Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary cause of goiter?
What is the primary cause of goiter?
- Excessive iodine intake
- Autoimmune disorders
- Lack of iodine (correct)
- Genetic factors
What might be necessary to remove a sinus tract originating from the piriform fossa?
What might be necessary to remove a sinus tract originating from the piriform fossa?
- Total thyroidectomy
- Lazarus procedure
- Thyroid biopsy
- Partial thyroidectomy (correct)
Where can aberrant thyroid glandular tissue commonly be found?
Where can aberrant thyroid glandular tissue commonly be found?
- Near the wrist
- At the base of the skull
- Root of the tongue (correct)
- In the pituitary gland
In which scenario is it crucial to preserve the posterior part of each thyroid lobe during a thyroidectomy?
In which scenario is it crucial to preserve the posterior part of each thyroid lobe during a thyroidectomy?
What percentage of people have a pyramidal lobe associated with their thyroid gland?
What percentage of people have a pyramidal lobe associated with their thyroid gland?
What is hemothorax primarily caused by?
What is hemothorax primarily caused by?
Which of the following best describes a pulmonary embolism?
Which of the following best describes a pulmonary embolism?
What is the primary function of phagocytes in relation to carbon particles in the lungs?
What is the primary function of phagocytes in relation to carbon particles in the lungs?
What condition may result from a pulmonary embolism if the blood supply is deprived?
What condition may result from a pulmonary embolism if the blood supply is deprived?
What changes occur in the lungs of smokers and people in urban environments?
What changes occur in the lungs of smokers and people in urban environments?
What is a serious risk associated with bleeding after a near-total thyroidectomy?
What is a serious risk associated with bleeding after a near-total thyroidectomy?
What is a common consequence of accidentally removing the parathyroid glands during a thyroidectomy?
What is a common consequence of accidentally removing the parathyroid glands during a thyroidectomy?
What procedure may be performed to preserve parathyroid glands during thyroid surgery?
What procedure may be performed to preserve parathyroid glands during thyroid surgery?
What happens to the diaphragm when the phrenic nerve is injured?
What happens to the diaphragm when the phrenic nerve is injured?
How may surgeons block the phrenic nerve during lung surgery?
How may surgeons block the phrenic nerve during lung surgery?
What is the primary reason for the high risk of mortality and morbidity in injuries located in zones I and III of the neck?
What is the primary reason for the high risk of mortality and morbidity in injuries located in zones I and III of the neck?
Which anatomical structures are preserved during a radical dissection of the neck?
Which anatomical structures are preserved during a radical dissection of the neck?
What is a common consequence of penetrating wounds that reach the pleural cavity?
What is a common consequence of penetrating wounds that reach the pleural cavity?
Which type of pleura is insensitive to pain?
Which type of pleura is insensitive to pain?
In case of segmental atelectasis, what happens to the adjacent segments of the lung?
In case of segmental atelectasis, what happens to the adjacent segments of the lung?
What is the primary action when a penetrating wound disrupts the thoracic wall?
What is the primary action when a penetrating wound disrupts the thoracic wall?
What is the term for the collapse of a previously inflated lung?
What is the term for the collapse of a previously inflated lung?
Which area is commonly referred for pain originating from the mediastinal pleura?
Which area is commonly referred for pain originating from the mediastinal pleura?
Which structures are NOT typically preserved during a radical dissection?
Which structures are NOT typically preserved during a radical dissection?
What is the primary physiological reason that normal lungs remain distended?
What is the primary physiological reason that normal lungs remain distended?
What could cause increased risk of lung collapse in children compared to adults?
What could cause increased risk of lung collapse in children compared to adults?
What are the signs of pulmonary collapse visible on imaging?
What are the signs of pulmonary collapse visible on imaging?
What is the term for air entering the pleural cavity leading to lung collapse?
What is the term for air entering the pleural cavity leading to lung collapse?
Which of the following describes the visceral pleura?
Which of the following describes the visceral pleura?
What should you do if a person is unable to breathe but can cough?
What should you do if a person is unable to breathe but can cough?
In which area should the fist be placed when performing the Heimlich maneuver?
In which area should the fist be placed when performing the Heimlich maneuver?
What is a common symptom of laryngeal cancer?
What is a common symptom of laryngeal cancer?
What happens to the anteroposterior diameter of the rima glottidis in pubertal males?
What happens to the anteroposterior diameter of the rima glottidis in pubertal males?
Which method is more accessible for patients to measure lung function at home?
Which method is more accessible for patients to measure lung function at home?
What should be performed if a foreign object persists in a person's airway after backslaps?
What should be performed if a foreign object persists in a person's airway after backslaps?
What happens to the larynx of females during puberty compared to males?
What happens to the larynx of females during puberty compared to males?
What is the first step in using a Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) device?
What is the first step in using a Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR) device?
What device may be necessary for vocal rehabilitation after a laryngectomy?
What device may be necessary for vocal rehabilitation after a laryngectomy?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of laryngeal cancer?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of laryngeal cancer?
What is the primary cause of lung cancer?
What is the primary cause of lung cancer?
Which condition is characterized by coughing up blood?
Which condition is characterized by coughing up blood?
What is the most common cause of epistaxis?
What is the most common cause of epistaxis?
During a Valsalva maneuver, what happens to the glottis?
During a Valsalva maneuver, what happens to the glottis?
Which structure is most commonly injured in a nasal fracture?
Which structure is most commonly injured in a nasal fracture?
What common symptom is associated with lung cancer?
What common symptom is associated with lung cancer?
Which treatment is NOT typically used for epistaxis?
Which treatment is NOT typically used for epistaxis?
What complication can arise from a deviated nasal septum?
What complication can arise from a deviated nasal septum?
Which of the following is a potential consequence of laryngeal fractures?
Which of the following is a potential consequence of laryngeal fractures?
Which method can be used to assess the presence of sinusitis?
Which method can be used to assess the presence of sinusitis?
What is the most frequent origin of bleeding in epistaxis?
What is the most frequent origin of bleeding in epistaxis?
What is the primary danger of chronic bronchitis?
What is the primary danger of chronic bronchitis?
What anatomical feature helps to spread infections from the nasal cavity to the middle ear?
What anatomical feature helps to spread infections from the nasal cavity to the middle ear?
During which activity is the Valsalva maneuver commonly utilized?
During which activity is the Valsalva maneuver commonly utilized?
Flashcards
Hydrothorax
Hydrothorax
A buildup of fluid in the pleural cavity, often caused by a pleural effusion.
Hemothorax
Hemothorax
A buildup of blood in the pleural cavity, often caused by an injury to an intercostal or internal thoracic vessel.
Pulmonary embolism
Pulmonary embolism
A blockage of a pulmonary artery by a blood clot, fat globule, or air bubble.
Cor pulmonale
Cor pulmonale
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pulmonary infarct
Pulmonary infarct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zone I of the neck
Zone I of the neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zone II of the neck
Zone II of the neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zone III of the neck
Zone III of the neck
Signup and view all the flashcards
Severity of neck trauma in Zones I and III
Severity of neck trauma in Zones I and III
Signup and view all the flashcards
Severity of neck trauma in Zone II
Severity of neck trauma in Zone II
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radical neck dissection
Radical neck dissection
Signup and view all the flashcards
Visceral pleura
Visceral pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parietal pleura
Parietal pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referred pain from costal and peripheral diaphragmatic pleura
Referred pain from costal and peripheral diaphragmatic pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Referred pain from mediastinal and central diaphragmatic pleura
Referred pain from mediastinal and central diaphragmatic pleura
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pneumothorax
Pneumothorax
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atelectasis
Atelectasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Segmental atelectasis
Segmental atelectasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Air entering the pleural cavity through an open wound
Air entering the pleural cavity through an open wound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sinus tract from piriform fossa
Sinus tract from piriform fossa
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aberrant Thyroid Glandular Tissue
Aberrant Thyroid Glandular Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pyramidal lobe of the thyroid
Pyramidal lobe of the thyroid
Signup and view all the flashcards
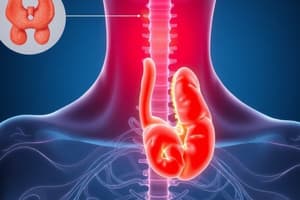
Goiter
Goiter
Signup and view all the flashcards
Thyroidectomy
Thyroidectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is hemoptysis?
What is hemoptysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the most common cause of hemoptysis?
What is the most common cause of hemoptysis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is lung carcinoma?
What is lung carcinoma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the main cause of lung carcinoma?
What is the main cause of lung carcinoma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some common symptoms of lung carcinoma?
What are some common symptoms of lung carcinoma?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is metastasis?
What is metastasis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Where does lung carcinoma first metastasize?
Where does lung carcinoma first metastasize?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a nasal fracture?
What is a nasal fracture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some consequences of a nasal fracture?
What are some consequences of a nasal fracture?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is a deviated nasal septum?
What is a deviated nasal septum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some consequences of a deviated nasal septum?
What are some consequences of a deviated nasal septum?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is rhinitis?
What is rhinitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is epistaxis?
What is epistaxis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are some causes of epistaxis?
What are some causes of epistaxis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is sinusitis?
What is sinusitis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What's the risk of bleeding after a near-total thyroidectomy?
What's the risk of bleeding after a near-total thyroidectomy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is inadvertent parathyroid removal a concern during neck surgery?
Why is inadvertent parathyroid removal a concern during neck surgery?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the precautions taken and complications associated with a complete thyroidectomy?
What are the precautions taken and complications associated with a complete thyroidectomy?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can a phrenic nerve injury affect breathing?
How can a phrenic nerve injury affect breathing?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the difference between temporary and permanent phrenic nerve injury?
What is the difference between temporary and permanent phrenic nerve injury?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heimlich Maneuver
Heimlich Maneuver
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysphagia
Dysphagia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hoarseness
Hoarseness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Otalgia
Otalgia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laryngectomy
Laryngectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Electrolarynx
Electrolarynx
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tracheo-esophageal prosthesis
Tracheo-esophageal prosthesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Esophageal speech
Esophageal speech
Signup and view all the flashcards
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Peak Expiratory Flow Rate (PEFR)
Signup and view all the flashcards
PEFR Diary
PEFR Diary
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Clinical Anatomy of the Thorax
- Focuses on applying anatomical knowledge to clinical situations.
- Covers the thoracic respiratory system, including lungs, bronchi, trachea, and pleura.
- Details penetrating neck trauma, differentiating by zones (I, II, and III) and their associated structures.
- Discusses the structures of each zone in detail. Zone I covers the area from the clavicles-manubrium to the cricoid cartilage, including cervical pleura, apices of lungs, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, trachea, esophagus, common carotid arteries, jugular veins, and cervical vertebral column. Zone II expands from the cricoid cartilage to the angle of the mandible, including the superior part of the thyroid gland, thyroid cartilage, cricoid cartilages, larynx, laryngopharynx, carotid arteries, jugular veins, esophagus, and cervical vertebral column. Zone III encompasses the superior area above the angle of the mandible, including salivary glands, oral and nasal cavities, oropharynx, and nasopharynx.
- Highlights injury patterns, complications, and repair strategies for each zone. Zone I and III injuries are associated with airway obstruction, high mortality and morbidity, and challenging surgical complications for repair of the injured structures and vascular damage. Zone II injuries are more common with less severe mortality and morbidity; direct pressure can manage hemorrhages and injuries are readily identifiable for repair.
- Explains radical dissections of the neck to remove deep cervical nodes and surrounding structures.
- Details preserved and not preserved structures during these procedures. Preserved structures include vagus and phrenic nerves, brachial plexus, and major arteries. No preserved structures include cutaneous branches of cervical plexus and deep cervical nodes.
- Defines and describes pleural pain, distinguishing between visceral pleura, insensitive to pain due to lack of sensory nerves, and parietal pleura, highly sensitive due to its innervation (e.g., intercostal nerves, phrenic nerves). This section highlights referred pain areas from different parts of the diaphragmatic and mediastinal pleura.
- Discusses injuries of the pleura, including pneumothorax (a condition where air enters the pleural cavity).
- Identifies areas for pleural injury (e.g., right infrasternal angle, costovertebral angles).
- Defines pulmonary collapse/atelectasis and describes its types (primary and secondary).
- Explains that pleural cavities have a negative pressure which helps in lung inflation.
- Provides radiological signs of pulmonary collapse.
- Elevation of the diaphragm, intercostal space narrowing, and displacement of the mediastinum.
- Describes a whitened lung area surrounded by a black halo (to diagnose lung collapse).
- Describes segmental atelectasis due to blockage of a segmental bronchus .
- Explains pneumothorax and hydrothorax. This section distinguishes causes (e.g., penetrating wound, fractured ribs) and liquid types (blood -hemothorax).
- Explains the inhalation of carbon particles, indicating that normal lung color is pink, and that smokers and those in industrial areas tend to have darker mottled lungs due to buildup.
- Describes pulmonary embolism, including its causes (blood clot, fat globule, air bubble) and how it obstructs pulmonary arteries.
- Discusses consequences of pulmonary embolism, including right heart overload, risk of pulmonary infarct, and possible inflammation of pleura around the affected area.
- Describes symptoms of hemoptysis (coughing up blood).
- Covers lung carcinoma, including metastasis and main cause.
- Covers the anatomy of nasal fractures and possible consequences.
- Discusses deviation of the nasal septum including causes, consequences, and treatment.
- Characterizes rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal mucosa).
- Discusses epistaxis (nosebleeds), including causes, location of the bleeding source (Kiesselbach area), and typical treatments (anterior/posterior nasal packs, surgical embolization).
- Explores sinusitis, how infections spread to the paranasal sinuses, and how swelling blocks sinus openings (meatus).
- Explains transillumination of sinuses and describes its use in dark environments.
- Expands description of fractures of laryngeal skeleton caused by traumas in sports and seatbelt compressions in car accidents.
- Details consequences of laryngeal fractures (e.g., hemorrhage, edema, breathing issues, hoarseness).
- Explains the Valsalva maneuver, including its function (maintaining glotis closure during forced expiration), and its use in diagnostics.
- Outlines the stages of the Valsalva maneuver. This highlights the significance of deep inspiration and forced expiration.
- Details about the mechanism of the Valsalva maneuver, particularly the role of anterolateral abdominal muscles, pressure changes, and impact on venous return.
- Describes the history of the Valsalva maneuver.
- Describes the Heimlich maneuver including its use in cases of choking.
- Describes the method of the Heimlich maneuver, steps for performing in adults and children.
- Covers cancer of the larynx, its symptoms, diagnostics, and possible treatments like laryngectomy and vocal rehabilitation methods (e.g., electrolarynx, tracheo-esophageal prosthesis).
- Outlines the age changes in the larynx, such as consistent growth during childhood, significant changes in puberty for males, and the presence, though less significant, of changes for females.
- States that artificial testosterone does not always result in a lower voice.
- Covers the different components of the throat, such as the thyroid, cricoid, and arytenoid cartilages that can become ossified with age, that make them visible in radiographic images.
- Details about Peak Expiratory Flow Rate test (PEFR) method use for diagnosing respiratory conditions.
- Presents ways for performing a PEFR test, such as setting up the machine, positioning the patient, instructions for breathing, and repeating procedure.
- Discusses the thyroid and parathyroid glands, including their anatomy and the causes and implications of goiter and their removal (thyroidectomy).
- Looks at the different parts where the sinus tract from the piriform fossa to the thyroid gland is found and their treatment.
- Details a collection of congenital abnormalities involving the thyroid gland (e.g., aberrant thyroid tissue, pyramidal lobe).
- Provides information on the causes, impact, and location of possible abnormalities.
- Discusses injury of a phrenic nerve, particularly paralysis of diaphragm half.
- States that the anesthetic is used to block phrenic nerves during lung surgery.
- Provides radiographic images for diagnostics and anatomy study purposes of injury of the phrenic nerve.
- Lists the sources for the references.
Thoracic Respiratory System
- Includes the lungs, bronchi, trachea, and pleura.
- Presents their clinical anatomy; application of anatomical knowledge to clinical reality.
Penetrating Traumatisms in the Neck
- Explains the methodology for diagnosing severity of neck trauma.
- Explains in detail the structure in each zone.
Radical Dissections of the Neck
- Describes the purpose of the procedure.
- Presents preserved and non-preserved structures.
Pleural Pain
- Differentiates visceral and parietal pleura.
- Defines referred pain areas for both.
Injuries of Pleura
- Describes pneumothorax and its causes.
- Identifies areas for injury.
Pulmonary Collapse/Atelectasis
- Details primary and secondary atelectasis.
- Explains negative pleural pressure and lung elasticity.
Neurological Injuries
- Discusses phrenic nerve injury and paralysis of the diaphragm.
Injuries to the Thoracic Cavity and Respiratory Tract
- Presents a thorough description of the different components involved in these types of injuries.
Other Topics
- Covering various other topics like pulmonary embolism, lung carcinoma, hemoptysis, nasal fractures, nasal septum deviations, rhinitis, epistaxis, sinusitis, laryngeal fractures, Valsalva maneuver, Heimlich maneuver, and the use of PEFR.
- Providing a deeper understanding of the anatomical structures and their implications in various clinical situations.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.