Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the epididymis?
What is the primary function of the epididymis?
- To transport sperm to the urethra
- To store and mature sperm (correct)
- To secrete fluid for sperm motility
- To produce testosterone
What percentage of total semen volume is secreted by the seminal vesicles?
What percentage of total semen volume is secreted by the seminal vesicles?
- 50%
- 20%
- 30%
- 60% (correct)
Which hormone is synthesized by Leydig cells from cholesterol?
Which hormone is synthesized by Leydig cells from cholesterol?
- Dihydrotestosterone
- Insulin
- Testosterone (correct)
- Estrogen
Which gland secretes a thin alkaline fluid that contains zinc and citric acid?
Which gland secretes a thin alkaline fluid that contains zinc and citric acid?
What is the primary role of the bulbourethral glands?
What is the primary role of the bulbourethral glands?
At what stage does testosterone promote the growth of male reproductive organs?
At what stage does testosterone promote the growth of male reproductive organs?
What is converted to dihydrotestosterone in target organs?
What is converted to dihydrotestosterone in target organs?
Which substance does testosterone NOT significantly influence?
Which substance does testosterone NOT significantly influence?
What is the primary function of the interstitial cells of Leydig in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the interstitial cells of Leydig in the male reproductive system?
Which structure in the male reproductive system is primarily responsible for spermatogenesis?
Which structure in the male reproductive system is primarily responsible for spermatogenesis?
What percentage of the testis is composed of seminiferous tubules?
What percentage of the testis is composed of seminiferous tubules?
What are Sertoli cells mainly responsible for in the male reproductive system?
What are Sertoli cells mainly responsible for in the male reproductive system?
Which statement correctly describes the testis in relation to its anatomical components?
Which statement correctly describes the testis in relation to its anatomical components?
What occurs in the fluid-filled lumen of seminiferous tubules?
What occurs in the fluid-filled lumen of seminiferous tubules?
What type of hormone is primarily produced by the testes?
What type of hormone is primarily produced by the testes?
Which of the following best describes the function of the duct systems in the male reproductive system?
Which of the following best describes the function of the duct systems in the male reproductive system?
What results from the action of testosterone on the vocal cords?
What results from the action of testosterone on the vocal cords?
How does testosterone influence growth during puberty?
How does testosterone influence growth during puberty?
Which hormone does testosterone stimulate to promote erythropoiesis?
Which hormone does testosterone stimulate to promote erythropoiesis?
What is the role of the hypothalamus in testosterone regulation?
What is the role of the hypothalamus in testosterone regulation?
What action does LH have in relation to testosterone?
What action does LH have in relation to testosterone?
What effect does testosterone have on the secretion of LH?
What effect does testosterone have on the secretion of LH?
What is the primary function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the ovaries in the female reproductive system?
During prenatal development, what does testosterone do?
During prenatal development, what does testosterone do?
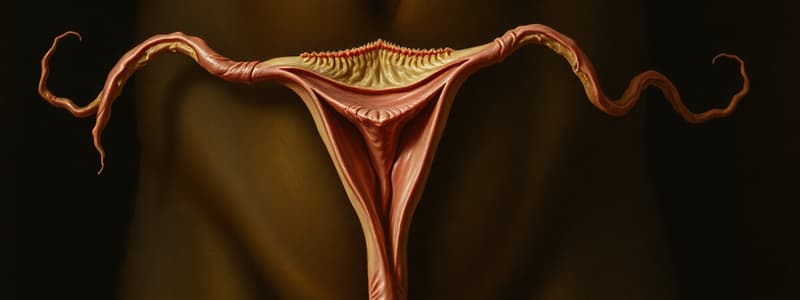
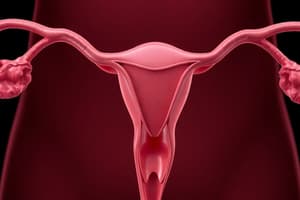
Which part of the uterus is involved in opening into the vagina?
Which part of the uterus is involved in opening into the vagina?
What role do Sertoli cells play in testosterone regulation?
What role do Sertoli cells play in testosterone regulation?
How long are the fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system?
How long are the fallopian tubes in the female reproductive system?
What is one of the actions of estrogen on the vagina?
What is one of the actions of estrogen on the vagina?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the growth of the sex organs at puberty?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the growth of the sex organs at puberty?
What change does estrogen promote in the breast tissue?
What change does estrogen promote in the breast tissue?
What effect does estrogen have on body fat distribution?
What effect does estrogen have on body fat distribution?
What is the consequence of estrogen deficiency after menopause?
What is the consequence of estrogen deficiency after menopause?
What effect does estrogen have on epiphyseal closure in girls compared to boys?
What effect does estrogen have on epiphyseal closure in girls compared to boys?
What is a metabolic effect of certain hormones mentioned?
What is a metabolic effect of certain hormones mentioned?
How does progesterone impact the uterus during pregnancy?
How does progesterone impact the uterus during pregnancy?
What role does progesterone play in mammary gland development?
What role does progesterone play in mammary gland development?
What initiates the secretion of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary?
What initiates the secretion of FSH and LH from the anterior pituitary?
What type of feedback does estrogen produce during a moderate increase?
What type of feedback does estrogen produce during a moderate increase?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing basal body temperature?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for increasing basal body temperature?
What is the role of FSH and LH in ovarian function?
What is the role of FSH and LH in ovarian function?
Flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
The process of sperm formation within the seminiferous tubules of the testes.
Sertoli cells
Sertoli cells
Specialized cells within the seminiferous tubules that nourish and support developing sperm cells.
Leydig cells
Leydig cells
Located in the connective tissue between seminiferous tubules, these cells produce androgens, primarily testosterone.
Androgens
Androgens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone
Testosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male Reproductive System
Male Reproductive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ducts of the Male Reproductive System
Ducts of the Male Reproductive System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis
Penis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vas Deferens
Vas Deferens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ejaculatory Duct
Ejaculatory Duct
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicles
Seminal Vesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Glands
Bulbourethral Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dihydrotestosterone
Dihydrotestosterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Male secondary sexual development
Male secondary sexual development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone's impact on growth
Testosterone's impact on growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone's effect on bone growth
Testosterone's effect on bone growth
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epiphyseal plate closure
Epiphyseal plate closure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone and erythropoiesis
Testosterone and erythropoiesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testosterone's role in prenatal development
Testosterone's role in prenatal development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testis descent
Testis descent
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regulation of testosterone secretion
Regulation of testosterone secretion
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the parts of the female reproductive system?
What are the parts of the female reproductive system?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the ovaries?
What is the function of the ovaries?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of the uterus?
What is the function of the uterus?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the vagina do?
What does the vagina do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are fallopian tubes for?
What are fallopian tubes for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does estrogen do?
What does estrogen do?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does estrogen affect different organs?
How does estrogen affect different organs?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the secondary sex characteristics developed by estrogen?
What are the secondary sex characteristics developed by estrogen?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone
Progesterone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone's effect on mammary glands
Progesterone's effect on mammary glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone's thermogenic effect
Progesterone's thermogenic effect
Signup and view all the flashcards
Progesterone's role in pregnancy
Progesterone's role in pregnancy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen
Estrogen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's effect on uterus
Estrogen's effect on uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's role in female development
Estrogen's role in female development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's role in ovulation
Estrogen's role in ovulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Physiology & Anatomy II - Reproduction - Sex Hormones
- Competency Objectives: Students will be able to illustrate the anatomy of the male and female genital systems, detail the chemical nature, actions, and regulation of testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone hormones, and describe ovarian hormone regulation.
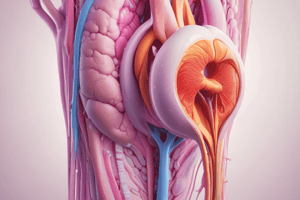
Male Reproductive System
- Anatomy: Includes two testes producing sperm and secreting androgens (primarily testosterone).
- Testis Structure: Composed of:
- Seminiferous Tubules (80%): Coiled tubes (900) where sperm are formed (spermatogenesis). Bounded by a basement membrane, contain fluid-filled lumen with spermatozoa. Sertoli cells within the tubules provide nutrients, hormones, and enzymes to growing spermatids.
- Leydig Cells (20%): Interstitial cells located in the connective tissue between seminiferous tubules; these cells primarily secrete testosterone.
- Ducts: Series of ducts leading from testes to penis:
- Epididymis: Coiled tube (6 meters) where sperm undergo maturation.
- Vas Deferens: Sperm remain viable here for months; dilated terminal part is the ampulla
- Ejaculatory Duct: Opens into the urethra.
- Accessory Glands: Secrete fluid suspending ejaculated sperm:
- Prostate: Secretes thin alkaline fluid (20% of semen volume), containing cholesterol, phospholipids, zinc, and citric acid.
- Seminal Vesicles: Secrete mucoid material (60% of semen volume), containing fructose and other nutrients.
- Bulbourethral Glands: Secrete mucus.
Testosterone Hormone
- Chemical Nature: A steroid hormone synthesized by Leydig cells from cholesterol, sometimes converted to dihydrotestosterone (more active form) in target organs (e.g., prostate).
- Actions:
- Growth of Sex Organs: Increased secretion at puberty promotes growth of testes, scrotum, and penis, and increases secretory activity of epididymis, prostate, and seminal vesicles.
- Secondary Sex Characteristics:
- Body Hair: Increases hair on face, chest, and other body areas. Influences male hair distribution (e.g., hairline recession).
- Voice: Enlargement of the larynx and thickening of vocal cords lead to a deeper voice.
- Body Configuration: Broader shoulders and enlarged muscles.
- Skin: Thickening of skin and increased secretion of sebaceous glands.
- Growth: Increases protein synthesis, leading to overall body growth and skeletal muscle development. Stimulates bone growth during puberty (linear growth spurt).
- Erythropoiesis: Stimulates the production of erythropoietin hormone.
- Prenatal Development: Stimulates fetal differentiation of the male genital tract and the descend of the testes.
Regulation of Testosterone Secretion
- Hypothalamic Regulation: Hypothalamus secretes GnRH into hypothalamic-hypophyseal portal vessels, stimulating FSH and LH secretion from the anterior pituitary.
- Anterior Pituitary Regulation: Anterior pituitary secretes FSH and LH. FSH acts on Sertoli cells to maintain spermatogenesis; LH acts on Leydig cells to promote testosterone synthesis.
- Negative Feedback: Testosterone inhibits LH secretion by inhibiting GnRH release from the hypothalamus and inhibiting LH secretion directly from the anterior pituitary. Sertoli cells secrete inhibin, which also inhibits FSH.
Female Reproductive System
- Functional Anatomy:
- Ovaries: Produce ova and secrete estrogen and progesterone.
- Uterus: Divided into fundus, body, and cervix; lined by the endometrium, thick muscular wall (myometrium).
- Vagina: Muscular tube (10 cm) lined by stratified squamous epithelium.
- Fallopian Tubes: (2) Each tube is 10 cm long and 8 mm in diameter, with a fimbriated end opening into the abdominal cavity.
Estrogen Hormone
- Chemical Nature: A steroid hormone synthesized by ovaries from cholesterol, secreted by growing follicles.
- Actions:
- Growth of Sex Organs: Stimulates growth and development of the uterus, fallopian tubes, vagina, and breasts; also, increases myometrial contractions and responsiveness to oxytocin during pregnancy, and prepares the endometrium for progesterone actions.
- Secondary Sex Characteristics:
- Figure: Deposition of body fat (breasts, thighs, buttocks), narrower shoulders, broader hips, less body hair, more scalp hair, and higher-pitched voice.
- Growth: Stimulates linear bone growth during puberty (pubertal growth spurt), resulting in early closure of the epiphyses, potentially leading to shorter adult height compared with males.
- Metabolic Effects: Promotes salt and water retention.
- Prolactin Secretion: Stimulates prolactin secretion by anterior pituitary but inhibits prolactin's milk-producing action on the breasts (can result in increased prolactin with no milk formation), particularly during pregnancy.
Progesterone Hormone
- Chemical Nature: A steroid hormone synthesized by the ovary from cholesterol secreted by the corpus luteum.
- Actions:
- Uterus: Essential for preparing the endometrium for fertilized ovum implantation, increasing vascularity and secretory activity. During pregnancy, it decreases myometrial excitability and sensitivity to oxytocin.
- Mammary Glands: Promotes growth of acini and increases secretory function in estrogen-primed mammary glands.
- Thermogenic Effect: Increases basal body temperature.
Regulation of Ovarian Hormones
- Hypothalamic Regulation: Hypothalamus secretes GnRH, stimulating anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH.
- Anterior Pituitary Regulation: FSH and LH stimulate:
- Secretion of Estrogen and Progesterone.
- Follicular Development.
- Ovulation.
- Corpus Luteum Formation.
- Feedback Regulation:
- Estrogen: Provides negative feedback with moderate increase, positive feedback with marked increase.
- Progesterone: Provides negative feedback on the anterior pituitary and hypothalamus.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.