Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the epidermis in the integumentary system?
What is the primary role of the epidermis in the integumentary system?
- Senses pleasant stimulation
- Regulates body temperature
- Acts as the body's protective covering (correct)
- Eliminates waste through perspiration
Which of the following is NOT a function of the integumentary system?
Which of the following is NOT a function of the integumentary system?
- Sensing unpleasant stimuli
- Serving as an organ of elimination
- Producing hormones for growth (correct)
- Preventing microorganisms from entering the body
What changes occur in the integumentary system as a person ages?
What changes occur in the integumentary system as a person ages?
- Increased sensation in the skin
- Thickening of the dermis layer
- Decreased elasticity and hydration (correct)
- Enhanced ability to regulate temperature
Which component is included in the structure of the integumentary system?
Which component is included in the structure of the integumentary system?
Which of the following diseases is commonly associated with the integumentary system?
Which of the following diseases is commonly associated with the integumentary system?
What is a major threat associated with wound injuries?
What is a major threat associated with wound injuries?
What is the primary purpose of wound care?
What is the primary purpose of wound care?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of skin tears?
Which of the following is NOT a common cause of skin tears?
What should you do if you cause or find a skin tear?
What should you do if you cause or find a skin tear?
What part of the body is considered the first line of defense against infection?
What part of the body is considered the first line of defense against infection?
Which of the following is a typical site for skin tears?
Which of the following is a typical site for skin tears?
What should you observe about wounds during care?
What should you observe about wounds during care?
Which activity could possibly lead to a skin tear?
Which activity could possibly lead to a skin tear?
What is the primary purpose of placing a client at risk for pressure ulcers on a specialized surface?
What is the primary purpose of placing a client at risk for pressure ulcers on a specialized surface?
Which of the following does NOT serve as a protective device to prevent or treat pressure ulcers?
Which of the following does NOT serve as a protective device to prevent or treat pressure ulcers?
What significant risk factor for pressure ulcers does Mr. Montoya have due to his medical history?
What significant risk factor for pressure ulcers does Mr. Montoya have due to his medical history?
Which intervention should be prioritized by Kristin to reduce Mr. Montoya's skin breakdown risks after noticing a blister?
Which intervention should be prioritized by Kristin to reduce Mr. Montoya's skin breakdown risks after noticing a blister?
Which of the following lifestyle choices made by Mr. Montoya could contribute to his risk of developing pressure ulcers?
Which of the following lifestyle choices made by Mr. Montoya could contribute to his risk of developing pressure ulcers?
In assessing Mr. Montoya, which category of the Braden Scale would be noted as particularly relevant regarding his mobility?
In assessing Mr. Montoya, which category of the Braden Scale would be noted as particularly relevant regarding his mobility?
How does Mr. Montoya's history of smoking potentially impact his risk for skin breakdown?
How does Mr. Montoya's history of smoking potentially impact his risk for skin breakdown?
What could be a consequence of Mr. Montoya's weight loss in the context of pressure ulcer development?
What could be a consequence of Mr. Montoya's weight loss in the context of pressure ulcer development?
Which of the following individuals is at the highest risk for developing a pressure ulcer?
Which of the following individuals is at the highest risk for developing a pressure ulcer?
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for skin tears?
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for skin tears?
Which of the following is the most effective way to prevent pressure ulcers?
Which of the following is the most effective way to prevent pressure ulcers?
What is the primary reason why individuals with altered mental awareness are at a higher risk of skin tears and pressure ulcers?
What is the primary reason why individuals with altered mental awareness are at a higher risk of skin tears and pressure ulcers?
Which of the following contributes to pressure ulcer development?
Which of the following contributes to pressure ulcer development?
Which of the following is the most common cause of pressure ulcers?
Which of the following is the most common cause of pressure ulcers?
Why is it important to keep the client's nails short when providing care?
Why is it important to keep the client's nails short when providing care?
What is the primary difference between a skin tear and a pressure ulcer?
What is the primary difference between a skin tear and a pressure ulcer?
What sign indicates that skin may be losing its strength during the aging process?
What sign indicates that skin may be losing its strength during the aging process?
Which skin disorder is characterized by painful raised blisters?
Which skin disorder is characterized by painful raised blisters?
What is a common cause of hives?
What is a common cause of hives?
What typically characterizes dermatitis?
What typically characterizes dermatitis?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of eczema?
Which of the following is NOT a symptom of eczema?
What is the most common cause of boils?
What is the most common cause of boils?
Which type of skin cancer is considered the most dangerous?
Which type of skin cancer is considered the most dangerous?
Which condition is characterized by intense itching caused by a mite?
Which condition is characterized by intense itching caused by a mite?
What describes a skin tag?
What describes a skin tag?
Which statement is true regarding athletes foot?
Which statement is true regarding athletes foot?
What is a common treatment for an impetigo infection?
What is a common treatment for an impetigo infection?
What is the primary cause of pressure ulcers?
What is the primary cause of pressure ulcers?
What is a characteristic of skin cancer?
What is a characteristic of skin cancer?
Which symptom is commonly associated with aging skin?
Which symptom is commonly associated with aging skin?
Flashcards
Integumentary System
Integumentary System
The largest body system that includes skin and its functions.
Epidermis
Epidermis
The outer layer of the skin that acts as a barrier.
Dermis
Dermis
The inner layer of skin that contains nerve endings and blood vessels.
Functions of Integumentary System
Functions of Integumentary System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aging Effects
Aging Effects
Signup and view all the flashcards
Risk Factors for Skin Tears
Risk Factors for Skin Tears
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nail Care for Prevention
Nail Care for Prevention
Signup and view all the flashcards
Causes of Pressure Ulcers
Causes of Pressure Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bony Prominences
Bony Prominences
Signup and view all the flashcards
Moisture and Pressure Ulcers
Moisture and Pressure Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Characteristics of Pressure Ulcers
Characteristics of Pressure Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clients at High Risk for Ulcers
Clients at High Risk for Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing Pressure Ulcers
Preventing Pressure Ulcers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound
Wound
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infection Risk
Infection Risk
Signup and view all the flashcards
Wound Care Goals
Wound Care Goals
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Tear
Skin Tear
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Causes of Skin Tears
Common Causes of Skin Tears
Signup and view all the flashcards
Painful Skin Tears
Painful Skin Tears
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pressure Points
Pressure Points
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preventing Skin Injury
Preventing Skin Injury
Signup and view all the flashcards
Care Plan for At-Risk Clients
Care Plan for At-Risk Clients
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pressure Relief Surfaces
Pressure Relief Surfaces
Signup and view all the flashcards
Types of Protective Devices
Types of Protective Devices
Signup and view all the flashcards
Braden Scale Components
Braden Scale Components
Signup and view all the flashcards
Examples of Protective Devices
Examples of Protective Devices
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mr. Montoya's Risk Factors
Mr. Montoya's Risk Factors
Signup and view all the flashcards
Interventions for Skin Breakdown
Interventions for Skin Breakdown
Signup and view all the flashcards
Heel Elevation Protocol
Heel Elevation Protocol
Signup and view all the flashcards
Signs of Skin Aging
Signs of Skin Aging
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hives
Hives
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dermatitis
Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eczema
Eczema
Signup and view all the flashcards
Shingles
Shingles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Scabies
Scabies
Signup and view all the flashcards
Psoriasis
Psoriasis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Boil
Boil
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cyst
Cyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Impetigo
Impetigo
Signup and view all the flashcards
Athlete's Foot
Athlete's Foot
Signup and view all the flashcards
Skin Cancer
Skin Cancer
Signup and view all the flashcards
Common Skin Disorders
Common Skin Disorders
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physical Indicators of Skin Condition
Physical Indicators of Skin Condition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Integumentary System (HCAP 1210)
- The integumentary system is the body's largest system.
- It consists of two layers: the epidermis (outer) and dermis (inner).
- The system serves as a protective barrier, preventing microorganisms and other substances from entering the body.
- It helps regulate body temperature through perspiration.
- Nerve endings in the skin allow for the sensation of pleasant and unpleasant stimuli.
- Skin color can indicate a physical condition.
Physical Changes with Aging
- Skin becomes dry, fragile, and easily injured.
- Skin loses strength and elasticity, becoming thinner and sagging.
- Skin becomes itchy.
- Brown spots appear on wrists and hands.
- Nails become thicker and tougher.
- Hair whitens or greys and thins.
- Facial hair may increase in some women.
- Blood vessels and nerve endings decrease in number.
- Fatty tissue layer is lost.
Integumentary Disorders
- Hives (urticaria)
- Relativel common allergic reaction.
- Causes raised red skin welts (wheals).
- Wheals vary in size from a few millimeters to larger.
- Potential causes include allergies (shellfish, drugs)
- Dermatitis
- Inflammation of the skin caused by irritant or allergy.
- Contact dermatitis (allergic response to material like chemicals).
- Irritant dermatitis (reaction to chemicals in soaps).
- Eczema
- Inflammatory skin condition varying in presentation per person.
- Characterized by dry, red, and extremely itchy patches of skin.
- Can involve papular or vesicular lesions (raised bumps or fluid-filled blisters)
- Shingles
- Viral infection by herpes varicella-zoster virus.
- Causes painful rash of raised blisters that can appear anywhere on the body.
- Blister outbreak typically lasts 2 weeks.
- Often accompanied by debilitating pain, itching, and tingling.
- Scabies
- Highly contagious skin infection caused by a mite.
- Mites burrow under the skin and lay eggs causing intense itching.
- Transmitted by skin-to-skin contact.
- Contagious for at least a month.
- Psoriasis
- Persistent skin disorder causing red scaly plaques (patches) on the skin.
- Patches can appear anywhere on the body.
- Areas of excessive skin accumulation that are inflamed.
- Cause is not fully understood; stress and alcohol can worsen the rash.
- Boil (furuncle)
- Skin disorder caused by infection of hair follicles usually by Staphylococcus bacteria.
- Boils appear as painful, red, pus-filled lumps.
- Commonly found on the back, underarms, shoulders, thighs, and buttocks.
- Cyst
- Abnormal, closed sac that can develop anywhere on the body.
- Contains air, fluids, or semi-solid material and has a distinct membrane.
- Will remain in the tissue unless removed surgically or by medication.
- Impetigo
- Contagious skin disorder caused by Streptococcus or Staphylococcus bacteria.
- Infected area forms crusts that drain and spread bacteria.
- Spread by client scratching the area and touching other parts of the body.
- Skin Tag
- Small flap of flesh-colored skin that looks like a droplet or tag.
- Not painful, Most common in women and older adults.
- Athletes Foot
- Highly contagious fungal skin infection.
- Affected foot peels, burns, itches, and turns red.
- Easily spread through contact.
- Skin Cancer
- Malignant growths on the skin usually presenting in epidermis.
- Easily visible.
- Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas are the two most common types.
- Malignant melanoma is the most dangerous type and can be fatal if not treated early.
Wound Care
- Skin is the body's first line of defense against infection.
- Preventing skin injury is crucial to prevent breakdown.
- Wounds are breaks in the skin or mucous membranes, and infection is a major concern.
- Wound care involves: infection prevention; preventing further injury; preventing blood loss; preventing pain.
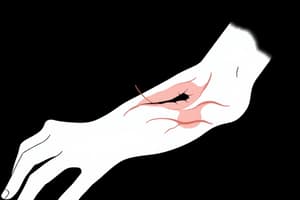
Skin Tear
- A skin tear is a break or rip in the skin's epidermis.
- Common locations are hands, arms, and lower legs.
- Causes:
- Friction and shearing
- Pulling or pressure
- Bumping against a hard surface
- Tightly holding a limb
- Repositioning, bathing, dressing
- Pulling buttons/zippers
- Risk factors: elderly; frail skin; poor nutrition; impaired mobility; hydration issues; altered mental status.
- Important to report tears or injuries; careful handling and assessment is needed to prevent further injury.
Pressure Ulcers
- Decubitus ulcers, bed sores.
- Injury caused by unrelieved pressure on skin and underlying tissues.
- Often develop over bony prominences (shoulders, hips, heels).
- Risk factors: pressure, shearing, friction; breaks in skin; poor circulation to an area; moisture; dry, flaky skin; irritation by urine and feces; immobility, poor nutrition, altered mental status, diabetes, vascular disease.
- Clients at risk for pressure ulcers: confined to bed or chair; require help in moving; bowel/bladder issues; poor nutrition; altered mental status; circulatory problems; elderly; obese/very thin individuals
- Stages of Pressure Ulcers (I-IV) characterized by increasing tissue damage. Stage I is non-blanchable redness; Stage IV is exposed bone, tendon, or muscle.
Complications of Wounds
- Infection can occur at any time (signs: tenderness, drainage, fever)
- Dehiscence: separation of wound layers
- Evisceration: protrusion of abdominal organs with wound separation.
- Hemorrhage (excessive blood loss internally or externally): (signs: shock, vomiting blood, coughing up blood, loss of consciousness.)
- Shock (not enough blood supply): (signs: low blood pressure, rapid/weak pulse, pale/moist/cold skin)
Wound Drainage
- Serous: clear, watery fluid.
- Sanguineous: bloody fluid
- Serosanguineous: thin, blood-tinged fluid.
- Purulent: thick, yellow or green (or brown) fluids; likely foul-smelling. The type of drainage can indicate the cause of the wound.
Treatment Options (for Leg & Foot Ulcers)
- Follow care plans and procedures to limit skin breakdown.
- Carefully handle, move, and reposition clients.
- Ensure clients receive appropriate foot care.
- Medicated bandages, wound care products, and devices often prescribed by the doctor.
- Elastic bandages or stockings.
Protective Devices
- Special beds
- Bed cradles
- Elbow protectors
- Heel protectors
- Flotation pads/cushions
- Egg crate mattresses
- Pillows
- Trochanter rolls
- Footboards
- Used to prevent pressure ulcers and skin breakdown
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.