Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the period of the cell cycle between cell divisions called?
What is the period of the cell cycle between cell divisions called?
- Interphase (correct)
- Telophase
- Metaphase
- Prophase
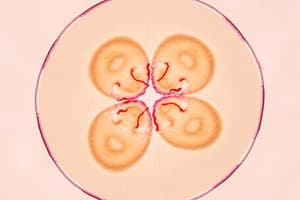
What happens during Prophase?
What happens during Prophase?
Chromosomes become visible, nuclear envelope dissolves, spindle forms.
What occurs during Metaphase?
What occurs during Metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell.
What is Anaphase?
What is Anaphase?
What is Telophase?
What is Telophase?
What are spindle fibers?
What are spindle fibers?
What are sister chromatids?
What are sister chromatids?
What is the function of centrosomes?
What is the function of centrosomes?
What is chromatin?
What is chromatin?
What is a replicated chromosome?
What is a replicated chromosome?
What are new daughter cells?
What are new daughter cells?
What is the role of the nucleolus?
What is the role of the nucleolus?
What is the nuclear membrane?
What is the nuclear membrane?
What is the cell membrane?
What is the cell membrane?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Mitosis Key Concepts
- Interphase: The stage in the cell cycle where the cell prepares for division, occurring between cell divisions.
- Prophase: Chromosomes become visible as they condense, the nuclear envelope dissolves, and spindle fibers begin to form.
- Metaphase: Chromosomes align along the cell's equatorial plane, positioning themselves in preparation for separation.
- Anaphase: Chromatids are pulled apart to opposite ends of the cell, ensuring each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
- Telophase: Chromatids reach the poles, the nuclear envelope re-forms around each set of chromosomes, marking the final stage of mitosis.
Cell Structure and Components
- Spindle Fibers: Essential for the even distribution of chromosomes during cell division, important in both mitosis and meiosis.
- Sister Chromatids: Identical copies of a chromosome connected at the centromere, formed during DNA replication.
- Centrosomes: Organizing centers for microtubules that facilitate the formation and organization of the mitotic spindle during mitosis.
- Chromatin: A complex of DNA, RNA, and proteins within the nucleus, which condenses to form chromosomes during cell division.
- Replicated Chromosome: Consists of two sister chromatids joined at the centromere, providing genetic information for daughter cells.
Post-Mitosis Cell Characteristics
- New Daughter Cells: Resulting from mitosis, these diploid cells contain two complete sets of chromosomes, ensuring genetic continuity.
- Nucleolus: The site within the nucleus responsible for the assembly of ribosomes, critical for protein synthesis.
- Nuclear Membrane: A double lipid bilayer that encloses the nucleus, separating genetic material from the cytoplasm.
- Cell Membrane/Plasma Membrane: A semi-permeable biological membrane that encases the cell, regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.