Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two types of gametes produced by the male and female sex organs?
What are the two types of gametes produced by the male and female sex organs?
The process by which sperm cells are formed is known as oogenesis.
The process by which sperm cells are formed is known as oogenesis.
False (B)
The male reproductive system lies inside the abdominal cavity.
The male reproductive system lies inside the abdominal cavity.
False (B)
What is the primary role of the scrotum?
What is the primary role of the scrotum?
Signup and view all the answers
Which cells are responsible for providing nutrition to the germ cells in the seminiferous tubules?
Which cells are responsible for providing nutrition to the germ cells in the seminiferous tubules?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the hormone secreted by the Leydig cells?
What is the name of the hormone secreted by the Leydig cells?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the male sex accessory ducts?
What are the male sex accessory ducts?
Signup and view all the answers
The urethra, which carries urine, also serves as the passage for sperm.
The urethra, which carries urine, also serves as the passage for sperm.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the loose fold of skin that covers the glans penis?
What is the name of the loose fold of skin that covers the glans penis?
Signup and view all the answers
Which gland, present in the male reproductive system, is responsible for the production of seminal plasma?
Which gland, present in the male reproductive system, is responsible for the production of seminal plasma?
Signup and view all the answers
Name the primary female sex organs.
Name the primary female sex organs.
Signup and view all the answers
How many ovaries are present in a human female?
How many ovaries are present in a human female?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the two zones of the ovarian stroma?
What are the two zones of the ovarian stroma?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the parts of the female reproductive system located in the pelvic region?
What are the parts of the female reproductive system located in the pelvic region?
Signup and view all the answers
The fallopian tubes are attached to the uterus at the lower end.
The fallopian tubes are attached to the uterus at the lower end.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the funnel-shaped structure present at the lower end of the fallopian tube?
What is the funnel-shaped structure present at the lower end of the fallopian tube?
Signup and view all the answers
What are the finger-like projections present at the edges of the infundibulum?
What are the finger-like projections present at the edges of the infundibulum?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the other name for the uterus?
What is the other name for the uterus?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the opening between the uterus and vagina?
What is the name of the opening between the uterus and vagina?
Signup and view all the answers
The uterus is lined by a single layer of tissue called the myometrium.
The uterus is lined by a single layer of tissue called the myometrium.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the thin membranous outer layer of the uterus?
What is the name of the thin membranous outer layer of the uterus?
Signup and view all the answers
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for strong contraction during birth?
Which layer of the uterus is responsible for strong contraction during birth?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening?
What is the name of the membrane that partially covers the vaginal opening?
Signup and view all the answers
Which structure in the female reproductive system is considered a tiny finger-like protrusion above the urethral opening?
Which structure in the female reproductive system is considered a tiny finger-like protrusion above the urethral opening?
Signup and view all the answers
The presence or absence of hymen is a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience.
The presence or absence of hymen is a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience.
Signup and view all the answers
What are the clusters of cells in the mammary glands called?
What are the clusters of cells in the mammary glands called?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the wider duct formed by the joining of several mammary ducts?
What is the wider duct formed by the joining of several mammary ducts?
Signup and view all the answers
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are both processes of reduction division.
Spermatogenesis and oogenesis are both processes of reduction division.
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the immature male germ cell present in the seminiferous tubules?
What is the name of the immature male germ cell present in the seminiferous tubules?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the number of chromosomes in each spermatogonium?
What is the number of chromosomes in each spermatogonium?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the cell that undergoes the first meiotic division during spermatogenesis?
What is the name of the cell that undergoes the first meiotic division during spermatogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the haploid cell formed after the second meiotic division in spermatogenesis?
What is the name of the haploid cell formed after the second meiotic division in spermatogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the process of transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa called?
What is the process of transformation of spermatids into spermatozoa called?
Signup and view all the answers
Which hormone stimulates the process of spermatogenesis?
Which hormone stimulates the process of spermatogenesis?
Signup and view all the answers
What is the name of the hormone that stimulates the Leydig cells to secrete androgens?
What is the name of the hormone that stimulates the Leydig cells to secrete androgens?
Signup and view all the answers
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty due to the increase in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Spermatogenesis begins at puberty due to the increase in the secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH).
Signup and view all the answers
Flashcards
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis
The process of gamete production in males, where immature sperm cells called spermatogonia mature into sperm.
Sertoli Cells
Sertoli Cells
A type of cell within the seminiferous tubules that provide nourishment to the developing sperm cells.
Androgens
Androgens
Hormones produced by the testes, mainly testosterone, that are crucial for the development and maintenance of male reproductive characteristics.
Scrotum
Scrotum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes
Testes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vasa Efferentia
Vasa Efferentia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epididymis
Epididymis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vas Deferens
Vas Deferens
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urethra
Urethra
Signup and view all the flashcards
Penis
Penis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Glans Penis
Glans Penis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Foreskin
Foreskin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Vesicles
Seminal Vesicles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Prostate Gland
Prostate Gland
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bulbourethral Glands
Bulbourethral Glands
Signup and view all the flashcards
Seminal Plasma
Seminal Plasma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Oogenesis
Oogenesis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries
Ovaries
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervix
Cervix
Signup and view all the flashcards
Uterus
Uterus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vagina
Vagina
Signup and view all the flashcards
Vulva
Vulva
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mons Pubis
Mons Pubis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labia Majora
Labia Majora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Labia Minora
Labia Minora
Signup and view all the flashcards
Clitoris
Clitoris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hymen
Hymen
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Human Reproduction
- Humans are sexually reproducing and viviparous
- Reproductive events include gametogenesis (sperm/ovum), insemination, fertilisation, zygote formation, blastocyst formation, implantation, embryonic development, and parturition
- Puberty marks the start of these reproductive events
- There are notable differences in reproductive events between males and females (e.g., sperm production continues throughout life, while ovum production ceases at around age 50)
The Male Reproductive System
- Located in the pelvis, comprising testes, accessory ducts, glands, and external genitalia
- Testes are outside the abdominal cavity in a pouch called the scrotum
- Scrotum regulates testis temperature (2-2.5°C lower than body temperature) for spermatogenesis
- Each testis has about 250 compartments called testicular lobules, each containing seminiferous tubules
- Sperms are produced in the seminiferous tubules, involving germ cells (spermatogonia) and Sertoli cells
- Interstitial spaces contain Leydig cells, producing androgens (e.g., testosterone)
- Male accessory ducts include rete testis, vasa efferentia, epididymis, and vas deferens; these transport sperm from testis to outside
- Seminal vesicles, prostate, and bulbourethral glands produce seminal fluid, combined with sperm during ejaculation
- Urethra extends from urinary bladder to external opening (urethral meatus), through penis
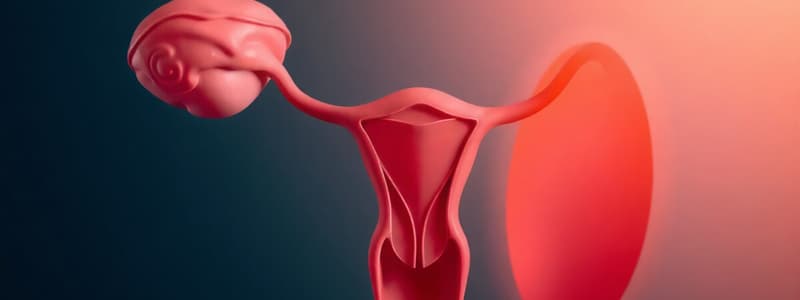
The Female Reproductive System
- Located in the pelvis, encompassing ovaries, oviducts, uterus, cervix, vagina, and external genitalia, and mammary glands.
- Ovaries are the primary female sex organs, producing ova and ovarian hormones
- Each ovary is connected to the uterus by ligaments, and covered by an epithelium enclosing ovarian stroma
- The oviducts, also called fallopian tubes, have funnel-shaped infundibulum with fimbriae to collect ova; they lead to the uterus
- The uterus, or womb, is a muscular organ with three layers (perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium) to support pregnancy and childbirth
- Cervix connects the uterus to the vagina, which is the birth canal
- External genitalia (mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, hymen, clitoris) are the visible parts of the female reproductive system
Gametogenesis
- Gametogenesis is the process of producing gametes (sperm and ovum).
- In males, this process is called spermatogenesis, which begins at puberty and leads to the production of spermatozoa.
- In females, this process is called oogenesis, which begins before birth and results in the production of ova.
- Gametogenesis is a crucial aspect of sexual reproduction, as it involves the production of haploid gametes that will fuse during fertilization to form a diploid zygote.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the fascinating processes of human reproduction, including gametogenesis, fertilization, and embryonic development. Understand the intricacies of the male reproductive system, including the structure and function of the testes and sperm production. This quiz covers essential reproductive biology concepts to enhance your understanding.