Podcast
Questions and Answers
What does motor development primarily study?
What does motor development primarily study?
- The genetic predispositions affecting motor skills
- The influence of environmental factors on physical growth
- The changes in motor performance only during childhood
- The changes in growth, development, and motor performance across the lifespan (correct)
Which factor is NOT listed as influencing motor performance?
Which factor is NOT listed as influencing motor performance?
- Nutrition (correct)
- Heredity
- Maturation
- Experience
What does the term 'proximodistal' refer to in developmental sequences?
What does the term 'proximodistal' refer to in developmental sequences?
- Development of fine motor skills before gross motor skills
- Growth patterns that begin at the head and extend to the toes
- The sequence of brain maturation across different stages
- Growth patterns that occur from the center of the body outward (correct)
Which of the following sequences correctly describes the stages of brain and CNS development?
Which of the following sequences correctly describes the stages of brain and CNS development?
What is an example of an ontogenetic skill?
What is an example of an ontogenetic skill?
What is the primary focus of the study of motor development?
What is the primary focus of the study of motor development?
Which of the following pairs correctly describe the sequence of brain development processes?
Which of the following pairs correctly describe the sequence of brain development processes?
Which developmental sequence describes growth patterns in terms of directionality?
Which developmental sequence describes growth patterns in terms of directionality?
Which factor is primarily associated with physical changes in motor performance?
Which factor is primarily associated with physical changes in motor performance?
Which skill category would include behaviors that are biologically inherent rather than learned?
Which skill category would include behaviors that are biologically inherent rather than learned?
Which term refers to the process of neurons moving to various locations in the brain?
Which term refers to the process of neurons moving to various locations in the brain?
Which developmental sequence describes growth from the center of the body outward?
Which developmental sequence describes growth from the center of the body outward?
What is the initial stage in the brain and CNS development involving the generation of immature neurons?
What is the initial stage in the brain and CNS development involving the generation of immature neurons?
Which of the following is NOT a factor influencing motor performance?
Which of the following is NOT a factor influencing motor performance?
Which term describes skills or behaviors that are inherently acquired by a species?
Which term describes skills or behaviors that are inherently acquired by a species?
What does the term 'myelination' refer to in the context of brain development?
What does the term 'myelination' refer to in the context of brain development?
Which of the following descriptions best represents 'ontogenetic skills'?
Which of the following descriptions best represents 'ontogenetic skills'?
Which developmental process illustrates the interaction of existing neural groups?
Which developmental process illustrates the interaction of existing neural groups?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Motor Development
- Changes in growth, development, and motor performance throughout life.
- It is a lifespan study.
- Includes similarities in development between infants and older adults.
Factors Influencing Motor Performance
- Heredity: Inherited characteristics
- Maturation: Physical development of the body
- Experience: Learning and practice
- Growth: Increase in size and weight
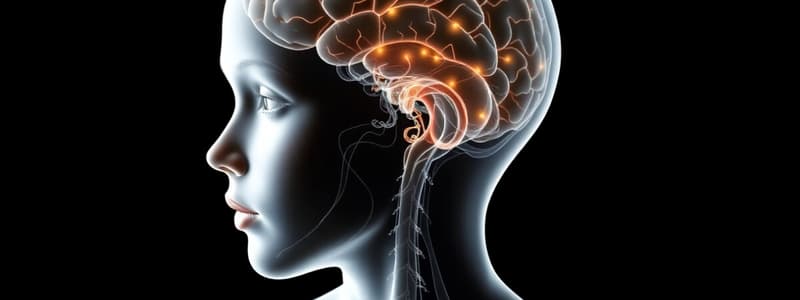
Brain and CNS Development
- Cell Proliferation: Process of generating immature neurons.
- Migration: Movement of neurons to different locations in the brain.
- Integration: Connection and interaction of neural groups.
- Differentiation: Gradual development of specialized control functions.
- Myelination: Coating of neural pathways with myelin, improving signal transmission.
Growth and Control Sequences
- Cephalocaudal: Pattern of growth that progresses from the head to the toes.
- Proximodistal: Development from the center of the body outward.
Phylogentic Skills
- Naturally acquired skills, inherited from a species.
- Examples: Crawling, grasping, sucking.
Ontogenetic Skills
- Skills that require learning and practice.
- Examples: Dancing, playing musical instruments, riding a bike.
Motor Development
- Motor Development studies changes in growth, development, and motor performance across the lifespan
- Infants and older adults share similarities in motor development
- Major factors influencing motor performance are heredity, maturation, experience, and growth
Brain and CNS Development
- The development of the brain and CNS occurs in a specific sequence
- Cell proliferation: involves the generation of immature neurons
- Migration: involves the movement of neurons to different locations in the brain
- Integration: involves the interaction of neural groups
- Differentiation: involves the progression of control
- Myelination: involving covering of neural pathways
Developmental Sequences
- Cephalocaudal growth proceeds from head to toe
- Proximodistal growth proceeds from the midline to periphery
Skills
- Phylogenetic skills are skills or behaviors that are naturally acquired by a species
- Ontogenetic skills are skills or behaviors that must be learned
Motor Development
- Motor development explores how movement abilities change throughout life, from infancy to adulthood.
- It considers the factors that contribute to these changes, including genetics, maturation, experience, and physical growth.
Factors Influencing Motor Performance
- Heredity: Inherited traits play a significant role in motor abilities.
- Maturation: The process of biological development, which affects our physical and neurological capabilities.
- Experience: The practice and learning of motor skills are crucial for improving performance.
- Growth: Physical growth, particularly in the musculoskeletal system, influences motor development.
Development of Brain and CNS
- Cell proliferation: New neurons, which are specialized nerve cells, are created.
- Migration: Neurons move to their specific locations within the brain.
- Integration: Established connections within the brain, enabling communication and function.
- Differentiation: Neurons develop specialized functions, leading to more complex control.
- Myelination: Formation of a protective layer around nerve fibers, which speeds up nerve impulses.
Developmental Sequences of Growth and Control
- Cephalocaudal: The development progresses in a head-to-toe direction.
- Proximodistal: Growth and control moves from the body's center outward towards the extremities.
Phylogenetic and Ontogenetic Skills
- Phylogenetic Skills: Develop naturally within a species and do not require formal learning. Crawling is an example.
- Ontogenetic Skills: Learned behaviors that are specific to an individual and culture, such as dancing.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.