Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is a characteristic of the Mercator projection that makes it suitable for navigation?
What is a characteristic of the Mercator projection that makes it suitable for navigation?
- Minimal distortion of countries near the Equator
- True compass bearings between points (correct)
- Planar representation of the globe
- Accurate representation of landmass sizes
What is a drawback of the Mercator projection?
What is a drawback of the Mercator projection?
- Inaccurate representation of compass bearings
- Limited use for navigation
- Distortion of landmass sizes near the Equator (correct)
- Planar representation of the globe
What is the primary goal of the Peters projection?
What is the primary goal of the Peters projection?
- To preserve true compass bearings between points
- To emphasize the size of countries near the poles
- To provide a planar representation of the globe
- To minimize distortion of countries near the Equator (correct)
What type of projection is used by the National Geographic society on its world maps?
What type of projection is used by the National Geographic society on its world maps?
What is the main difference between a planar projection and other types of projections?
What is the main difference between a planar projection and other types of projections?
What is a common criticism of the Mercator projection from equatorial countries?
What is a common criticism of the Mercator projection from equatorial countries?
What is the main reason why maps were invented?
What is the main reason why maps were invented?
What is the primary function of a map's legend?
What is the primary function of a map's legend?
What is the term for the ratio of distance on a map to the actual distance on the earth's surface?
What is the term for the ratio of distance on a map to the actual distance on the earth's surface?
Which type of map is most suitable for showing a large amount of detail over a small area?
Which type of map is most suitable for showing a large amount of detail over a small area?
What is the primary characteristic of a thematic map?
What is the primary characteristic of a thematic map?
What is the purpose of a map's title?
What is the purpose of a map's title?
What is the term for the lines that set a map apart from other information?
What is the term for the lines that set a map apart from other information?
Which type of map is most suitable for showing a small amount of detail over a large area?
Which type of map is most suitable for showing a small amount of detail over a large area?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Map Projections
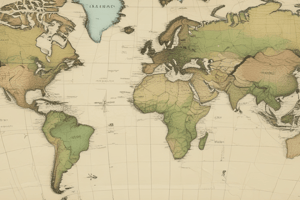
- A globe is the only accurate method to represent the earth, but globes are not easily transportable, leading to the creation of maps through map projections.
- Map projections involve transferring features of the globe onto a flat surface.
Map Facts
- Maps represent features of the Earth drawn on a flat surface, but cannot show the exact surface of the earth like a photograph can.
- Maps simplify the real world by not depicting every single item (e.g., street signs, buildings).
- Basic features of any map include:
- Title (describes the map's content)
- Legend (explains symbols and colors)
- Date of Publication (when the map was created)
Map Scale and Direction
- Scale compares distance on the map with actual distance on Earth's surface (e.g., 1:100,000).
- Large scale maps (1:50,000 and less) show large amounts of detail over a small area.
- Small scale maps (1:250,000) show a small amount of detail over a large area.
- Direction is represented by a direction arrow, symbol, or latitude and longitude.
Types of Maps
- General Purpose Maps: provide many types of information on one map (e.g., roads, water bodies, cities).
- Thematic Maps: show information on only one type of information (e.g., soil type, population density).
- Topographic Maps: use symbols to show various features (e.g., bridges, schools).
Mercator Projection
- The Mercator projection is suitable for navigation due to its accurate compass bearings between points.
- However, the Mercator projection greatly distorts the actual size of land masses, with countries near the Equator appearing smaller and those near the poles appearing longer.
Peters Projection
- The Peters projection is an equal-area projection that minimizes distortion of countries near the Equator.
- The National Geographic society adopted a type of equal projection (Winkel Tripel) on its world maps, providing a more realistic representation of Earth.
Planar Projection
- A Planar Projection map is like taking a piece of paper and transferring a picture of the part of the globe that touches the paper.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.