Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following is NOT a known trigger for Rosacea flare-ups?
Which of the following is NOT a known trigger for Rosacea flare-ups?
- Strenuous exercise
- Spicy foods, hot beverages, alcohol
- Direct sunlight
- Extreme temperatures (correct)
What is the most common trigger for Erythema Multiforme?
What is the most common trigger for Erythema Multiforme?
- Herpes Simplex Virus (correct)
- Medication
- Fungal infection
- Bacterial infection
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Psoriatic Arthritis?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of Psoriatic Arthritis?
- Itching (correct)
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Pain
What is the primary cause of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
What is the primary cause of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Which of the following skin conditions is considered contagious?
Which of the following skin conditions is considered contagious?
What is the characteristic symptom of Urticaria?
What is the characteristic symptom of Urticaria?
Which stage of Decubitus Ulcers involves deep tissue destruction exposing muscle or bone?
Which stage of Decubitus Ulcers involves deep tissue destruction exposing muscle or bone?
What is the most common presentation of Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)?
What is the most common presentation of Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)?
Which of the following skin conditions is NOT a type of Dermatitis?
Which of the following skin conditions is NOT a type of Dermatitis?
Which of these skin conditions is characterized by a bulbous nose as a potential symptom?
Which of these skin conditions is characterized by a bulbous nose as a potential symptom?
What does the 'B' in the ABCDEs of moles stand for?
What does the 'B' in the ABCDEs of moles stand for?
Which type of skin cancer is considered benign and never metastasizes?
Which type of skin cancer is considered benign and never metastasizes?
What is the main cause of malignant melanoma?
What is the main cause of malignant melanoma?
What characteristic is associated with cutaneous papilloma?
What characteristic is associated with cutaneous papilloma?
What is the 5-year survival rate for malignant melanoma if detected early?
What is the 5-year survival rate for malignant melanoma if detected early?
What is the primary reason for the appearance of sebaceous neoplasms?
What is the primary reason for the appearance of sebaceous neoplasms?
Which type of skin condition is ichthyosis?
Which type of skin condition is ichthyosis?
What is a common symptom of ichthyosis?
What is a common symptom of ichthyosis?
Basosquamous carcinoma is best described as:
Basosquamous carcinoma is best described as:
For patients with ichthyosis, which statement is true regarding massage therapy?
For patients with ichthyosis, which statement is true regarding massage therapy?
What skin condition is characterized by chronic, itchy inflammation often leading to dry, scaly skin?
What skin condition is characterized by chronic, itchy inflammation often leading to dry, scaly skin?
Which condition is associated with a rash that arises from contact with an irritant and resolves upon its removal?
Which condition is associated with a rash that arises from contact with an irritant and resolves upon its removal?
In which dermatitis type do erythematic vesicles often appear and pruritus occurs after a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
In which dermatitis type do erythematic vesicles often appear and pruritus occurs after a delayed hypersensitivity reaction?
Which skin condition is primarily caused by chronic venous insufficiency and leads to chronic redness and swelling in lower legs?
Which skin condition is primarily caused by chronic venous insufficiency and leads to chronic redness and swelling in lower legs?
What is a primary symptom of Neurodermatitis?
What is a primary symptom of Neurodermatitis?
Which treatment is not applicable to Stasis Dermatitis?
Which treatment is not applicable to Stasis Dermatitis?
What distinguishes Photoallergic Dermatitis from Phototoxic Dermatitis?
What distinguishes Photoallergic Dermatitis from Phototoxic Dermatitis?
Which skin condition is associated with excessive sebum production and may lead to dandruff?
Which skin condition is associated with excessive sebum production and may lead to dandruff?
Which element is crucial in managing allergic contact dermatitis effectively?
Which element is crucial in managing allergic contact dermatitis effectively?
What is a notable symptom of seborrheic dermatitis that differentiates it from other skin conditions?
What is a notable symptom of seborrheic dermatitis that differentiates it from other skin conditions?
Flashcards
What is Psoriasis?
What is Psoriasis?
A chronic, non-contagious, inflammatory autoimmune disease of hyper-proliferation.
What is the Etiology of Psoriasis?
What is the Etiology of Psoriasis?
Autoimmune, but the specific cause is unknown. It can be linked to genetics, smoking, obesity, alcohol, infections, and more.
What is Plaque Psoriasis?
What is Plaque Psoriasis?
A common type of psoriasis characterized by raised, red patches of skin covered in silvery scales.
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
What is Psoriatic Arthritis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Rosacea?
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Rosacea?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
How is Rosacea Treated?
How is Rosacea Treated?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Primary Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Primary Irritant Contact Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
What is Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the Etiology of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
What is the Etiology of Hidradenitis Suppurativa?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phototoxic Dermatitis
Phototoxic Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Erythema Multiforme?
What is Erythema Multiforme?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
What is Stevens-Johnson Syndrome?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Photoallergic Dermatitis
Photoallergic Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neurodermatitis (Localized Scratch Dermatitis)
Neurodermatitis (Localized Scratch Dermatitis)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Perioral Dermatitis
Perioral Dermatitis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Melanocytic Nevi (Moles)
Melanocytic Nevi (Moles)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Atypical Nevus
Atypical Nevus
Signup and view all the flashcards
ABCDEs of Moles
ABCDEs of Moles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Basosquamous Carcinoma (BSC)
Basosquamous Carcinoma (BSC)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sebaceous Neoplasms
Sebaceous Neoplasms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cutaneous Papilloma (Skin Tag)
Cutaneous Papilloma (Skin Tag)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ichthyosis
Ichthyosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant Melanoma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Massage Contraindications for Skin Neoplasms
Massage Contraindications for Skin Neoplasms
Signup and view all the flashcards
Massage & Ichthyosis
Massage & Ichthyosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Inflammatory Reactions of the Skin
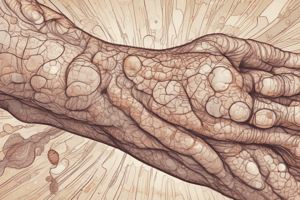
- Psoriasis: A chronic, non-contagious, inflammatory autoimmune disease characterized by hyper-proliferation.
- Etiology: Autoimmune, likely with a genetic component, exacerbated by smoking, obesity, alcohol use, and infections.
- Epidemiology: More common in Caucasians and certain age groups.
- Signs & Symptoms: Erythematous papules and plaques covered in silvery scales, severe itching (pruritus), Auspitz's sign (punctate bleeding upon scraping), Koebner phenomenon (new psoriasis develops at sites of skin trauma). Common affected areas include scalp, extensor surfaces, back, chest, groin, armpits.
- Common Comorbidities: Psoriatic arthritis (5-30% of psoriasis patients), characterized by joint pain, stiffness, swelling, and tenderness. Nail bed involvement (1/3 of psoriasis patients).
- Diagnosis: Clinical examination, skin biopsy for complex cases.
- Treatment: Topical corticosteroids, over-the-counter moisturizers, controlled UV light, antihistamines for pruritus. Massage is a local contraindication if broken skin is present, light massage may be performed with patient consent.
- Rosacea: A chronic, progressive, erythematic skin condition causing facial redness.
- Etiology: Idiopathic, with possible genetic and/or immune system involvement.
- Epidemiology: Most common age range 30-50, more common in females and those with fair complexions.
- Signs & Symptoms: Persistent facial erythema, dryness, warmth, swelling, tiny pustules, telangiectasia (spider veins), thickened skin, possible rhinophyma (bulbous nose). Symptoms tend to have flare-up/remission phases. Triggered by various factors.
- Rosacea Phases: Pre-rosacea (redness), vascular (spider veins), inflammatory (acne), late-stage (rhinophyma).
- Treatment: Avoiding known triggers (sunlight, exercise, extreme temperatures, spicy foods, alcohol). Topical antibiotics for inflammatory phase. No cure exists.
- Prognosis: Increased risk of migraines; association with IBD, celiac disease, IBS/SIBO. Massage is affected by the severity of the disease; avoiding areas with pustules.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: A chronic, scarring, acne-like inflammatory process, most common in axillae, groin, and around nipples and anus.
- Etiology: Idiopathic, hair follicle blockage potentially related to hormonal imbalances, genetics, smoking, or obesity.
- Symptoms: Small, painful nodules under the skin, followed by pus drainage, painful fibrotic bands in chronic cases, foul odor. No pruritus.
- Treatment & Prognosis: Drug therapy not always effective, but potentially topical antibiotics and steroids, warm compresses to drain, laser hair removal, surgical excision. Can cause scarring.
- Massage: Local contraindication due to pustules. Inquire about patient sensitivity.
Drug Eruptions and Reactions
- Erythema Multiforme: An inflammatory reaction characterized by target-shaped skin lesions, oral mucosa involvement, considered a type IV hypersensitivity reaction.
- Etiology: Primarily triggered by herpes simplex virus (HSV).
- Symptoms: Mildly itchy, symmetrically distributed red, raised skin with target lesions, blistering, and mucous membrane involvement. Potential for oozing blood. Systemic symptoms like fatigue, joint pain, and fever.
- Treatment: Self-limiting (2-4 weeks), antiviral treatment if HSV is the cause. Massage is a local contraindication until lesions have fully healed.
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS): Life-threatening type IV hypersensitivity reaction with dermis separation from epidermis, involves mucous membranes.
- Etiology: Primarily due to medications (especially sulfa drugs). Infections can also be a cause.
- Symptoms: Severe blistering, pain when moving mouth/eating (drooling), dysphagia, painful eye swelling with pus, dysuria with genital involvement. Systemic symptoms (fever, fatigue, sore throat).
- Treatment: Supportive care (analgesics, IV fluids, NG tube/parenteral nutrition). Massage is a contraindication until full recovery.
- Urticaria (Hives): Inflammatory skin disorder usually associated with allergic reactions (Type I hypersensitivity).
- Etiology: Allergen triggers immune response (medications, insect bites, foods, idiopathic).
- Symptoms: Itching followed by wheals (small, elevated lesions) and flares (surrounding redness), often last few hours, immediate appearance. Angioedema (edema of deeper tissues) is a serious complication.
- Treatment: Oral antihistamines, topical corticosteroids, monitor for lesions around mouth, hives in throat can be life-threatening. EpiPen for anaphylaxis. Massage is contraindicated in acute/allergic urticaria, and is a local contraindication in chronic cases.
Pressure/Decubitus Ulcers
- Definition: Breakdown of skin integrity due to prolonged pressure, reduced blood flow, and tissue necrosis.
- Etiology: Prolonged pressure (bedridden, wheelchair-bound, casts), paralysis, coma, diabetes.
- Stages:
- Stage I: Non-blanchable erythema of intact skin.
- Stage II: Partial thickness skin loss with exposed dermis.
- Stage III: Full thickness skin loss to subcutaneous fat.
- Stage IV: Full thickness skin loss to muscle/bone.
- Treatment: Repositioning of the client, medical treatment (wound care specialist), antibiotics for infection.
- Massage: Local contraindication, avoid working over infected or discharging ulcers.
Dermatitis
- Definition: Superficial inflammation of the skin, common presentations including pruritus, redness, edema, oozing, crusting, and scaling.
- Types:
- Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Most common inflammatory skin disorder, immune-mediated inflammation, often linked with asthma and allergies. Triggers include food, environmental allergies, stress, humidity, and irritation.
- Primary Irritant Contact Dermatitis: Inflammation due to contact with irritant non-immunological response, symptoms resolve within days of removal of the irritant.
- Allergic Contact Dermatitis (ACD): Type IV delayed hypersensitivity reaction, rash at the site of contact, caused by exposure to allergens like cosmetics, metals, plants, or chemicals.
- Phototoxic Dermatitis: Skin reaction within minutes/hours after sun exposure to light-absorbing substances, no allergy reaction.
- Photoallergic Dermatitis: Type IV cell-mediated immune response 1-3 days after sun exposure to photosensitizing agents, prior exposure required.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Inflammation of the lower legs due to chronic venous insufficiency (blood/fluid pooling). Risk factors include history of DVT, varicose veins, obesity, pregnancy, lack of physical activity, and smoking.
Neurodermatitis (Localized Scratch Dermatitis or Lichen Simplex Chronicus):
- Chronic, itchy inflammation that leads to thickened epidermis. Linked to psychogenic factors.
- Etiology: Unknown; potentially psychological factors, anxiety, stress.
- Symptoms: Itchy, dry, scaling rash with dark, thickened patches resulting from the itch-scratch cycle. Common areas include arms, legs, neck, anus, vagina.
- Treatment: Address the cause of the itching (psyc psychological factors). Patient education regarding scratching, topical corticosteroids, antihistamines.
Seborrheic Dermatitis:
- Chronic inflammatory disease of skin rich with sebaceous glands (like "cradle cap").
- Etiology: Associated with the yeast Malassezia Furfur, weakened immune system, stress, cold/dry climate, diet, and/or genetics.
- Symptoms: Pruritus, dandruff, yellow, greasy flakes due to excess sebum. Common on face, hairline, scalp.
- Treatment: Anti-inflammatory shampoos, antifungal topicals.
- Massage: Assess patient history, sensitivity, and use thin, water-based lubrication.
Perioral Dermatitis:
- Dermatitis surrounding the mouth, often mistaken for acne or rosacea.
- Etiology: Idiopathic, often associated with topical steroid use.
- Symptoms: Acne-like papules/pustules, scaling, erythema, but NO pruritus. Often limited to immediately around the mouth.
- Treatment: Remove potential triggers, appropriate antibiotic/anti-inflammatory creams
Neoplasms of the Skin
- Melanocytic Nevi (Moles): Atypical or dysplastic moles need further evaluation due to potential for melanoma. (ABCDEs: A=asymmetry, B=borders, C=color, D=diameter, E=evolving).
- Malignant Melanoma: UV light exposure = primary cause, fast growing, metastases, early detection crucial for high survival rate.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): Most common skin cancer, never metastasizes, appears as a pearly white nodule, 100% 5-year survival rate if detected early.
- Basosquamous Carcinoma (BSC): Rare, aggressive cancer, BCC with mutation/differentiation, high risk of UV exposure.
- Sebaceous Neoplasm: Often benign, but may be malignant, may mimic other tumors.
- Cutaneous Papilloma (Skin Tag): Benign skin growth, common in regions where skin rubs, may be associated with HPV.
- Massage: All neoplasms are local contraindications. Follow cancer guidelines, observant of new lesions, encourage doctor evaluations.
Ichthyosis:
- Over 30 diseases with similar presentations, involving redness, itchiness, and flaky skin.
- Etiology: Genetic mutation /inheritance.
- Symptoms: Varying, but commonly involve redness, pruritus, flaky/leathery skin, large/hard plates.
- Treatment: Varies depending on the type. Typically involves skin moisturizing creams.
- Massage: Not contraindicated, but may be sensitive skin.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz covers the inflammatory skin condition known as psoriasis, including its etiology, epidemiology, signs and symptoms, and common comorbidities. It also discusses diagnosis and treatment options available for managing this chronic autoimmune disease.