin (AVP) play in the collecting tubule?
How do thiazide diuretics affect the distal convoluted tubule?
How do thiazide diuretics affect the distal convoluted tubule?
Which mechanism allows water to be reabsorbed in response to high sodium concentration in the interstitium?
Which mechanism allows water to be reabsorbed in response to high sodium concentration in the interstitium?
What is the function of intercalated cells in the collecting tubule?
What is the function of intercalated cells in the collecting tubule?
What triggers the insertion of sodium channels in the collecting tubule?
What triggers the insertion of sodium channels in the collecting tubule?
Which segment of the nephron has the primary function of reabsorbing substances like sodium, glucose, and water?
Which segment of the nephron has the primary function of reabsorbing substances like sodium, glucose, and water?
What is the primary mechanism of sodium transport from the tubular lumen into the vasculature?
What is the primary mechanism of sodium transport from the tubular lumen into the vasculature?
Which of the following correctly describes the permeability characteristics of the loop of Henle?
Which of the following correctly describes the permeability characteristics of the loop of Henle?
What role does the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle play in nephron function?
What role does the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle play in nephron function?
How do solutes primarily move from the tubular lumen into tubular cells?
How do solutes primarily move from the tubular lumen into tubular cells?
What is the primary outcome of the countercurrent mechanism in the nephron?
What is the primary outcome of the countercurrent mechanism in the nephron?
In which segment of the nephron does bulk reabsorption of solutes primarily occur?
In which segment of the nephron does bulk reabsorption of solutes primarily occur?
Which of the following functions does the collecting tubule NOT perform?
Which of the following functions does the collecting tubule NOT perform?
Which statement accurately describes the function of the countercurrent mechanism in relation to sodium?
Which statement accurately describes the function of the countercurrent mechanism in relation to sodium?
What is the role of aldosterone in the collecting duct?
What is the role of aldosterone in the collecting duct?
How does vasopressin (AVP) affect urine concentration?
How does vasopressin (AVP) affect urine concentration?
Which of the following is a function of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger in the proximal tubule?
Which of the following is a function of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger in the proximal tubule?
Which of the following options is NOT a primary function of the proximal tubule?
Which of the following options is NOT a primary function of the proximal tubule?
What is the primary mechanism for solute transport from the tubular lumen back into the vasculature?
What is the primary mechanism for solute transport from the tubular lumen back into the vasculature?
What effect does parathyroid hormone have in relation to the collecting duct?
What effect does parathyroid hormone have in relation to the collecting duct?
Which of the following accurately describes the function of the loop of Henle?
Which of the following accurately describes the function of the loop of Henle?
Which hormone primarily influences sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
Which hormone primarily influences sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
What is the impact of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) on the kidneys?
What is the impact of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) on the kidneys?
Which of the following best describes the permeability of the descending and ascending loops of Henle?
Which of the following best describes the permeability of the descending and ascending loops of Henle?
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT involved in sodium reabsorption in the nephron?
Which of the following mechanisms is NOT involved in sodium reabsorption in the nephron?
Which statement correctly describes the effect of the countercurrent mechanism on urine production?
Which statement correctly describes the effect of the countercurrent mechanism on urine production?
How does the release of vasopressin affect hydration status?
How does the release of vasopressin affect hydration status?
Flashcards
Glomerular Filtration
Glomerular Filtration
The process where substances from the blood move into the nephron.
Reabsorption
Reabsorption
The process where substances move from the tubular lumen back into the blood.
Secretion
Secretion
The process where substances move from the blood into the tubular lumen.
Glomerulus
Glomerulus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bowman's Capsule
Bowman's Capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop of Henle
Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Macula Densa
Macula Densa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Signup and view all the flashcards
Angiotensin II
Angiotensin II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium-Potassium ATPase
Sodium-Potassium ATPase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium-Chloride Co-transporter
Sodium-Chloride Co-transporter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Collecting Tubule
Collecting Tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intercalated Cells
Intercalated Cells
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arginine Vasopressin (AVP)
Arginine Vasopressin (AVP)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump
Sodium-Potassium ATPase Pump
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glucose and Sodium Reabsorption in the PCT
Glucose and Sodium Reabsorption in the PCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hydrogen Secretion in the PCT
Hydrogen Secretion in the PCT
Signup and view all the flashcards
Descending Limb of the Loop of Henle
Descending Limb of the Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sodium Reabsorption in the Thick Ascending Limb
Sodium Reabsorption in the Thick Ascending Limb
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent System
Countercurrent System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thiazide Diuretics
Thiazide Diuretics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Combined Thiazide and Loop Diuretics
Combined Thiazide and Loop Diuretics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loop Diuretics
Loop Diuretics
Signup and view all the flashcards
PCT and Loop of Henle function
PCT and Loop of Henle function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Countercurrent Mechanism
Countercurrent Mechanism
Signup and view all the flashcards
Final Urine Concentration
Final Urine Concentration
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does vasopressin affect urine concentration?
How does vasopressin affect urine concentration?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What role does aldosterone play in the collecting duct?
What role does aldosterone play in the collecting duct?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger in the proximal tubule
Function of the sodium-hydrogen exchanger in the proximal tubule
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is NOT a function of the proximal tubule?
What is NOT a function of the proximal tubule?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Primary function of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Function of the loop of Henle
Function of the loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
How are solutes transported out of the tubular lumen?
How are solutes transported out of the tubular lumen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Permeability differences in the loop of Henle
Permeability differences in the loop of Henle
Signup and view all the flashcards
What makes the loop of Henle unique?
What makes the loop of Henle unique?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the proximal tubule reabsorb?
What does the proximal tubule reabsorb?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is the PCT so important?
Why is the PCT so important?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the PCT contribute to acid-base balance?
How does the PCT contribute to acid-base balance?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do the countercurrent mechanism and aldosterone work together?
How do the countercurrent mechanism and aldosterone work together?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the relationship between the countercurrent mechanism and ANP?
What is the relationship between the countercurrent mechanism and ANP?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Nephron Segments and Reabsorption Mechanisms
- Nephrons perform glomerular filtration, secretion, and reabsorption. Filtration moves substances from blood into the nephron; secretion moves them from the blood into the tubular lumen; and reabsorption moves them from the tubular lumen back into the blood.
Filtration Process and Tubular System
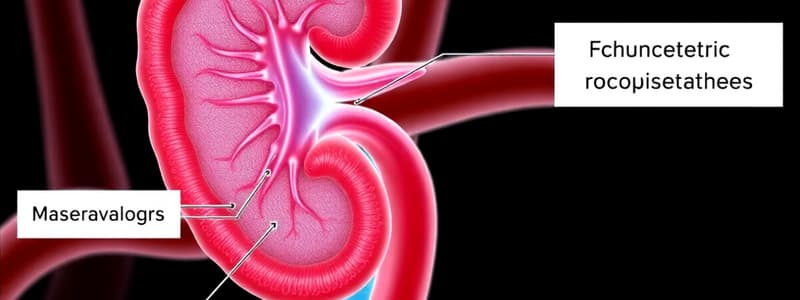
- Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, filtrate collects in Bowman's capsule.
- Reabsorption percentages vary significantly along the nephron.
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT): 67%
- Thick Ascending Loop of Henle: 25%
- Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT): 5-8%
- Collecting Tubule: 3%
- Remaining 0.4% is excreted as urine.
Reabsorption Process
- Reabsorption is the movement of substances from the tubular system back into the blood.
- A "LAB" (lumen, apical membrane, basolateral membrane) framework is used to understand substance movement through the nephron wall.
- Substances cross the apical membrane, enter the tubular cell, and then cross the basolateral membrane to enter the blood vessels.
- Sodium-potassium ATPase is a key pump for this process, moving sodium out of the tubular cell into the blood.
Sodium Reabsorption
- Sodium moves from the lumen across the apical membrane, into the tubular cell.
- The sodium-potassium ATPase pump on the basolateral membrane pumps sodium out of the cell, creating a sodium gradient that drives reabsorption.
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT) Details
- The PCT is the initial segment after Bowman's Capsule, where most reabsorption occurs (67% of the filtered load).
- Key substances reabsorbed in PCT: sodium, chloride, bicarbonate, water, calcium, phosphate, sulfate, glucose, and amino acids.
- Glucose is completely reabsorbed normally, it should not be present in urine.
- PCT is vital for sodium reabsorption, glucose handling, regulating pH (acid-base balance), and calcium/phosphate homeostasis.
- The peritubular capillaries secrete hydrogen ions for pH regulation.
PCT Reabsorption Mechanisms
- Sodium-glucose co-transporter (SGLT) on the apical membrane moves sodium and glucose into the cell simultaneously.
- Sodium-hydrogen exchanger (NHE) on the apical membrane exchanges sodium for hydrogen, contributing to pH balance.
- Aquaporins (water channels) allow water to follow sodium into the cells.
Loop of Henle Details
- Two parts: descending and thick ascending Loop of Henle.
- Descending Limb: permeable to water but not to ions.
- Thick Ascending Limb: permeable to ions but not to water; actively pumps sodium into the interstitial fluid to generate a concentrated medullary environment. 25% of filtered sodium is reabsorbed here.
- Key transport proteins include sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter (NKCC) on the apical membrane, and sodium-potassium ATPase on the basolateral membrane that pump sodium out into the interstitium.
Countercurrent System
- The loop of Henle's countercurrent setup creates a concentration gradient critical for water reabsorption in the collecting duct.
- Sodium reabsorption in the loop of Henle generates the osmotic gradient that drives water reabsorption in the collecting duct.
- The descending limb is permeable to water, and the ascending limb is permeable to ions, creating the concentration gradient.
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT)
- The DCT fine-tunes salt and water excretion.
- Sodium chloride co-transporter is a key reabsorption mechanism (inhibited by thiazide diuretics); it contributes to reabsorbing 5-8% of the filtered sodium.
- Calcium reabsorption is regulated by parathyroid hormone (PTH) and vitamin D.
- Vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding proteins bring calcium into the cell. Calcium channels and calcium-sodium exchangers on the basolateral membranes facilitate reabsorption.
Collecting Tubule
- Final place for filtrate collection, 3-4% of filtrate is reabsorbed here.
- Relatively impermeable to water in the absence of antidiuretic hormone (ADH/AVP), permeability is dependent on water channels.
- Sodium and water channels are regulated by hormones, aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption, and atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) inhibits it.
- ADH/AVP insertion of aquaporins (water channels) leads to water reabsorption.
Autoregulation: Tubuloglomerular Feedback
- Maintains glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- Reduced GFR reduces sodium and chloride delivery to the macula densa, stimulates renin production.
- Renin leads to angiotensin II, causing efferent arteriole vasoconstriction, restoring GFR.
Diuretics
- Loop diuretics block sodium/potassium/chloride cotransporter in the thick ascending loop of Henle.
- Thiazide diuretics block sodium/chloride co-transporter in the DCT.
- Combination use requires careful monitoring.
Summary of Questions
- Question 1: The proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) reabsorbs the majority of filtered solutes, while the loop of Henle creates crucial concentration gradients in the medulla.
- Question 2: Solutes move from the lumen through the apical membrane into cells, then through the basolateral membrane into the blood, using sodium-potassium ATPase.
- Question 3: The descending loop of Henle is permeable to water but not solutes, while the ascending loop is permeable to solutes but not water, establishing the medullary concentration gradient.
- Question 4: The countercurrent mechanism generates a medullary osmotic gradient. Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) regulates water permeability in the collecting duct, influencing urine concentration. Aldosterone also plays a role in sodium reabsorption.
- Question 5: The sodium-hydrogen exchanger (NHE) in the proximal tubule reabsorbs sodium and secretes hydrogen into the lumen.
- Question 6: Fine control of salt and water excretion is a function of the distal tubule and collecting duct, not the proximal tubule.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Test your understanding of the nephron's structure and the various mechanisms for reabsorption. This quiz will cover key filtration processes, percentages of reabsorption at different segments, and the LAB framework for substance movement. Dive deep into the fascinating world of renal biology!