Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the term used for the characteristic changes in tissue and cells produced by a disease?
What is the term used for the characteristic changes in tissue and cells produced by a disease?
- Epidemiology
- Morphology
- Pathogenesis
- Lesion (correct)
What is the primary focus of the field of pathology?
What is the primary focus of the field of pathology?
- Investigating the social and environmental factors that contribute to disease
- Studying the causes of disease and their effects on cells, tissues, and organs (correct)
- Developing new treatments for various diseases
- Analyzing genetic mutations related to disease development
Which of the following terms is the most comprehensive description of the state of being unwell due to an underlying abnormality?
Which of the following terms is the most comprehensive description of the state of being unwell due to an underlying abnormality?
- Health
- Disease
- Illness (correct)
- Syndrome
Which of the following best describes the study of the cause of a disease?
Which of the following best describes the study of the cause of a disease?
What is the term used for the process of a disease developing and progressing?
What is the term used for the process of a disease developing and progressing?
Which of the following is NOT a key element to consider when understanding a disease?
Which of the following is NOT a key element to consider when understanding a disease?
The term 'syndrome' is used to describe:
The term 'syndrome' is used to describe:
What is the primary function of the 'General Pathology' branch in the 'Tree of Medicine' diagram?
What is the primary function of the 'General Pathology' branch in the 'Tree of Medicine' diagram?
A disease whose cause is unknown is referred to as a:
A disease whose cause is unknown is referred to as a:
Which of the following is NOT considered a root component of 'General Pathology' according to the provided information?
Which of the following is NOT considered a root component of 'General Pathology' according to the provided information?
What is the difference between a 'symptom' and a 'sign' in the context of a disease?
What is the difference between a 'symptom' and a 'sign' in the context of a disease?
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of pathological examination as described in the text?
Which of the following is NOT a purpose of pathological examination as described in the text?
Why is understanding the pathogenesis of a disease important? (Select the best answer.)
Why is understanding the pathogenesis of a disease important? (Select the best answer.)
In the context of disease, what does the term 'pathogenesis' refer to?
In the context of disease, what does the term 'pathogenesis' refer to?
What distinguishes a pathogenic strain of bacteria from a nonpathogenic strain?
What distinguishes a pathogenic strain of bacteria from a nonpathogenic strain?
Which of the following is NOT a major class of etiologic factors that can cause disease?
Which of the following is NOT a major class of etiologic factors that can cause disease?
What is the term used to describe a disease whose cause is unknown?
What is the term used to describe a disease whose cause is unknown?
What type of changes are referred to as 'morphologic changes' in pathology?
What type of changes are referred to as 'morphologic changes' in pathology?
How do morphologic changes influence the clinical manifestations of a disease?
How do morphologic changes influence the clinical manifestations of a disease?
Which of these terms is NOT associated with the progression of a disease?
Which of these terms is NOT associated with the progression of a disease?
Which of these is considered a subdivision of pathology that focuses on general principles of disease?
Which of these is considered a subdivision of pathology that focuses on general principles of disease?
Flashcards
General Pathology
General Pathology
The study of disease processes and their effects on the body.
Symptom
Symptom
Any evidence of a disease as reported by the patient.
Sign
Sign
Any evidence of a disease that can be observed by a clinician.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prognosis
Prognosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Idiopathic disease
Idiopathic disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Etiologic factors
Etiologic factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Incubation period
Incubation period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathogenicity
Pathogenicity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morphologic changes
Morphologic changes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clinical manifestations
Clinical manifestations
Signup and view all the flashcards
General vs Systemic Pathology
General vs Systemic Pathology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pathology
Pathology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health
Health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Disease
Disease
Signup and view all the flashcards
Illness
Illness
Signup and view all the flashcards
Syndrome
Syndrome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Etiology
Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morphology
Morphology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Pathology
- Pathology is derived from two Greek words: "Pathos" (suffering) and "Logos" (study)
- Pathology is the study of structural, biochemical, and functional changes in cells, tissues, and organs that lead to disease.
- It connects basic science with clinical practice.
- It investigates the causes of disease and associated changes in cells, tissues, and organs, leading to patient symptoms.
- The range of structural changes studied is diverse, from sub-cellular organelles (molecular pathology) to visible changes (gross pathology).
Health and Disease
- Health describes complete physical, mental, and social well-being, not just the absence of disease.
- Disease is the manifestation of discomfort due to structural or functional abnormalities.
- Illness describes a condition marked by a significant deviation from a normal healthy state.
- A syndrome is a combination of clinical features caused by altered physiologic processes.
Terminology in Pathology
- A patient is a person affected by a disease.
- A lesion is a characteristic change in tissue or cells caused by disease.
- Morphology is the examination of diseased tissue.
- Etiology is the cause of disease ("why").
- Pathogenesis describes the mechanism by which lesions develop ("how").
What Should We Know About Disease?
- A disease's definition is important.
- Epidemiology explores where and when diseases occur.
- Etiology determines the cause of a disease.
- Pathogenesis is the evolution of the disease.
- Morphology describes the structural changes.
- Functional changes resulting from diseases are also relevant.
- Management refers to how to treat the disease.
- Prognosis predicts the likely outcome of a disease.
- Prevention aims to avoid disease.
Disease Process
- Pathology studies how diseases affect organs from initial cause (etiology) to the final clinical manifestations. This includes understanding pathogenesis – the steps from cause to symptom – and the resulting morphologic changes.
Etiology
- Etiology is the cause of a disease.
- Primary etiology means the cause is known.
- Idiopathic means the cause is unknown.
- Etiologic factors can be genetic or acquired (e.g., infectious, nutritional, chemical, physical).
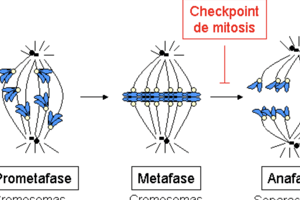
Pathogenesis
- Pathogenesis describes the process by which a disease develops.
- It's the mechanism by which a cause produces both pathological and clinical manifestations.
Pathogenicity
- Pathogenicity is the ability of a pathogen (often a microorganism) to cause disease.
- Examples include highly pathogenic influenza (H5N1) and non-pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli.
Morphologic Changes
- Morphologic changes are the structural alterations in cells and tissues following the pathogenic process.
- These alterations can be seen with the naked eye (gross pathology) or only under a microscope (microscopic changes).
Clinical Manifestations
- The morphologic changes influence the normal function of an organ.
- These changes determine the signs, symptoms, the course, and prognosis of the disease.
Summary of Pathology Studies
- Pathology studies etiology (cause), pathogenesis (development), morphologic changes, and clinical features/prognosis.
Subdivisions of Pathology
- General pathology studies common principles of disease (e.g., inflammation, cancer, aging).
- Systemic pathology focuses on diseases specific to organs and body systems.
The Tree of Medicine
- A diagram showing the relationships between various medical branches, demonstrating pathology as fundamental to many aspects of medicine.
Symptoms, Signs, Diagnosis, Prognosis
- Symptoms are evidence of disease as reported by the patient.
- Signs are detectable evidence of disease by a clinician.
- Diagnosis is identifying a specific disease based on signs and symptoms.
- Prognosis is the prediction of the likely outcome of a disease.
In Summary:
- Pathology studies the "what" (the lesion) and the "how" (the pathogenesis) of a disease to guide treatments, control, and disease prevention strategies.
Objective and Purpose of Pathological Examination
- Diagnosing disease
- Determining treatment, prognosis, and grading
- Investigating medico-legal conditions (e.g., cause of death)
- Supporting research and medical innovation
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.