Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary organ responsible for urine formation?
What is the primary organ responsible for urine formation?
- Urethra
- Liver
- Kidneys (correct)
- Bladder
What condition is characterized by inflammation of the kidneys?
What condition is characterized by inflammation of the kidneys?
- Nephritis (correct)
- Pyelonephritis
- Cystitis
- Glomerulonephritis
Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the urinary system?
- Regulating blood volume
- Digesting nutrients (correct)
- Producing hormones
- Maintaining electrolyte balance
Which part of the urinary system stores urine until it is expelled from the body?
Which part of the urinary system stores urine until it is expelled from the body?
What is the primary waste product found in urine?
What is the primary waste product found in urine?
Which statement accurately describes the anatomy of the urinary system?
Which statement accurately describes the anatomy of the urinary system?
What is one of the main functions of the urinary system?
What is one of the main functions of the urinary system?
Which term is related to the medical terminology of the urinary system?
Which term is related to the medical terminology of the urinary system?
What does the abbreviation 'UTI' commonly refer to in medical terms?
What does the abbreviation 'UTI' commonly refer to in medical terms?
Which of the following is NOT a recognized function of the urinary system?
Which of the following is NOT a recognized function of the urinary system?
Flashcards
What is the Urinary System?
What is the Urinary System?
The urinary system is a group of organs responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
What is the role of the kidneys?
What is the role of the kidneys?
The kidneys are the organs responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and producing urine.
What is Nephritis?
What is Nephritis?
Nephritis is inflammation of the kidneys. It can be caused by infections, autoimmune diseases, or other factors.
How is urine formed and excreted?
How is urine formed and excreted?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anatomy of the Urinary System
Anatomy of the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main Functions of the Urinary System
Main Functions of the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medical Terminology of the Urinary System
Medical Terminology of the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Main Abbreviations in the Urinary System
Main Abbreviations in the Urinary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interpreting Urinary System Terms
Interpreting Urinary System Terms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Medical Terminology - Urinary System
- Learning Objectives:
- Define the anatomy of the urinary system
- Identify the main functions of the urinary system
- Identify medical terminology of the urinary system
- Interpret abbreviations and terms.
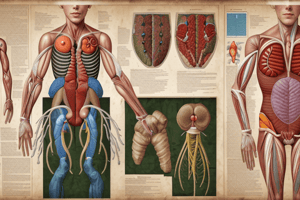
Urinary System Structure
- Organs:
- Two kidneys (form urine)
- Two ureters (transport urine from kidneys to bladder)
- Urinary bladder (stores and eliminates urine)
- Urethra (carries urine out of the body)
Key Terms and Definitions
- Root cyst/o: urinary bladder, refers to bladder
- Nephritis: inflammation of the kidney
- Diuretic: substance increasing urine excretion
- Erythropoietin (EPO): hormone stimulated red blood cell production in bone marrow
- Renin: enzyme raising blood pressure
- Nephrons: The tiny working units of the kidneys
- Glomerular capsule: Part of nephron, filters blood, in nephron
- Tubular reabsorption: process of returning substances to blood from the glomerular filtrate.
- Urea: main nitrogenous waste product in urine
- Urine: fluid excreted by kidneys, contains water, electrolytes, urea, other metabolic wastes, pigments, and other substances in disease cases.
Related Terms
- Cystitis: inflammation of the urinary bladder. often due to infection
- Glomerulonephritis: inflammation of the kidneys, primarily the glomeruli
- Renal colic: radiating pain in kidney region associated with stone passage.
- Renal failure: loss of kidney function. Loss of kidney function often resulting from loss or damage to the kidney nephrons.
- Dialysis: separation of substances by a semipermeable membrane for treating kidney failure.
- Renal transplantation: surgical implantation of a donor's kidney to a recipient
- Diabetes insipidus: condition caused by inadequate production of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) leading to excess water excretion.
- Glycosuria: presence of glucose in urine, often in diabetes mellitus.
- Polydipsia: excessive thirst
- Polyuria: excessive urination
- Dehydration: excessive loss of body fluids
- Acidosis: excessive acidity of body fluids
- Nocturia: excessive urination at night
- Anuresis: lack of urination
- Bacteriuria: presence of bacteria in urine
- Hypokalaemia: deficiency of potassium in the blood
- Hyponatremia: deficiency of sodium in the blood
- Proteinuria: presence of protein, mostly albumin, in the urine
- Creatinine: nitrogen byproduct of muscle metabolism; elevated levels can indicate kidney failure.
- Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN): blood nitrogen in the form of urea; elevated BUN suggests potential kidney problems
- Glomerular filtration rate (GFR): amount of filtrate produced per minute by both kidneys.
Medical Terminology Roots (e.g. ren/o, ur/o, nephr/o)
- ren/o: kidney
- ur/o: urine, urinary tract
- nephr/o: kidney
- glomerul/o: glomerulus
- urethr/o: urethra
- cyst/o: urinary bladder
Important Test Questions & Answers
- Hormone erythropoietin stimulates production of: red blood cells
- Micturition: scientific term for urination
- The tube that carries urine out of the body is: urethra.
- Separation of substances by passage through a membrane: dialysis.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.