Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main function of the glomerulus?
What is the main function of the glomerulus?
- To reabsorb electrolytes and nutrients
- To regulate blood pressure
- To filter blood for water, waste, and solutes (correct)
- To secrete waste into the urinary bladder
What is the outer layer of the kidney called?
What is the outer layer of the kidney called?
- Nephron
- Medulla
- Renal pyramid
- Cortex (correct)
What brings blood into the kidney?
What brings blood into the kidney?
- Renal artery (correct)
- Ureter
- Renal vein
- Collecting duct
What is the renal pelvis responsible for collecting?
What is the renal pelvis responsible for collecting?
What is the term for the tuft of capillaries inside the membranous sac called a Bowman's capsule?
What is the term for the tuft of capillaries inside the membranous sac called a Bowman's capsule?
What is the location where the filtration takes place in the kidney?
What is the location where the filtration takes place in the kidney?
What is the primary function of aquaporins in a lipid bilayer membrane?
What is the primary function of aquaporins in a lipid bilayer membrane?
What is the term for a membrane that allows some molecules through it, but not others?
What is the term for a membrane that allows some molecules through it, but not others?
What is the process by which essential molecules are transported back into the blood after filtration?
What is the process by which essential molecules are transported back into the blood after filtration?
What is the term for organisms that maintain internal fluids at a stable osmotic pressure that is distinct from that of the environment?
What is the term for organisms that maintain internal fluids at a stable osmotic pressure that is distinct from that of the environment?
What is the byproduct of protein and nucleic acid breakdown that is toxic to living cells?
What is the byproduct of protein and nucleic acid breakdown that is toxic to living cells?
What are the two mechanisms by which nitrogenous wastes are removed from the blood?
What are the two mechanisms by which nitrogenous wastes are removed from the blood?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in the midgut?
What is the primary function of the pancreas in the midgut?
What is the purpose of the hormone secretin in the midgut?
What is the purpose of the hormone secretin in the midgut?
What is the function of the villi and microvilli in the small intestine?
What is the function of the villi and microvilli in the small intestine?
How do glucose and other hydrophilic nutrients move into the bloodstream in the small intestine?
How do glucose and other hydrophilic nutrients move into the bloodstream in the small intestine?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in the midgut?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder in the midgut?
What is the primary function of the large intestine (hindgut)?
What is the primary function of the large intestine (hindgut)?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
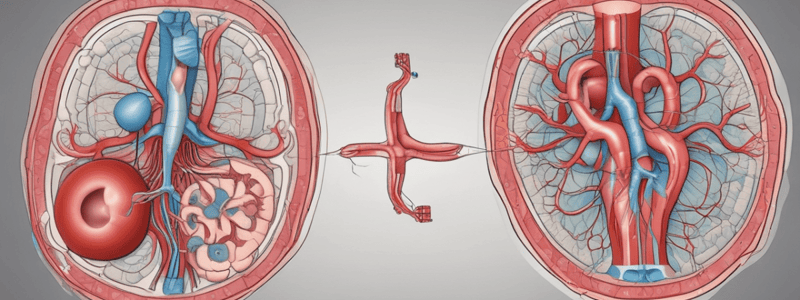
Mammalian Kidney
- Kidneys filter nitrogenous waste and help regulate blood pressure and blood volume.
- The renal artery brings blood into the kidney, and the filtered blood is returned via the renal vein.
- The ureter leads to the urinary bladder.
- Filtration takes place in the renal pyramids, which are filled with nephrons (renal tubules and associated capillaries).
Kidney Anatomy
- The outer layer of the kidney is called the cortex, and the inner layer is called the medulla.
- The medulla is further subdivided into the inner and outer medulla.
- The glomerulus is a tuft of capillaries inside the membranous sac called a Bowman's capsule.
- Individual renal tubules in a renal pyramid flow into a collecting duct.
Bowman's Capsule
- The Bowman's capsule is the location where blood is first filtered for water, waste, and solutes.
- Blood moves from the capillary into the Bowman's space.
Renal Tubules
- Renal tubules are divided into:
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Loop of Henle
- Distal convoluted tubule
- Proximal convoluted tubule: reabsorbs electrolytes, glucose, amino acids, sodium, and chloride into the blood.
- Loop of Henle: descending side is water permeable, and ascending side is water impermeable and actively transports electrolytes out.
- Distal convoluted tubule: main site of secretion, regulates K+, Na+, and Ca+2, and regulates urine pH with bicarbonate.
Collecting Duct
- Permeability is regulated by antidiuretic hormone (ADH), which is secreted by the posterior pituitary to control the amount of water in the body.
Controlling Blood Pressure
- The kidney monitors blood pressure due to its high blood flow.
- Specialized cells (juxtaglomerular apparatus) in the blood vessels leaving the glomerulus detect low or high blood pressure.
- When blood pressure is low, the juxtaglomerular apparatus triggers the hormone angiotensin to be activated, which causes smooth muscles in the blood vessels to contract, raising blood pressure.
Renal System Vocabulary
- Selectively permeable: a membrane that allows some molecules through, but not others.
- Aquaporins: channels in a lipid bilayer membrane that allow water to move through it.
- Osmoconformers: keep internal fluids at the same osmotic pressure as the environment.
- Osmoregulators: maintain internal fluids at a stable osmotic pressure that is distinct from that of the environment.
Nitrogenous Waste Removal
- Ammonia is produced when proteins and nucleic acids are broken down, and it is toxic to living cells.
- Different organisms deal with ammonia production in different ways:
- Ammonia: most toxic, requires high volumes of water
- Urea: less toxic, but requires energy to produce and water to eliminate
- Uric Acid: least toxic, energetically most expensive
- Nitrogenous wastes are removed from the blood through two mechanisms: filtration and secretion.
- Reabsorption: process by which essential molecules are transported back into blood after filtration.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.