Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the angle of the femoral shaft from vertical for an average adult?
What is the angle of the femoral shaft from vertical for an average adult?
- 20°
- 15°
- 5°
- 10° (correct)
Which bone is embedded in the tendon of the large quadriceps femoris muscle?
Which bone is embedded in the tendon of the large quadriceps femoris muscle?
- Patella (correct)
- Tibia
- Femur
- Fibula
What is the function of the patella in the knee joint?
What is the function of the patella in the knee joint?
- To provide leverage to the hamstrings muscle
- To increase the leverage of the quadriceps femoris muscle (correct)
- To protect the posterior aspect of the knee joint
- To attach the tibial tuberosity to the femur
What is the adductor tubercle?
What is the adductor tubercle?
Which ligament extends from the femur to the lateral proximal fibula?
Which ligament extends from the femur to the lateral proximal fibula?
What is the name of the smooth, shallow, triangular depression at the distal portion of the anterior femur?
What is the name of the smooth, shallow, triangular depression at the distal portion of the anterior femur?
Which bone is located anteriorly to the distal femur and positioned superior or proximal to the actual knee joint by approximately 1.25 cm in this position with the lower leg fully extended?
Which bone is located anteriorly to the distal femur and positioned superior or proximal to the actual knee joint by approximately 1.25 cm in this position with the lower leg fully extended?
Which aspect of the medial condyle receives the tendon of an adductor muscle?
Which aspect of the medial condyle receives the tendon of an adductor muscle?
Flashcards
Distal Femur
Distal Femur
Long bone featuring two rounded condyles separated by the intercondylar fossa.
Patella
Patella
Largest sesamoid bone, anterior to the distal femur.
Patellar Surface
Patellar Surface
Smooth, shallow, triangular depression on femur, where patella rests.
Adductor Tubercle
Adductor Tubercle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Popliteal Surface
Popliteal Surface
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella Function
Patella Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femorotibial Joint
Femorotibial Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee Ligaments
Knee Ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
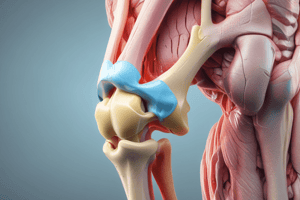
- The femur is a long bone with a slender, elongated shaft and has two large, rounded condyles that are separated distally and posteriorly by the deep intercondylar fossa or notch.
- The patella, the largest sesamoid bone in the body, is located anteriorly to the distal femur and is positioned superior or proximal to the actual knee joint by approximately 1.25 cm in this position with the lower leg fully extended.
- The patellar surface is the smooth, shallow, triangular depression at the distal portion of the anterior femur that extends up under the lower part of the patella.
- The distal femoral condyles are parallel to the floor at the knee joint, and the femoral shaft is at an angle of approximately 10° from vertical for an average adult.
- The angle would be greater on a person of short stature and a wider pelvis and would be less on a person of tall stature with a narrow pelvis. In general, this angle is greater on a woman than on a man.
- The medial condyle extends lower or more distally than the lateral condyle when the femoral shaft is vertical, as in Fig. 6.20.
- The adductor tubercle, a slightly raised area that receives the tendon of an adductor muscle, is present on the posterolateral aspect of the medial condyle.
- The patella is embedded in the tendon of the large quadriceps femoris muscle, and as the lower leg is flexed, the patella moves downward and is drawn inward into the intercondylar groove or sulcus.
- The posterior surface of the distal femur just proximal to the intercondylar fossa is called the popliteal surface, over which popliteal blood vessels and nerves pass.
- The patella serves to protect the anterior aspect of the knee joint and acts as a pivot to increase the leverage of the large quadriceps femoris muscle, the tendon of which attaches to the tibial tuberosity of the lower leg.
- The knee joint proper primarily involves the femorotibial joint between the two condyles of the femur and the corresponding condyles of the tibia.
- The proximal fibula is not part of the knee joint because it does not articulate with any aspect of the femur, even though the fibular (lateral) collateral ligament (LCL) extends from the femur to the lateral proximal fibula. The knee joint is highly dependent on major knee ligaments for stability, including the tibial (medial) collateral ligament (MCL) and the major posterior and anterior cruciate (PCL and ACL) ligaments.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.