Podcast
Questions and Answers
Where does sperm mature and transform into motile spermatozoa?
Where does sperm mature and transform into motile spermatozoa?
- Epididymis (correct)
- Prostate gland
- Bulbourethral glands
- Seminal vesicles
Which gland produces a fluid that serves as a nutritive medium for sperm?
Which gland produces a fluid that serves as a nutritive medium for sperm?
- Prostate gland (correct)
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Testes
What hormone is crucial for male development, sexual function, and sperm production?
What hormone is crucial for male development, sexual function, and sperm production?
- Inhibin
- Testosterone (correct)
- Activin
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
Where are the testes located in males?
Where are the testes located in males?
Which organ carries sperm to the urethra?
Which organ carries sperm to the urethra?
Which of the following regulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)?
Which of the following regulates the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)?
Where does spermatogenesis occur in males?
Where does spermatogenesis occur in males?
What is the function of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) in the male reproductive system?
What is the function of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) in the male reproductive system?
What is the primary function of the seminal vesicles in sexual reproduction?
What is the primary function of the seminal vesicles in sexual reproduction?
Which hormone is responsible for regulating sperm production in males?
Which hormone is responsible for regulating sperm production in males?
What is the final destination of mature sperm before being ejaculated from the male body?
What is the final destination of mature sperm before being ejaculated from the male body?
During sexual activity, what causes the penis to become erect?
During sexual activity, what causes the penis to become erect?
Study Notes
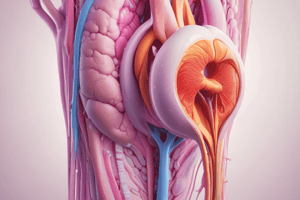
The male reproductive system is a complex network of internal and external organs that work together to produce and transport sperm, maintain sexual function, and contribute to the process of fertilization. The system consists of the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, seminal vesicles, bulbourethral glands, and the penis.
Testes
The testes are the primary source of sperm production in males. They are located in the scrotum, outside of the abdominal cavity, and are responsible for synthesizing and secreting hormones, including testosterone, which is crucial for male development, sexual function, and sperm production. The testes also produce inhibin and activin, which regulate the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland.
Epididymis and Vas Deferens
The epididymis is a highly coiled tube that lies at the back of the testes. It serves as a site for sperm maturation and storage, where sperm transform from immotile spermatids to motile spermatozoa. The epididymis also acts as a conduit for sperm to pass through, eventually joining the vas deferens, which carries sperm to the urethra.
Prostate Gland and Seminal Vesicles
The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland that sits in the middle of the pelvis. It produces a fluid that serves as a nutritive medium for sperm and helps to protect the urethra from damage during sexual activity. The seminal vesicles are two small glands located above the prostate gland that contribute the majority of the fluid in semen.
Sexual Reproduction
Sexual reproduction is the process by which two genetically distinct individuals produce offspring through the fusion of their gametes (sperm and egg). In males, this process begins with spermatogenesis, which occurs within the testes. During spermatogenesis, diploid spermatogonia cells undergo mitosis to form primary spermatocytes, which then undergo meiosis to produce haploid secondary spermatocytes. These cells further divide to form haploid spermatids, which transform into spermatozoa. The sperm are stored in the epididymis, where they mature and gain motility before being carried to the vas deferens.
During sexual activity, the penis becomes erect due to increased blood flow, and sperm is ejaculated through the urethra and out of the body. The semen, which consists of sperm and fluid from the prostate, seminal vesicles, and bulbourethral glands, serves to transport the sperm to the female reproductive tract for fertilization.
Hormonal Regulation
The male reproductive system is regulated by several hormones, including gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), testosterone, and inhibin. These hormones work together to regulate sperm production, sexual development, and the release of sperm during ejaculation.
In summary, the male reproductive system is a complex network of internal and external organs that work together to produce sperm, maintain sexual function, and contribute to the process of fertilization. The system is regulated by hormones, and spermatogenesis is a crucial process that produces haploid sperm cells, which are then transported to the female reproductive tract for fertilization.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
Learn about the complex network of organs in the male reproductive system that produce and transport sperm, maintain sexual function, and contribute to fertilization. Explore the process of spermatogenesis, from spermatogonia cells to spermatozoa, and understand the hormonal regulation involved.