Podcast
Questions and Answers
What significant change occurs at Week 8 in embryonic development?
What significant change occurs at Week 8 in embryonic development?
- The embryo doubles in size from the previous week.
- Major organ systems reach rudimentary forms. (correct)
- Skin layers start to develop.
- The embryo begins to form limbs.
At Week 8, which of the following features is becoming more defined?
At Week 8, which of the following features is becoming more defined?
- The trunk length relative to the head.
- The distinct appearance of external features. (correct)
- The ratio of limbs to body size.
- The size of internal organs.
Which organ system is specifically mentioned as having its basic regions developed by Week 8?
Which organ system is specifically mentioned as having its basic regions developed by Week 8?
- Digestive system
- Respiratory system
- Circulatory system
- Nervous system (correct)
Which of the following developmental milestones indicates the transition from embryo to the fetal stage at Week 8?
Which of the following developmental milestones indicates the transition from embryo to the fetal stage at Week 8?
The embryo at Week 8 measures approximately how many millimeters in length?
The embryo at Week 8 measures approximately how many millimeters in length?
What happens to the growth rate of the embryo at Week 8 compared to earlier weeks?
What happens to the growth rate of the embryo at Week 8 compared to earlier weeks?
Which organ system's formation is highlighted as undergoing rapid differentiation during Week 8?
Which organ system's formation is highlighted as undergoing rapid differentiation during Week 8?
Which of the following correctly states an impact of developmental disruptions at Week 8?
Which of the following correctly states an impact of developmental disruptions at Week 8?
Which organ system is fully formed with four chambers by Week 8?
Which organ system is fully formed with four chambers by Week 8?
What significant change occurs in the embryo beginning in Week 9?
What significant change occurs in the embryo beginning in Week 9?
Which system shows the first signs of differentiation during the embryonic stage?
Which system shows the first signs of differentiation during the embryonic stage?
What developmental process occurs in the musculoskeletal system by Week 8?
What developmental process occurs in the musculoskeletal system by Week 8?
Which of the following statements about the respiratory system is true by Week 8?
Which of the following statements about the respiratory system is true by Week 8?
What is a key feature of limb development observed by Week 8?
What is a key feature of limb development observed by Week 8?
What happens to the eyelids during the key events of embryo development?
What happens to the eyelids during the key events of embryo development?
What is one of the major changes in organ systems as the embryo transitions to the fetal stage?
What is one of the major changes in organ systems as the embryo transitions to the fetal stage?
What marks the first step in the formation of external genitalia during indifferent genitalia development?
What marks the first step in the formation of external genitalia during indifferent genitalia development?
What significant facial features become visible by the end of week 8?
What significant facial features become visible by the end of week 8?
What event occurs during limb development in week 8?
What event occurs during limb development in week 8?
What is a crucial aspect of the early spontaneous limb movements observed in week 8?
What is a crucial aspect of the early spontaneous limb movements observed in week 8?
What is the main function of rudimentary kidneys (metanephros) that begin during week 8?
What is the main function of rudimentary kidneys (metanephros) that begin during week 8?
What signifies the transition preparation into the fetal period at week 8?
What signifies the transition preparation into the fetal period at week 8?
During limb development in week 8, what begins to develop at the tips of fingers and toes?
During limb development in week 8, what begins to develop at the tips of fingers and toes?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of early spontaneous limb movements in week 8?
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of early spontaneous limb movements in week 8?
At what week do the metanephros, the permanent kidneys, begin to function?
At what week do the metanephros, the permanent kidneys, begin to function?
What is the primary role of urine produced by the kidneys during fetal development?
What is the primary role of urine produced by the kidneys during fetal development?
Why is the initiation of kidney function significant for the embryo?
Why is the initiation of kidney function significant for the embryo?
What happens to the midgut by week 8 of fetal development?
What happens to the midgut by week 8 of fetal development?
What is the significance of the midgut retraction during fetal development?
What is the significance of the midgut retraction during fetal development?
Which of the following statements about the small and large intestines is true after midgut retraction at week 8?
Which of the following statements about the small and large intestines is true after midgut retraction at week 8?
What critical development stage is marked by midgut retraction?
What critical development stage is marked by midgut retraction?
How would you describe the role of amniotic fluid during fetal development?
How would you describe the role of amniotic fluid during fetal development?
Flashcards
Week 8: Heart Development
Week 8: Heart Development
The heart develops four chambers and begins beating consistently. Blood vessels continue forming, and circulation becomes active.
Week 8: Musculoskeletal System
Week 8: Musculoskeletal System
Fingers and toes are distinct, and the cartilaginous skeleton continues to develop. Ossification begins in some bones, particularly the long bones of the arms and legs.
Week 8: Digestive System Development
Week 8: Digestive System Development
The intestinal loop continues developing, and the stomach, liver, and pancreas start to form.
Week 8: Lung Development
Week 8: Lung Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Week 8: External Genitalia Development
Week 8: External Genitalia Development
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Period (Week 9)
Fetal Period (Week 9)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Week 8: Embryo Movement
Week 8: Embryo Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Week 8: Eyelid Fusion
Week 8: Eyelid Fusion
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the significance of week 8 in embryonic development?
What is the significance of week 8 in embryonic development?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the size of the embryo at the end of week 8?
What is the size of the embryo at the end of week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What key anatomical changes occur in week 8?
What key anatomical changes occur in week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
How does the nervous system develop in week 8?
How does the nervous system develop in week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the primary event happening in week 8 regarding organ development?
What is the primary event happening in week 8 regarding organ development?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What major organ systems take shape by week 8?
What major organ systems take shape by week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the significance of heart septation in week 8?
What is the significance of heart septation in week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Why is it important to understand developmental disruptions at week 8?
Why is it important to understand developmental disruptions at week 8?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidney Function Begins
Kidney Function Begins
Signup and view all the flashcards
Urine's Role in Amniotic Fluid
Urine's Role in Amniotic Fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Retraction
Midgut Retraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Midgut Herniation
Midgut Herniation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intestinal Positioning
Intestinal Positioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of Kidney Function
Significance of Kidney Function
Signup and view all the flashcards
Amniotic Fluid's Importance
Amniotic Fluid's Importance
Signup and view all the flashcards
Significance of Midgut Retraction
Significance of Midgut Retraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Indifferent Genitalia
Indifferent Genitalia
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genital Tubercle Elongation
Genital Tubercle Elongation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Facial Features Become Defined
Facial Features Become Defined
Signup and view all the flashcards
Preparation for the Fetal Stages
Preparation for the Fetal Stages
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fingers and Toes Well-Defined
Fingers and Toes Well-Defined
Signup and view all the flashcards
Early Spontaneous Limb Movements
Early Spontaneous Limb Movements
Signup and view all the flashcards
Neuromuscular Coordination
Neuromuscular Coordination
Signup and view all the flashcards
Kidneys Begin Functioning
Kidneys Begin Functioning
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
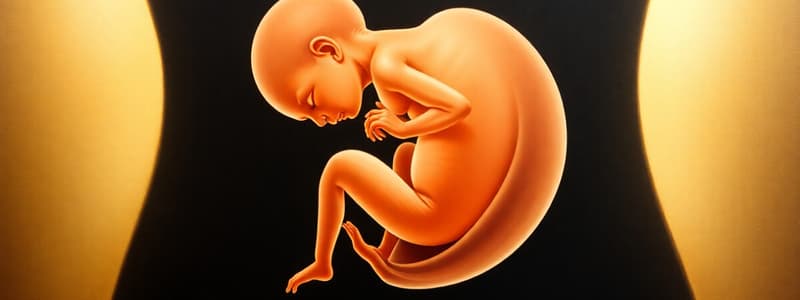
Human Embryology - Week 8 Development
- Week 8 marks the end of the embryonic period
- Embryo reaches a size of approximately 25-30mm (crown-rump length)
- All major organ systems are established in rudimentary forms
- Transition from embryo to fetal stage
- Rapid tissue differentiation and organogenesis (formation of organs)
- Formation of fundamental structures of major organ systems: heart, brain, liver, and kidneys
- Embryonic period characterized by rapid tissue differentiation and organogenesis
- Transition to fetal stage shifts focus from organ formation to growth and functional refinement
Embryo Size and Proportions at Week 8
- Embryo measures approximately 25-30mm in length
- Head proportions remain large compared to the body, although the neck begins to develop
- Limbs are elongated and fingers/toes become more distinct
- External features (eyes, nose, and mouth) are taking shape
- Growth rate slows compared to earlier weeks; organ system differentiation continues
Major Organ Systems at Week 8
- Nervous System: Brain has developed basic regions, spinal cord formation continues, motor neurons begin growing (though not capable of coordinated movement yet)
- Cardiovascular System: Heart fully formed with four chambers, consistent heartbeat, blood vessels continue to form and circulation is active
- Musculoskeletal System: Limbs have distinct fingers and toes; cartilaginous skeleton continues to form, ossification begins (especially in long bones of arms and legs)
- Digestive System: Intestinal loop continues to develop; stomach, liver, and pancreas are forming
- Respiratory System: Lungs begin developing basic structure; fetus is not yet capable of breathing
- Reproductive System: Genitalia becoming more defined, though differentiation between male and female genitalia is still rudimentary.
Transition from Embryo to Fetus (Week 8)
- Fetal period begins at week 9
- Shift from embryo's organ formation to growth and maturation
- Growth: Embryo grows in size and mass
- Functional Refinement: Organ systems refine their form and functionality.
- External Features: External ear, eyes, and face continue refinement; limbs grow in length and complexity
Lower Limb Development at Week 6
- Embryo begins showing signs of movement, though not fully developed for significant activity yet
- Transition to the fetal stage involves ceasing rapid organogenesis and initiating growth, refinement, and maturation
Progress in Facial Structure and External Features
- Fusion of Eyelids: Eyelids grow and fuse to protect developing eyes (temporary); will re-open later
- Formation of External Genitalia: Indifferent genitalia begin showing first signs of differentiation (similar in both sexes); Genital tubercle elongates (early stages of external genitalia development)
Formation of External Genitalia at Week 8
- Indifferent Genitalia: Early stage of genital development; initial signs of differentiation
- Both sexes appear similar externally at this stage
- Genital Tubercle Elongation: Genital tubercle elongates; this is the initial step in forming external genitalia
- This is an early stage in the development of either the penis (in males) or the clitoris (in females)
Significance of Week 8 Face and Neck Development
- Key events in facial features development. Facial features become more defined by the end of week 8 with visible eyes, nose, and mouth.
- Eyelid fusion and early genitalia formation signify preparation for the transition into the fetal period (growth of features like the face and neck continues)
Limb Development at Week 8
- Limbs become more defined, with clear differentiation of fingers and toes
- Webbing between digits disappears (apoptosis)
- Nails begin developing as tiny ridges
- Early spontaneous limb movements start
Coordinated Limb Movements in Week 8
- Early spontaneous limb movements are facilitated by the development of muscles and nerves
- These movements, though not voluntary, are crucial for neuromuscular coordination.
- Initial movements help establish communication between nervous and muscular systems.
- These movements are reflexive and part of early motor development
Internal Organ Development at Week 8
- Kidneys Begin Functioning: Rudimentary kidneys (metanephros) start producing urine contributing to amniotic fluid composition.
- Intestinal Loop Retraction: The midgut herniation retracts into the abdominal cavity, positioning intestines in their normal anatomical location.
Kidneys Begin Functioning at Week 8
- Rudimentary Kidneys (Metanephros): By week 8, permanent kidneys begin to function, marking the first stages of renal development; metanephros is the final stage in kidney development
- Urine Production: Kidneys start producing urine, a significant event in renal maturation, and contributing to the amniotic fluid
Kidneys Contribute to Amniotic Fluid
- Urine produced by the kidneys contributes to the composition of amniotic fluid providing a stable environment for growth and development.
- Initiation of kidney function prepares the embryo's excretory system, important for fetal development.
Intestinal Loop Retraction at Week 8
- Midgut Herniation: Prior to week 8, the midgut herniates into the umbilical cord due to limited space in the abdominal cavity. This herniated loop allows for rapid growth of the intestines in earlier stages
- Retraction of the Midgut: By week 8, the midgut herniation retracts back into the abdominal cavity
- Normal Anatomical Positioning of the Intestines: The intestines are now properly positioned within the abdomen, preparing them for further differentiation and functional maturation later.
- This retraction is crucial for proper alignment of intestines for digestive function after birth. It marks the completion of a critical stage of gastrointestinal development.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Related Documents
Description
Explore the critical changes that occur during week 8 of human embryonic development. This week signifies the end of the embryonic period, with major organ systems taking shape and the embryo transitioning to the fetal stage. Test your knowledge on tissue differentiation, organogenesis, and the growth of external features.