Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term for the organelle responsible for energy production in cells?
What is the term for the organelle responsible for energy production in cells?
- Nucleus
- Axon
- Dendrite
- Mitochondrion (correct)
Which part of a neuron receives signals from other neurons?
Which part of a neuron receives signals from other neurons?
- Axon
- Axon Hillock
- Dendrite (correct)
- Cell Body
What is the function of the cell body in a neuron?
What is the function of the cell body in a neuron?
Contains the nucleus and organelles, integrates signals.
What is the name of the substance that is involved in protein synthesis and contains rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons?
What is the name of the substance that is involved in protein synthesis and contains rough endoplasmic reticulum in neurons?
What part of the neuron contains the genetic material?
What part of the neuron contains the genetic material?
What is the term for the area in a neuron where the axon begins?
What is the term for the area in a neuron where the axon begins?
What is the main function of an axon?
What is the main function of an axon?
What term describes the branches of an axon that allow communication with multiple neurons?
What term describes the branches of an axon that allow communication with multiple neurons?
How many Schwann cells are typically associated with a single axon?
How many Schwann cells are typically associated with a single axon?
What is the role of the Node of Ranvier in neuron function?
What is the role of the Node of Ranvier in neuron function?
What is the role of Schwann cells in relation to axons?
What is the role of Schwann cells in relation to axons?
What is the term for the endpoint of an axon that releases neurotransmitters?
What is the term for the endpoint of an axon that releases neurotransmitters?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
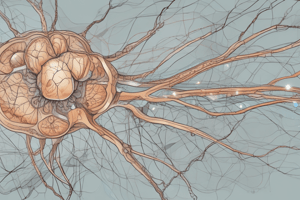
Motor Neuron Diagram Annotations
-
Mitochondrion: Organelles known as the powerhouses of the cell; generate ATP through aerobic respiration to provide energy for the neuron.
-
Dendrite: Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons, facilitating communication in the nervous system.
-
Cell Body: Also known as the soma, contains the nucleus and organelles; integrates incoming signals and supports cellular functions.
-
Nissl Substance: A collection of rough endoplasmic reticulum and ribosomes in the cell body; important for protein synthesis and neurotransmitter production.
-
Nucleus: The control center of the neuron; houses genetic material (DNA) and regulates cellular activities including growth and replication.
-
Axon Hillock: The specialized region where the axon begins; crucial for initiating action potentials based on summed incoming signals.
-
Axon: A long, slender projection that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body to other neurons or muscles.
-
Collateral Branch: Branches of the axon that allow a single neuron to communicate with multiple target cells, enhancing the transmission of signals.
-
One Schwann Cell: A type of glial cell in the peripheral nervous system; vital for the formation of myelin sheath that insulates axons, speeding up nerve signal conduction.
-
Node of Ranvier: Gaps in the myelin sheath along the axon; crucial for saltatory conduction, allowing electrical impulses to jump between nodes and improve signal transmission efficiency.
-
Schwann Cells (forming the myelin sheath on axon): Specialized cells that wrap around axons; increase the speed of electrical impulses and play a role in nerve regeneration.
-
Axon Terminal: The endpoint of an axon where neurotransmitters are released into the synapse, facilitating communication with other neurons or target tissues.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.