Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary function of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
What is the primary function of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)?
- Stabilizes the tibia against excessive internal rotation
- Prevents anterior displacement of the tibia on the fixed femur (correct)
- Prevents the femur from moving anterior during weight bearing
- Prevents posterior translation of the tibia on the fixed femur
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the medial and lateral tibial condyles?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the medial and lateral tibial condyles?
- The medial condyle is round and the lateral condyle is oval
- Both the medial and lateral condyles are oval in shape
- Both the medial and lateral condyles are round in shape
- The medial condyle is oval and the lateral condyle is round (correct)
What is the primary function of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)?
What is the primary function of the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)?
- Prevents posterior translation of the tibia on the fixed femur (correct)
- Stabilizes the tibia against excessive internal rotation
- Prevents anterior translation of the tibia on the fixed femur
- Prevents the femur from moving posterior during weight bearing
What is the primary role of the menisci in the knee joint?
What is the primary role of the menisci in the knee joint?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the articular capsule of the knee joint?
Which of the following is the most accurate description of the articular capsule of the knee joint?
What is the primary function of the popliteus tendon in the knee joint?
What is the primary function of the popliteus tendon in the knee joint?
What is the primary anatomical difference between the medial and lateral femoral condyles?
What is the primary anatomical difference between the medial and lateral femoral condyles?
What is the function of the PCL mentioned in the text?
What is the function of the PCL mentioned in the text?
Which ligament stabilizes against valgus stress applied to the lateral aspect of the joint capsule?
Which ligament stabilizes against valgus stress applied to the lateral aspect of the joint capsule?
What muscle is strengthened by the OBLIQUE POPLITEAL ligament?
What muscle is strengthened by the OBLIQUE POPLITEAL ligament?
Which ligament attaches to the lateral femoral epicondyle and head of fibula?
Which ligament attaches to the lateral femoral epicondyle and head of fibula?
What is the function of the Ligamentum Patellae?
What is the function of the Ligamentum Patellae?
During what knee position are both the MCL and LCL the tightest?
During what knee position are both the MCL and LCL the tightest?
Which action does the PCL prevent according to the text?
Which action does the PCL prevent according to the text?
Which muscle originates from the ischial tuberosity and inserts on the medial condyle of the tibia?
Which muscle originates from the ischial tuberosity and inserts on the medial condyle of the tibia?
Which muscle is innervated by the common fibular nerve and is involved in flexing the leg and laterally rotating the thigh?
Which muscle is innervated by the common fibular nerve and is involved in flexing the leg and laterally rotating the thigh?
The origin of the long head of the Biceps femoris muscle is from which structure?
The origin of the long head of the Biceps femoris muscle is from which structure?
Which muscle can extend the trunk when the thigh and leg are flexed?
Which muscle can extend the trunk when the thigh and leg are flexed?
The semitendinosus muscle inserts on which part of the tibia?
The semitendinosus muscle inserts on which part of the tibia?
Which nerve division innervates both Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus muscles?
Which nerve division innervates both Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus muscles?
The short head of Biceps femoris muscle originates from which structure?
The short head of Biceps femoris muscle originates from which structure?
Which muscle's insertion point is split by the fibular collateral ligament of the knee?
Which muscle's insertion point is split by the fibular collateral ligament of the knee?
What type of joint is considered structurally a hinge joint in the knee anatomy?
What type of joint is considered structurally a hinge joint in the knee anatomy?
Which ligament primarily provides lateral stabilization of the knee joint?
Which ligament primarily provides lateral stabilization of the knee joint?
Which of the following muscles does NOT contribute to medial stabilization of the knee?
Which of the following muscles does NOT contribute to medial stabilization of the knee?
Which ligament strengthens the fibrous capsule posteriorly and arises from the posterior aspect of the fibular head?
Which ligament strengthens the fibrous capsule posteriorly and arises from the posterior aspect of the fibular head?
Which artery does NOT contribute to the arterial supply of the skin covering the knee?
Which artery does NOT contribute to the arterial supply of the skin covering the knee?
A patient presents with knee instability and pain along the medial aspect of the joint. Which ligament is most likely torn?
A patient presents with knee instability and pain along the medial aspect of the joint. Which ligament is most likely torn?
Which nerve provides cutaneous innervation to the anterior aspect of the knee joint?
Which nerve provides cutaneous innervation to the anterior aspect of the knee joint?
A patient experiences lateral knee instability following a sports injury. Which muscle is most likely torn or strained?
A patient experiences lateral knee instability following a sports injury. Which muscle is most likely torn or strained?
Flashcards
Arcuate Popliteal Ligament
Arcuate Popliteal Ligament
Strengthens the fibrous capsule posteriorly, arising from the fibular head.
Lateral Stabilizers of Knee
Lateral Stabilizers of Knee
Provides lateral knee stabilization. Key muscles include the biceps femoris and gastrocnemius (lateral head).
Medial Stabilizers of Knee
Medial Stabilizers of Knee
Provides medial knee stabilization. Key muscles include the sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus.
Arterial Supply to Knee Skin
Arterial Supply to Knee Skin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semitendinosus Muscle
Semitendinosus Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Semimembranosus Muscle
Semimembranosus Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biceps Femoris Muscle
Biceps Femoris Muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bones of the Knee Joint
Bones of the Knee Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Femoral Condyles
Femoral Condyles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibial Plateau
Tibial Plateau
Signup and view all the flashcards
Patella
Patella
Signup and view all the flashcards
Components of Knee Joint
Components of Knee Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tibiofemoral Joint
Tibiofemoral Joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular Capsule of Knee
Articular Capsule of Knee
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ligaments of the Knee
Ligaments of the Knee
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menisci
Menisci
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
Medial Collateral Ligament (MCL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oblique Popliteal Ligament
Oblique Popliteal Ligament
Signup and view all the flashcards
Articular capsule
Articular capsule
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intracapsular ligaments
Intracapsular ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Extracapsular ligaments
Extracapsular ligaments
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterial supply branch 1
Arterial supply branch 1
Signup and view all the flashcards
Arterial supply branch 2
Arterial supply branch 2
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibula feature
Fibula feature
Signup and view all the flashcards
Type of joint
Type of joint
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infrapatellar branch
Infrapatellar branch
Signup and view all the flashcards
Knee Cover
Knee Cover
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Ligaments
- Arcuate popliteal ligament strengthens the fibrous capsule posteriorly and arises from the posterior aspect of the fibular head.
- Lateral stabilization is provided by the biceps, gastrocnemius (lateral head), iliotibial tract, and fibular collateral ligament.
- Medial stabilization is provided by the sartorius, gracilis, gastrocnemius (medial head), semitendinosus, semimembranosus, and tibial collateral ligament.
Skin and Arterial Supply
- The infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve and the peripatellar plexus provide cutaneous innervation.
- The arterial supply of the skin covering the knee is from the genicular branches of the popliteal artery, the descending genicular branch of the femoral artery, the anterior recurrent branch of the anterior tibial artery, and small contributions from the arteries to vastus medialis and the hamstrings.
Posterior Aspect of Thigh and Knee Joint
- The semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles originate from the ischial tuberosity and insert into the medial surface of the superior part of the tibia (semitendinosus) and the posterior part of the medial condyle of the tibia (semimembranosus).
- The semitendinosus and semimembranosus muscles are innervated by the tibial division of the sciatic nerve and extend the thigh, flex the leg, and rotate medially.
- The biceps femoris muscle originates from the ischial tuberosity and the linea aspera and lateral supracondylar line of the femur, and inserts into the lateral side of the head of the fibula.
- The biceps femoris muscle is innervated by the tibial and common fibular nerves and flexes the leg and laterally rotates; extends the thigh.
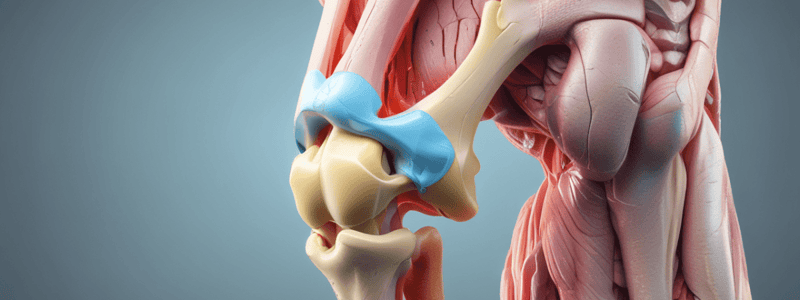
Knee Joint Anatomy
- The bones involved in the knee joint are the femur, tibia, fibula, and patella.
- The femur has medial and lateral femoral condyles that articulate with the tibia.
- The tibia has a flat tibial plateau that articulates with the femoral condyles.
- The fibula articulates with the tibia.
- The patella is a sesamoid bone that protects the anterior joint and is enclosed in the quadriceps/patellar tendon.
Knee Joint Structure
- The knee joint consists of the tibiofemoral joint (structurally a hinge joint and considered a condylar type of synovial joint), the patellofemoral joint (a saddle joint), and the superior tibiofibular joint.
- The tibiofemoral joint has lateral and medial articulations between the tibial condyles and their cartilaginous menisci and the corresponding femoral condyles.
- The articular surfaces are covered with hyaline cartilage.
Articular Capsule and Ligaments
- The articular capsule is thin and deficient in some areas, attaching superiorly proximal to the articular margins of the condyles and also intercondylar fossa posteriorly.
- The ligaments of the knee joint include intracapsular ligaments (cruciate ligaments and menisci) and extracapsular ligaments (patellar ligament, fibular collateral ligament, tibial collateral ligament, oblique popliteal ligament, and arcuate popliteal ligament).
Menisci
- The menisci are fibrocartilaginous discs that are thicker on the outside than inside, with poor blood supply.
- The menisci lie on top of the tibial plateau, increase stability, and make the condyles fit better.
- The menisci act as shock absorbers.
Ligaments
- The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) runs from the anterior tibia to the posterior femur and prevents anterior displacement of the tibia on a fixed femur and excessive internal rotation.
- The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) runs from the posterior tibia to the anterior femur and prevents posterior translation of the tibia on a fixed femur and excessive external rotation.
- The ACL and PCL "cross" or wrap around each other, becoming taut when in extension and looser when in flexion.
- The medial collateral ligament (MCL) attaches to the medial femoral epicondyle and anteromedial tibia and stabilizes against valgus stress applied to the lateral aspect of the joint capsule.
- The lateral collateral ligament (LCL) attaches to the lateral femoral epicondyle and head of the fibula and stabilizes against varus stress when force is applied to the medial aspect of the joint capsule.
- The oblique popliteal ligament is an expansion of the semimembranosus and strengthens the capsule posteriorly.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.