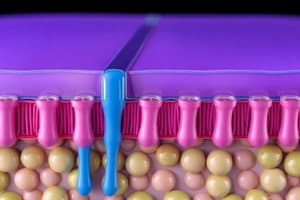
Podcast
Questions and Answers
What type of transport does not require an input of energy and may involve transport proteins?
What type of transport does not require an input of energy and may involve transport proteins?
- Active transport
- Bulk transport
- Passive transport (correct)
- Endocytosis
What type of molecules are phospholipids?
What type of molecules are phospholipids?
- Hydrophobic (correct)
- Hydrophilic
- Non-polar
- Polar
According to the text, what are the main components of cellular membranes?
According to the text, what are the main components of cellular membranes?
- Lipids and proteins (correct)
- Proteins and carbohydrates
- Phospholipids and carbohydrates
- Lipids and phospholipids
What is the main role of phospholipids in the cell membrane?
What is the main role of phospholipids in the cell membrane?
Which type of transport requires both energy and a transport protein?
Which type of transport requires both energy and a transport protein?
What process involves the movement of large molecules through the cell membrane using bulk transport mechanisms?
What process involves the movement of large molecules through the cell membrane using bulk transport mechanisms?
What is the effect of cholesterol on membrane fluidity at warm temperatures?
What is the effect of cholesterol on membrane fluidity at warm temperatures?
What primarily holds membranes together?
What primarily holds membranes together?
In what conditions do membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state?
In what conditions do membranes switch from a fluid state to a solid state?
What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
What is the role of proteins in the cell membrane?
Which lipid component contributes to membrane fluidity?
Which lipid component contributes to membrane fluidity?
What is the primary orientation of hydrophilic regions of membrane proteins?
What is the primary orientation of hydrophilic regions of membrane proteins?
What effect do unsaturated phospholipids have on membrane composition during winter in organisms?
What effect do unsaturated phospholipids have on membrane composition during winter in organisms?
What is the main role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes at cool temperatures?
What is the main role of cholesterol in animal cell membranes at cool temperatures?
What are membranes mainly composed of?
What are membranes mainly composed of?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying