Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the role of the outer ear in the process of hearing?
What is the role of the outer ear in the process of hearing?
Sound collection
Which part of the ear converts amplified sound waves into electrical signals?
Which part of the ear converts amplified sound waves into electrical signals?
The inner ear
What is the function of the middle ear in the process of hearing?
What is the function of the middle ear in the process of hearing?
Amplification
What is the main role of the brain in the auditory process?
What is the main role of the brain in the auditory process?
What is the pinna in the context of the ear's structure?
What is the pinna in the context of the ear's structure?
What is the function of the Eustachian tube?
What is the function of the Eustachian tube?
What are the three sections of the cochlea?
What are the three sections of the cochlea?
What is the role of the organ of Corti?
What is the role of the organ of Corti?
What are some common causes of hearing loss?
What are some common causes of hearing loss?
What is vertigo and how does it affect the inner ear?
What is vertigo and how does it affect the inner ear?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Title: Exploring Human Anatomy: A Comprehensive Journey through the Wonders of the Ear
Introduction
Human anatomy, the study of the structure and function of the human body, is a fascinating subject. Among various intricate systems that make up the human body, the ear is a remarkable organ that captures our attention due to its critical role in our auditory experience. In this article, we'll delve into human anatomy and focus on the marvel that is the ear, exploring how it functions, its structure, and the essential elements that make it a vital component of our sensory system.
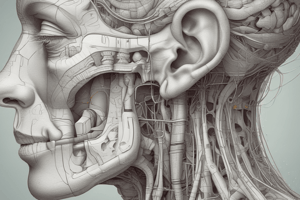
The Ear: A Key Component of Human Anatomy
The ear is the organ responsible for perceiving and interpreting sound. It is not just a simple receptor that senses sound; it is a complex system that performs a multitude of functions, including:
- Sound collection: The outer ear, which includes the pinna (the visible part of the ear) and the ear canal, collects and funnels sound waves into the ear.
- Amplification: The middle ear amplifies the sound waves, making them more powerful and suitable for the delicate inner ear.
- Conversion to electrical signals: The inner ear converts the amplified sound waves into electrical signals, which are then transmitted to the brain via the auditory nerve.
- Interpretation: The brain interprets these electrical signals, allowing us to perceive sound as a range of pitches, tones, and frequencies.
Human Anatomy of the Ear: A Step by Step Breakdown
Let's examine the different sections of the ear, their structure, and their functions in detail:
1. Outer ear:
- Pinna: The visible part of the ear that protrudes from the head.
- Ear canal: A tube that runs from the pinna to the eardrum (tympanic membrane).
2. Middle ear:
- Tympanic membrane (eardrum): A thin, cone-shaped membrane that separates the outer ear from the middle ear.
- Ossicles: Three small bones (malleus, incus, and stapes) that form a chain, allowing the eardrum to transmit sound vibrations to the inner ear.
- Eustachian tube: A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the throat, responsible for equalizing air pressure in the middle ear.
3. Inner ear:
- Cochlea: A spiral-shaped, fluid-filled structure that is responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals.
- Vestibular system: A series of interconnected structures that are responsible for maintaining balance and spatial orientation.
The Inner Workings of the Ear
Now, let's take a closer look at the inner ear, where the magic of our auditory experience takes place:
- The cochlea is divided into three sections: the basilar membrane, the organ of Corti, and the spiral ganglion.
- The basilar membrane is a flexible structure that vibrates according to the frequency of the sound waves.
- The organ of Corti is a collection of hair cells that are responsible for converting the vibrations of the basilar membrane into electrical signals. These signals are then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve.
- The spiral ganglion is a collection of nerve cells that transmit these electrical signals to the brain.
Common Ear Disorders and Conditions
Our ears can sometimes get injured or suffer from various disorders. Some of the common ear-related conditions include:
- Hearing loss: This can be caused by aging, exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or ear-related injuries.
- Ear infections: Common among children, ear infections can cause pain and hearing loss if left untreated.
- Otitis media: A type of ear infection that affects the middle ear.
- Vertigo: A condition that causes dizziness and unsteadiness, affecting the vestibular system in the inner ear.
Conclusion
As we've explored in this article, the ear is a fascinating and complex organ that plays a critical role in our sensory experience. Its intricate structure and multifunctional nature make it a central component of human anatomy. By understanding the ear and its various components, we can develop a deeper appreciation for the marvels of our body and the wonders of our auditory experience.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.