Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the main compartments of the thigh?
What are the main compartments of the thigh?
- Lateral and posterior
- Anterior and medial (correct)
- Medial and posterior
- Anterior and lateral
Which of the following is a function of the femoral triangle?
Which of the following is a function of the femoral triangle?
- Surrounds the popliteal fossa
- Connects the thigh to the leg
- Contains the gluteal muscles
- Serves as a passage for the femoral vessels (correct)
Which condition may occur as a result of weakness in the femoral triangle area?
Which condition may occur as a result of weakness in the femoral triangle area?
- Iliotibial band syndrome
- Achilles tendinopathy
- Popliteal aneurysm
- Femoral hernia (correct)
What is NOT a recommended reading for understanding the anatomy of the lower limb?
What is NOT a recommended reading for understanding the anatomy of the lower limb?
Which veins are important for understanding lower limb circulation?
Which veins are important for understanding lower limb circulation?
What may happen if varicose veins are left untreated?
What may happen if varicose veins are left untreated?
What structures are encompassed by the fascia lata in the lower limb?
What structures are encompassed by the fascia lata in the lower limb?
Which of the following is a key landmark for examining the anterior thigh?
Which of the following is a key landmark for examining the anterior thigh?
What is the role of the fascia lata in the thigh and gluteal region?
What is the role of the fascia lata in the thigh and gluteal region?
What forms the iliotibial tract?
What forms the iliotibial tract?
Where does the great saphenous vein drain?
Where does the great saphenous vein drain?
How does the small saphenous vein ascend in the leg?
How does the small saphenous vein ascend in the leg?
Why do varicose veins occur in superficial veins?
Why do varicose veins occur in superficial veins?
What is the relationship between the great saphenous vein and the saphenous nerve?
What is the relationship between the great saphenous vein and the saphenous nerve?
What happens to blood flow in the veins during the formation of varicose veins?
What happens to blood flow in the veins during the formation of varicose veins?
What anatomical feature assists in preventing backflow of blood in healthy veins?
What anatomical feature assists in preventing backflow of blood in healthy veins?
What is typically the cause of a patellar dislocation?
What is typically the cause of a patellar dislocation?
How long is the immobilization period for a non-displaced patellar fracture?
How long is the immobilization period for a non-displaced patellar fracture?
What is the primary treatment for a displaced patellar fracture?
What is the primary treatment for a displaced patellar fracture?
What may happen if the patella slips out of its normal position?
What may happen if the patella slips out of its normal position?
Which artery is the continuation of the external iliac artery?
Which artery is the continuation of the external iliac artery?
Where is the femoral artery palpably located?
Where is the femoral artery palpably located?
What structure does the femoral artery pass through to become the popliteal artery?
What structure does the femoral artery pass through to become the popliteal artery?
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the posterior tibial region?
Which of the following arteries supplies blood to the posterior tibial region?
What is the typical duration of rehabilitation following a patellar dislocation?
What is the typical duration of rehabilitation following a patellar dislocation?
What type of fracture involves the patella being displaced from its normal position?
What type of fracture involves the patella being displaced from its normal position?
What is the main artery of the medial compartment of the thigh?
What is the main artery of the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which artery is considered the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Which artery is considered the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
What can result from stagnant blood in the deep veins?
What can result from stagnant blood in the deep veins?
What is the consequence of thrombi detaching from the vein wall?
What is the consequence of thrombi detaching from the vein wall?
Which artery is NOT a branch of the lateral circumflex artery?
Which artery is NOT a branch of the lateral circumflex artery?
Which artery supplies blood to the superficial pudendal region?
Which artery supplies blood to the superficial pudendal region?
Where does deep venous thrombosis primarily occur?
Where does deep venous thrombosis primarily occur?
What vessel drains blood from the great saphenous vein?
What vessel drains blood from the great saphenous vein?
What forms the lateral boundary of the femoral triangle?
What forms the lateral boundary of the femoral triangle?
Which nerve is found within the contents of the femoral triangle?
Which nerve is found within the contents of the femoral triangle?
What lies in the floor of the femoral triangle medially?
What lies in the floor of the femoral triangle medially?
What is the apex of the femoral triangle continuous with?
What is the apex of the femoral triangle continuous with?
Which structure is NOT contained within the femoral sheath?
Which structure is NOT contained within the femoral sheath?
What allows the femoral artery and vein to glide during hip movement?
What allows the femoral artery and vein to glide during hip movement?
Which component forms the medial boundary of the femoral triangle?
Which component forms the medial boundary of the femoral triangle?
What is contained within the femoral canal?
What is contained within the femoral canal?
What anatomical feature is critical in the prevention of femoral hernias?
What anatomical feature is critical in the prevention of femoral hernias?
What is the primary function of the fascia lata in the leg?
What is the primary function of the fascia lata in the leg?
Which of the following is a common complication of untreated varicose veins?
Which of the following is a common complication of untreated varicose veins?
Which structure attaches to the iliotibial tract and assists in leg extension?
Which structure attaches to the iliotibial tract and assists in leg extension?
Which muscle group is primarily innervated by the femoral nerve?
Which muscle group is primarily innervated by the femoral nerve?
What happens to veins in the case of varicose veins?
What happens to veins in the case of varicose veins?
In the context of the lower limb, what does the term 'compartment syndrome' refer to?
In the context of the lower limb, what does the term 'compartment syndrome' refer to?
What is the significance of the femoral triangle in clinical examinations?
What is the significance of the femoral triangle in clinical examinations?
Where does the great saphenous vein primarily ascend in the leg?
Where does the great saphenous vein primarily ascend in the leg?
Which of the following veins plays a significant role in the venous return of blood from the lower limb?
Which of the following veins plays a significant role in the venous return of blood from the lower limb?
Which vein drains directly into the femoral vein?
Which vein drains directly into the femoral vein?
What structure serves as the primary boundary of the femoral triangle laterally?
What structure serves as the primary boundary of the femoral triangle laterally?
Which structure is characterized by dilated, elongated, and tortuous features in varicose veins?
Which structure is characterized by dilated, elongated, and tortuous features in varicose veins?
What are the potential clinical presentations of a femoral hernia?
What are the potential clinical presentations of a femoral hernia?
What anatomical feature supports the return of venous blood from the lower limbs to the heart?
What anatomical feature supports the return of venous blood from the lower limbs to the heart?
Which nerve is closely associated with the great saphenous vein?
Which nerve is closely associated with the great saphenous vein?
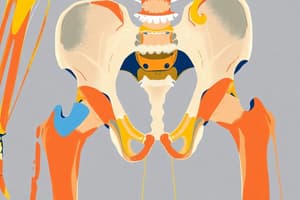
Which pelvic bones make up the irregular shape of the pelvic bone?
Which pelvic bones make up the irregular shape of the pelvic bone?
What structure is found on the medial side of the ankle?
What structure is found on the medial side of the ankle?
Which of the following accurately describes the deeper anatomy of the femur?
Which of the following accurately describes the deeper anatomy of the femur?
What structure is located at the head of the femur?
What structure is located at the head of the femur?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the iliac crest?
Which of the following statements is true regarding the iliac crest?
What is the significant feature of the deep fascia of the thigh?
What is the significant feature of the deep fascia of the thigh?
Where is the sacral canal located?
Where is the sacral canal located?
Which feature serves as a landmark for the anterior aspect of the sacrum?
Which feature serves as a landmark for the anterior aspect of the sacrum?
What is the primary function of the tarsal tunnel?
What is the primary function of the tarsal tunnel?
What typically causes a patellar dislocation?
What typically causes a patellar dislocation?
What is the initial treatment for a non-displaced patellar fracture?
What is the initial treatment for a non-displaced patellar fracture?
What is the primary consequence of a patellar dislocation?
What is the primary consequence of a patellar dislocation?
What is involved in the rehabilitation duration after a patellar dislocation?
What is involved in the rehabilitation duration after a patellar dislocation?
What type of blood supply is derived from the femoral artery?
What type of blood supply is derived from the femoral artery?
Which structures does the femoral artery pass through to become the popliteal artery?
Which structures does the femoral artery pass through to become the popliteal artery?
What is the typical time frame for immobilization of a displaced patellar fracture?
What is the typical time frame for immobilization of a displaced patellar fracture?
Which condition is likely to result from a blood supply issue in the femoral artery?
Which condition is likely to result from a blood supply issue in the femoral artery?
What may be a result of improper manual repositioning of a dislocated patella?
What may be a result of improper manual repositioning of a dislocated patella?
Where can the femoral artery be palpated?
Where can the femoral artery be palpated?
Which artery is primarily responsible for supplying blood to the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which artery is primarily responsible for supplying blood to the medial compartment of the thigh?
What condition can result from stagnant blood forming clots in the deep veins?
What condition can result from stagnant blood forming clots in the deep veins?
Which branch is NOT associated with the lateral circumflex artery?
Which branch is NOT associated with the lateral circumflex artery?
What is a potential consequence of an embolus formed from thrombi in the deep veins?
What is a potential consequence of an embolus formed from thrombi in the deep veins?
Which artery is classified as the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Which artery is classified as the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Which vessels form the superficial venous drainage of the lower limb?
Which vessels form the superficial venous drainage of the lower limb?
What is the function of the perforating branches of the deep (profunda) artery of the thigh?
What is the function of the perforating branches of the deep (profunda) artery of the thigh?
What complication can arise if thrombi propagate into the femoral veins?
What complication can arise if thrombi propagate into the femoral veins?
What anatomical structure assists in compressing veins during muscle contraction?
What anatomical structure assists in compressing veins during muscle contraction?
Which vein follows a path closely associated with the sural nerve in the posterior leg?
Which vein follows a path closely associated with the sural nerve in the posterior leg?
What condition occurs as a result of incompetent or congenitally absent valves in superficial veins?
What condition occurs as a result of incompetent or congenitally absent valves in superficial veins?
Where does the great saphenous vein primarily drain?
Where does the great saphenous vein primarily drain?
Which muscle group includes the tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus?
Which muscle group includes the tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus?
What is a significant characteristic of varicose veins?
What is a significant characteristic of varicose veins?
What is the role of the iliotibial tract in leg function?
What is the role of the iliotibial tract in leg function?
What is indicated by the presence of valve leaflets that do not meet properly in veins?
What is indicated by the presence of valve leaflets that do not meet properly in veins?
Which boundary is NOT associated with the femoral triangle?
Which boundary is NOT associated with the femoral triangle?
What is the primary clinical significance of the femoral canal?
What is the primary clinical significance of the femoral canal?
How do varicose veins primarily develop?
How do varicose veins primarily develop?
Which structure is NOT typically involved in the anatomy of the long saphenous vein?
Which structure is NOT typically involved in the anatomy of the long saphenous vein?
Which of the following muscles is primarily found in the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which of the following muscles is primarily found in the medial compartment of the thigh?
What could be a potential complication from varicose veins?
What could be a potential complication from varicose veins?
Which structure is critical for assisting in the movement of the femoral artery and vein during hip actions?
Which structure is critical for assisting in the movement of the femoral artery and vein during hip actions?
Which nerve is chiefly responsible for the innervation of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Which nerve is chiefly responsible for the innervation of the muscles in the anterior compartment of the thigh?
What structure lies laterally to the floor of the femoral triangle?
What structure lies laterally to the floor of the femoral triangle?
In which compartment of the femoral sheath is the femoral artery located?
In which compartment of the femoral sheath is the femoral artery located?
What demarcates the medial boundary of the femoral triangle?
What demarcates the medial boundary of the femoral triangle?
Which structure is NOT contained within the femoral sheath?
Which structure is NOT contained within the femoral sheath?
Which boundary of the femoral ring is formed by the pectineal ligament?
Which boundary of the femoral ring is formed by the pectineal ligament?
What does the great saphenous vein specifically penetrate to drain into the femoral vein?
What does the great saphenous vein specifically penetrate to drain into the femoral vein?
What is the primary content of the femoral canal within the femoral sheath?
What is the primary content of the femoral canal within the femoral sheath?
Which of the following statements about femoral hernias is correct?
Which of the following statements about femoral hernias is correct?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a patellar fracture?
Which of the following is a characteristic of a patellar fracture?
What is the primary consequence of a patellar dislocation?
What is the primary consequence of a patellar dislocation?
How is the femoral artery primarily positioned in relation to the inguinal ligament?
How is the femoral artery primarily positioned in relation to the inguinal ligament?
What is the usual duration for rehabilitation following a patellar dislocation?
What is the usual duration for rehabilitation following a patellar dislocation?
Which of the following arteries is a branch of the femoral artery?
Which of the following arteries is a branch of the femoral artery?
What is the consequence of a non-displaced patellar fracture if immobilization is not maintained?
What is the consequence of a non-displaced patellar fracture if immobilization is not maintained?
In which scenario does the patella primarily dislocate?
In which scenario does the patella primarily dislocate?
What is the expected treatment intervention for a displaced patellar fracture?
What is the expected treatment intervention for a displaced patellar fracture?
Which artery does the femoral artery become after passing through the adductor hiatus?
Which artery does the femoral artery become after passing through the adductor hiatus?
Which of the following statements about patellar immobilization is correct?
Which of the following statements about patellar immobilization is correct?
Which artery is considered the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
Which artery is considered the main artery of the anterior compartment of the thigh?
What is a potential consequence of thrombi breaking loose in the deep veins?
What is a potential consequence of thrombi breaking loose in the deep veins?
Which of the following describes the relationship of the perforating branches of the profunda artery?
Which of the following describes the relationship of the perforating branches of the profunda artery?
Which structure is classified as the main artery of the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which structure is classified as the main artery of the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which veins are primarily affected by deep venous thrombosis (DVT)?
Which veins are primarily affected by deep venous thrombosis (DVT)?
What condition can lead to swelling in peripheral tissues due to clot formation?
What condition can lead to swelling in peripheral tissues due to clot formation?
Which artery branches off the internal iliac artery and supplies the medial compartment of the thigh?
Which artery branches off the internal iliac artery and supplies the medial compartment of the thigh?
What happens to blood flow in veins during periods of inactivity?
What happens to blood flow in veins during periods of inactivity?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Lower Limb Anatomy
- The lower limb is divided into the gluteal region, thigh, leg, and foot.
- The thigh is further divided into the anterior, medial, and posterior compartments.
- The femoral triangle, popliteal fossa, and ankle are important transition areas.
Fascia Lata
- The fascia lata is a thick layer of connective tissue that surrounds the muscles of the thigh and gluteal region.
- It limits the outward extension of contracting muscles, making muscle contraction more efficient in compressing veins.
- The fascia lata is thickened laterally to form the iliotibial tract (IT tract), which extends from the tuberculum of the iliac crest to just below the knee.
- The tensor fascia lata and gluteus maximus muscles attach to the IT tract and work to keep the leg in extension once the leg is extended.
Superficial Veins of the Leg
- The small saphenous vein originates on the lateral side of the dorsal venous arch, runs posterior to the lateral malleolus, ascends in the posterior leg, and drains into the popliteal vein.
- The great saphenous vein originates on the medial side of the dorsal venous arch, runs anterior to the medial malleolus, ascends on the medial side of the leg, knee, and thigh, and drains into the femoral vein.
Varicose Veins
- Varicose veins occur when the valves in veins fail to prevent backward blood flow, causing blood to accumulate in superficial veins.
- This accumulation leads to dilated, elongated, and tortuous superficial veins with incompetent or congenitally absent valves.
Femoral Triangle
- The femoral triangle is a wedge-shaped depression in the upper thigh that is formed by muscles.
- The boundaries of the femoral triangle are:
- Superior: Inguinal ligament
- Medial: Medial margin of the adductor longus
- Lateral: Medial margin of the sartorius muscle
- The floor of the femoral triangle is formed by the:
- Adductor longus (medial)
- Pectineus (medial)
- Iliopsoas (lateral)
- The roof of the femoral triangle is formed by the fascia lata.
- The contents of the femoral triangle are:
- Femoral nerve
- Femoral artery
- Femoral vein
- Lymph nodes
- Empty space where the great saphenous vein penetrates the roof to drain into the femoral vein.
Femoral Canal (Adductor Canal)
- The apex of the femoral triangle is continuous with the adductor canal, a fascial canal containing the femoral artery and vein.
- The adductor canal passes through the adductor hiatus and opens into the popliteal fossa.
Femoral Sheath
- The femoral sheath surrounds the femoral artery and vein but not the femoral nerve.
- The femoral sheath is divided into three compartments:
- Lateral: Femoral artery
- Intermediate: Femoral vein
- Medial: Femoral canal, which contains loose connective tissue, fat, and lymphatics. The entrance to the canal is the femoral ring.
- The femoral sheath continues superiorly with the transversalis fascia and inferiorly with connective tissue around the vessels.
Femoral Hernia
- A femoral hernia occurs when abdominal content protrudes through the femoral ring, a weak point in the body.
- The boundaries of the femoral ring are:
- Anterior: Inguinal ligament
- Lateral: Femoral vein
- Medial: Lacunar ligament
- Posterior: Pectineal ligament
Patellar Fractures and Dislocations
- Patellar Fractures
- Frequently caused by a hard blow to the front of the knee.
- Non-displaced fractures are typically treated with immobilization in a cast for 4-6 weeks.
- Displaced fractures require surgical treatment followed by quadriceps strengthening.
- Patellar Dislocations
- Can occur due to a direct blow or sudden twisting of the leg.
- The patella slips out of its normal position in the patellofemoral groove, causing intense pain.
- Dislocation often occurs laterally.
- Typically treated with manual repositioning by extending the leg or an orthopedic reduction.
- Swelling and impaired mobility are common.
- Rehabilitation can take anywhere from 6 to 16 weeks.
Blood Supply to the Thigh
- The femoral artery is a continuation of the external iliac artery.
- The femoral artery is palpable in the femoral triangle at the mid-inguinal point, inferior to the inguinal ligament.
- It passes through the adductor canal and hiatus before becoming the popliteal artery at the popliteal fossa.
- Main Branches:
- Deep (profunda) artery of the thigh: The main artery of the anterior compartment that gives off:
- Lateral and medial circumflex femoral branches
- Perforating branches (4x) that penetrate the adductor magnus.
- Superficial epigastric artery
- Superficial circumflex iliac artery
- Superficial and deep external pudendal artery
- Deep (profunda) artery of the thigh: The main artery of the anterior compartment that gives off:
- The obturator artery is the main artery of the medial compartment and is a branch of the internal iliac artery.
Deep Veins
- The deep veins of the thigh include:
- Popliteal vein
- Femoral vein
- Deep femoral vein
- Anterior and posterior tibial veins
- Fibular veins
- The deep veins receive drainage from the superficial veins via the great saphenous vein and the small saphenous vein.
- Blood flow eventually progresses to the external iliac vein, common iliac vein, and inferior vena cava (IVC).
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
- Can occur when blood in the veins stagnates due to inactivity or injury, leading to the formation of clots in the lumen called thrombi.
- Thrombi can break loose and become emboli, potentially lodging in a vessel and preventing circulation.
- DVT can cause swelling in peripheral tissues and is generally found in the lower extremities, often propagating into the femoral veins.
Lymphatics
- Superficial inguinal lymph nodes are located in the femoral triangle.
- These nodes receive lymphatic drainage from the lower limb, external genitalia, and the lower abdominal wall.
Femoral Region
- Bones of the pelvis and lower limb: The pelvis is made up of three bones: ilium, pubis and ischium.
- Fascia lata and intramuscular septae: Fascia lata is a strong layer of deep fascia surrounding the thigh.
- Long and short saphenous veins: The great saphenous vein is located on the medial side of the leg, while the small saphenous vein runs on the lateral side.
- Varicose veins: Varicose veins develop when valves in veins become incompetent, causing blood to pool and distend the veins.
- Muscles and innervation: The anterior and medial compartments of the thigh contain several muscles responsible for various movements (e.g., hip flexion, knee extension).
- Femoral triangle: It is a space in the anterior thigh, bordered by the inguinal ligament (superior), sartorius (lateral), and adductor longus (medial). It contains the femoral artery, vein, and nerve.
- Femoral hernias: These occur when the abdominal contents protrude through a weak spot in the abdominal wall in the femoral canal, below the inguinal ligament. Typically present as a lump or bulge in the groin.
- Clinical landmarks: Several clinical landmarks are used to assess the anterior and medial thigh, such as the inguinal ligament, the femoral triangle, and the adductor canal.
- Radiological imaging: Radiological imaging techniques (e.g., X-rays, CT scans, MRI) are used to visualize the bones, vessels, and soft tissues within the thigh and pelvis, helping diagnose various conditions.
Blood Supply
- Femoral artery: It originates from the external iliac artery. It is palpable in the femoral triangle (mid-inguinal point) and supplies the thigh.
- Deep femoral (profunda) artery: It is a branch of the femoral artery and is the main arterial supply to the anterior compartment of the thigh.
- Medial circumflex artery: It is a branch of the external iliac artery and contributes to the blood supply of the medial compartment of the thigh.
- Obturator artery: It is a branch of the internal iliac artery, which supplies the medial compartment of the thigh.
Deep veins
- Deep veins of the thigh: These veins accompany the major arteries and include the femoral vein, deep femoral vein (profunda femoral vein), and popliteal vein.
- Deep venous thrombosis (DVT): DVT is a serious condition involving the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein, often in the legs.
Lymphatics
- Superficial inguinal nodes: These are located in the groin region and receive lymph drainage from the lower abdomen, perineum, and lower limbs.
Bones of the Pelvis and Lower Limb
- The bones of the pelvis and lower limb are important structures that support the body and allow for movement.
- It is important to identify the bones of the pelvis and lower limb and understand their relationships to each other.
Fascia Lata and Intramuscular Septae of the Lower Limb
- The fascia lata is a thick sheet of connective tissue that surrounds the muscles of the thigh.
- It is thickened laterally to form the iliotibial tract (IT tract), which runs from the iliac crest to the knee.
- The IT tract is important for maintaining leg extension.
- Intramuscular septae divide the thigh into compartments, providing structural support for the muscles within.
Anatomy of the Long and Short Saphenous Veins
- The long saphenous vein is the longest vein in the body, beginning on the medial side of the foot and ascending to the thigh, draining into the femoral vein.
- The short saphenous vein ascends on the posterior leg and drains into the popliteal vein.
Varicose Veins
- Varicose veins are dilated, elongated, and tortuous superficial veins with incompetent valves.
- Valve incompetence allows blood to flow backward, causing pooling and dilation of the veins.
- Varicose veins are common in the lower limbs and can cause pain, swelling, and fatigue.
Anatomy of the Anterior and Medial Compartments of the Thigh
- The anterior compartment of the thigh contains the following muscles:
- Sartorius
- Quadriceps femoris (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius)
- The medial compartment of the thigh contains the following muscles:
- Adductor longus
- Adductor brevis
- Adductor magnus
- Gracilis
- Pectineus
- The anterior compartment of the thigh is responsible for knee extension and hip flexion.
- The medial compartment is responsible for hip adduction.
Boundaries and Contents of the Femoral Triangle
- The femoral triangle is a wedge-shaped depression on the anterior thigh.
- Boundaries:
- Superior: Inguinal ligament
- Medial: Adductor longus muscle
- Lateral: Sartorius muscle
- Floor:
- Iliopsoas muscle
- Pectineus muscle
- Adductor longus muscle
- Roof: Fascia lata
- Contents:
- Femoral nerve
- Femoral artery
- Femoral vein
- Lymph nodes
Femoral Hernias
- A femoral hernia occurs when abdominal contents protrude through the femoral ring, a weak area within the femoral canal.
- Femoral hernias are more common in women.
Femoral Sheath
- The femoral sheath surrounds the femoral artery and vein.
- It is a continuation of the transversalis fascia and provides support and allows for smooth movement of the vessels during hip motion.
Clinical Landmarks on Examination of the Anterior and Medial Thigh
- The inguinal ligament, the adductor longus, and the sartorius are important landmarks to identify during examination of the anterior and medial thigh.
Radiological Imaging of the Bones and Vessels of the Thigh and Pelvis
- Radiological imaging techniques, such as x-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, are essential for the evaluation of the bones and vessels of the thigh and pelvis.
Blood Supply to the Thigh
- The main blood supply to the thigh is provided by the femoral artery, a continuation of the external iliac artery.
- The femoral artery gives off several branches that supply the muscles and tissues of the thigh.
- The deep femoral artery (profunda femoris) is the main artery of the anterior compartment and gives off branches that supply the muscles of the medial compartment.
Obturator Artery
- The obturator artery supplies blood to the medial compartment of the thigh and is a branch of the internal iliac artery.
Deep Veins of the Lower Limb
- The deep veins of the thigh and lower limb are responsible for returning blood from the legs to the heart.
- The deep veins of the thigh and lower limb run alongside the arteries, with the same names as the arteries, such as the femoral vein and popliteal vein.
Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT)
- DVT is a serious condition that occurs when blood clots form in the deep veins of the legs.
- These clots can break loose and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
- Risk factors for DVT include inactivity, injury, and certain medical conditions.
Lymphatics of the Lower Limb
- The lymphatic system is responsible for draining excess fluid from the body.
- The superficial inguinal lymph nodes are located in the region of the groin and drain lymph from the lower limbs, external genitalia, and lower abdominal wall.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.