Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is Microsoft Excel?
What is Microsoft Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program developed by Microsoft.
What are Excel documents called?
What are Excel documents called?
Workbooks
How is data organized in Excel?
How is data organized in Excel?
Data is entered into individual cells, and cells are organized into rows and columns.
How do you perform calculations in Excel?
How do you perform calculations in Excel?
Give three examples of data analysis tools provided by Excel.
Give three examples of data analysis tools provided by Excel.
Excel documents can only be edited by one user at a time.
Excel documents can only be edited by one user at a time.
What is the name of the small square that appears at the bottom-right corner of a cell?
What is the name of the small square that appears at the bottom-right corner of a cell?
What are the basic steps for applying conditional formatting in Excel? (Select all that apply)
What are the basic steps for applying conditional formatting in Excel? (Select all that apply)
What is used to sort complex data by multiple columns, specify custom sort orders, and more in Excel?
What is used to sort complex data by multiple columns, specify custom sort orders, and more in Excel?
What are the steps to clear filters in Excel?
What are the steps to clear filters in Excel?
What is the main purpose of creating a table in Excel?
What is the main purpose of creating a table in Excel?
When creating a table in Excel, you should always check the box for 'Create table with headers' if your data has headers.
When creating a table in Excel, you should always check the box for 'Create table with headers' if your data has headers.
Which of the following are common paste special options in Excel? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are common paste special options in Excel? (Select all that apply)
You cannot protect individual cells in Excel.
You cannot protect individual cells in Excel.
What is the purpose of a chart in Excel?
What is the purpose of a chart in Excel?
Which of the following are common types of charts in Excel? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following are common types of charts in Excel? (Select all that apply)
What is the primary difference between a column chart and a bar chart?
What is the primary difference between a column chart and a bar chart?
Name a common application of a line chart.
Name a common application of a line chart.
What is a pie chart used for?
What is a pie chart used for?
What is the purpose of a scatter plot?
What is the purpose of a scatter plot?
What is the main difference between formulas and functions in Excel?
What is the main difference between formulas and functions in Excel?
Which of the following tabs in Excel contains a variety of tools and functions for working with formulas, performing calculations, and managing data? (Select all that apply)
Which of the following tabs in Excel contains a variety of tools and functions for working with formulas, performing calculations, and managing data? (Select all that apply)
What is the purpose of the 'SUM' function in Excel?
What is the purpose of the 'SUM' function in Excel?
How would you calculate the average of numbers in cells B1 to B10 using the 'AVERAGE' function in Excel?
How would you calculate the average of numbers in cells B1 to B10 using the 'AVERAGE' function in Excel?
What does the 'COUNT' function do in Excel?
What does the 'COUNT' function do in Excel?
How would you use the 'MIN' function to find the smallest value in the range A1 to A10 in Excel?
How would you use the 'MIN' function to find the smallest value in the range A1 to A10 in Excel?
The 'TODAY' function returns the current date and time.
The 'TODAY' function returns the current date and time.
When using the 'YEAR' function to determine the year of a date in Excel, what format should the date be provided?
When using the 'YEAR' function to determine the year of a date in Excel, what format should the date be provided?
How would you use the 'COUNTIF' function to count the number of cells in the range A1:A5 that contain values greater than 50 in Excel?
How would you use the 'COUNTIF' function to count the number of cells in the range A1:A5 that contain values greater than 50 in Excel?
Give the syntax of the 'IF' function in Excel.
Give the syntax of the 'IF' function in Excel.
The 'AND' function will return 'True' if all conditions are met.
The 'AND' function will return 'True' if all conditions are met.
What is the purpose of direct typing to insert functions in Excel?
What is the purpose of direct typing to insert functions in Excel?
How can you find the 'Insert Function' dialog box in Excel?
How can you find the 'Insert Function' dialog box in Excel?
The 'AutoSum' function is only capable of performing addition.
The 'AutoSum' function is only capable of performing addition.
Name two popular Date and Time functions in Excel.
Name two popular Date and Time functions in Excel.
Flashcards
What is Excel?
What is Excel?
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet program used for data organization, analysis, and visualization.
What is an Excel workbook?
What is an Excel workbook?
A workbook is a single Excel document that contains one or more worksheets.
What is an Excel worksheet?
What is an Excel worksheet?
A worksheet is a single sheet within an Excel workbook.
What are cells in Excel?
What are cells in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are rows in Excel?
What are rows in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are columns in Excel?
What are columns in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are formulas in Excel?
What are formulas in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are functions in Excel?
What are functions in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are charts in Excel?
What are charts in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you sort data in Excel?
How do you sort data in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you filter data in Excel?
How do you filter data in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is an Excel table?
What is an Excel table?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is conditional formatting in Excel?
What is conditional formatting in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are frozen panes in Excel?
What are frozen panes in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you protect data in Excel?
How do you protect data in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you move cells in Excel?
How do you move cells in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you copy cells in Excel?
How do you copy cells in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is AutoFill in Excel?
What is AutoFill in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you format numbers in Excel?
How do you format numbers in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the SUM function do in Excel?
What does the SUM function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the AVERAGE function do in Excel?
What does the AVERAGE function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the COUNT function do in Excel?
What does the COUNT function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the TODAY function do in Excel?
What does the TODAY function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the IF function do in Excel?
What does the IF function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can you directly use functions in Excel?
How can you directly use functions in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How can you use the Insert Function dialog box in Excel?
How can you use the Insert Function dialog box in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the COUNTIF function do in Excel?
What does the COUNTIF function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the AND function do in Excel?
What does the AND function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the OR function do in Excel?
What does the OR function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does the NOT function do in Excel?
What does the NOT function do in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you insert a new column in Excel?
How do you insert a new column in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you delete a column in Excel?
How do you delete a column in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How do you hide a column in Excel?
How do you hide a column in Excel?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Introduction to Excel
- Excel is a spreadsheet program developed by Microsoft.
- It's popular for organizing, analyzing, and visualizing data.
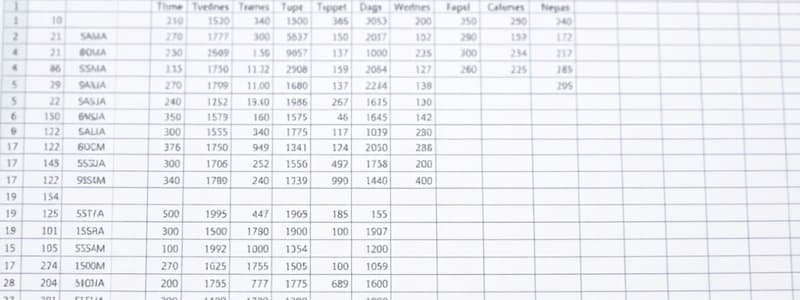
- Data is arranged in cells within rows and columns.
- Cells can contain numbers, text, formulas, and functions.
Key Features of Using Excel
- Worksheets and Workbooks: Excel documents are workbooks, containing multiple worksheets.
- Cells, Rows, and Columns: Data is entered into individual cells organized into rows and columns. Columns are labeled with letters (A, B, C...), and rows with numbers (1, 2, 3...). Cells are referenced using column letters and row numbers (e.g., A5, D2).
- Formulas and Functions: Excel allows calculations on data using formulas (user-created equations) and functions (predefined formulas). This covers mathematical, statistical, and financial tasks.
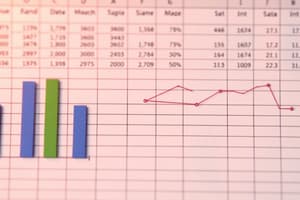
- Charts and Graphs: Excel has tools to create different charts/graphs for visual representation of data trends and patterns.
- Data Analysis Tools: Tools like sorting, filtering, and pivot tables make large datasets manageable for analysis.
- Conditional Formatting: Formatting cells based on specific conditions helps highlight important data points and trends.
- Data Import and Export: Excel supports importing/exporting data from various formats.
- Collaboration: Excel files can be shared and edited simultaneously in real-time.
Creating a New Workbook in Excel
- Sign in to office.com.
- Select Excel to open the online app.
Main Excel Interface
- Workbook: Main Excel document.
- Worksheets: Individual sheets within a workbook.
- Cells: Individual data points.
- Rows: Horizontal lines of cells.
- **Columns:**Vertical lines of cells.
- Formula Bar: Displays the value or formula for the active cell.
- Pointer: The active cell highlighted in the spreadsheet.
- Adding Sheets: Option to add new worksheets within a workbook.
Changing Permissions
- Editing: Make changes to the workbook.
- Viewing: View the file, but no changes allowed.
Renaming Workbooks and Worksheets
- Rename Workbook: Click the file name and rename it.
- Rename Worksheet: Click on the sheet name and rename it in a dialog box.
Inserting, Deleting, and Hiding Columns and Rows
- Column Operations: Select column, right-click, choose insert, delete, or hide.
- Row Operations: Select row, right-click, choose insert, delete, or hide.
- Unhiding: To un-hide columns/rows, select above or below the hidden content and right-click, select unhide.
Freezing Panes
- Excel lets you keep certain rows/columns visible while scrolling through the rest of the worksheet, ideal for large datasets.
- Can freeze rows and/or columns.
- Excel has options to unfreeze if needed.
Moving Cell Contents
- Select Cells: Drag to choose desired area.
- Cut Cells: Right-click, select "Cut."
- Navigate to Destination: Position to the desired cell.
- Paste Cells: Right-click, select "Paste" or use Ctrl+V.
Copying Cell Contents
- Select Cells: Click and drag to choose the area to copy.
- Copy Cells: Right-click, select "Copy."
- Navigate to Destination: Move to desired cell location.
- Paste Cells: Right-click, select "Paste" or Ctrl+V.
AutoFill
- AutoFill helps fill cells with sequences (repeating numbers, dates, text, etc.).
- It can fill adjacent cells with series of numbers and other data using a 'fill handle' by clicking a small square in a cell´s corner.
Number Formats
- Quick Number Options (in ribbon, right-click cell): general, number, currency, percentage, etc.)
- Increase/Decrease Decimal places in ribbon: used to adjust number output.
Charts
- Visual representations of data for trends and relationships.
- Common chart types include column, bar, line, pie, scatter.
- Customize using Chart Design and Format tabs.
- Add titles and labels to improve clarity.
Formulas and Functions
- Formulas and functions allow for calculations and data manipulation.
- The "Formulas" tab provides tools for using formulas and functions.
- Basic Arithmetic Operators (+, -, *, /) used to work with formulas.
- Cell references (e.g., A1) used within formulas to refer to specific data.
- Statistical Functions (SUM, AVERAGE, COUNT, MIN, MAX).
- Date and Time Functions (TODAY, NOW, YEAR, MONTH, DAY).
- Logical Functions (IF, AND, OR, NOT).
- Insert Functions: Use the "Insert Function" dialog box to choose/work with functions or type directly.
Conditional Formatting
- Conditional formatting formats cells based on specific conditions (e.g., data trends, outliers).
- Steps for applying conditional formatting: Select cells, go to the "Home" tab, choose conditional formatting rules, then set formatting options.
Sorting Data
- Sort data ascending or descending by selecting data, going to the "Data" tab, then select "custom sort".
- Advanced sort options available for complex sorts, sorting by multiple columns/multiple criteria, etc.
Filtering Data
- Filter data by selecting a range, going to the "Data" tab, and clicking the "Filter" button.
- Use filter options in the selected columns.
- To clear filters, select "clear" in the "Data" tab.
Creating a Table
- Select your data, go to the "Insert" tab, click "Table."
- Ensure that the "Create Table" dialog box displays your selected range.
- Optionally check the "Table with Header" checkbox.
Common Paste Special Options
- Paste Values: Paste only numerical contents without formulas or formats.
- Paste Formulas: Paste only the formulas without any formatting or values.
- Paste Formatting: Copy just the formatting styles.
- Transpose: Swaps rows and columns.
Workbook Protection
- Protect workbook, worksheets, or individual cells.
- Use passwords to restrict access for prevention from unwanted/unauthorized changes.
- Unprotecting the Workbook: Use the 'Unprotect Workbook' option in 'Review' tab. If protected, a password will be required to access unprotected mode.
- Use the 'Manage Protection' options for further protection features.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.