Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is an example of negative feedback in the body?
What is an example of negative feedback in the body?
- Ripening of fruit
- Regulation of blood glucose levels (correct)
- Contractions during childbirth
- Amplification of hormone secretion
Which layer of the endometrium is responsible for building up new endometrial tissue?
Which layer of the endometrium is responsible for building up new endometrial tissue?
- Cuboidal ciliated epithelium layer
- Myometrium
- Basal layer
- Functional layer (correct)
During which phase does the vaginal bleeding occur as the uterine endometrium is shed?
During which phase does the vaginal bleeding occur as the uterine endometrium is shed?
- Proliferative phase
- Menstrual phase (correct)
- Luteal phase
- Ovulation
What triggers positive feedback during childbirth?
What triggers positive feedback during childbirth?
What is the average duration for the ovulation phase in a regular menstrual cycle?
What is the average duration for the ovulation phase in a regular menstrual cycle?
Which layer of the endometrium is the uppermost layer that covers the functional layer?
Which layer of the endometrium is the uppermost layer that covers the functional layer?
What characterizes the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle?
What characterizes the proliferative phase of the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary function of positive feedback in the context of childbirth?
What is the primary function of positive feedback in the context of childbirth?
What happens to the functional layer of the endometrium if fertilization does not occur?
What happens to the functional layer of the endometrium if fertilization does not occur?
What is the primary site of fertilization in the female reproductive system?
What is the primary site of fertilization in the female reproductive system?
What is the process that occurs after fertilization that involves cell division?
What is the process that occurs after fertilization that involves cell division?
How many sperm typically penetrate the zona pellucida to achieve fertilization?
How many sperm typically penetrate the zona pellucida to achieve fertilization?
What happens to the membrane of the ovum after one sperm successfully fertilizes it?
What happens to the membrane of the ovum after one sperm successfully fertilizes it?
What is the name given to the 2nd cell stage reached after 30 hours of fertilization?
What is the name given to the 2nd cell stage reached after 30 hours of fertilization?
What is the role of the decidua basalis in early pregnancy?
What is the role of the decidua basalis in early pregnancy?
Which layer of the decidua encapsulates the surface of the trophoblast?
Which layer of the decidua encapsulates the surface of the trophoblast?
What is the primary function of hyaluronidase enzymes released by sperm?
What is the primary function of hyaluronidase enzymes released by sperm?
What term describes the subjective signs that may indicate pregnancy?
What term describes the subjective signs that may indicate pregnancy?
What refers to the portion of the decidua lining the uterine cavity outside the site of implantation?
What refers to the portion of the decidua lining the uterine cavity outside the site of implantation?
What is the length of a fetus at the end of six lunar months?
What is the length of a fetus at the end of six lunar months?
Which of the following indicates the start of fetal viability?
Which of the following indicates the start of fetal viability?
What major development occurs in the fetus at seven lunar months?
What major development occurs in the fetus at seven lunar months?
What is the weight of a fetus at the end of seven lunar months?
What is the weight of a fetus at the end of seven lunar months?
Which characteristic is associated with a full-term baby?
Which characteristic is associated with a full-term baby?
At which week does the passive transfer of antibodies from the mother to the fetus begin?
At which week does the passive transfer of antibodies from the mother to the fetus begin?
What is the period known as absolute fertility?
What is the period known as absolute fertility?
What triggers the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
What triggers the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary hormone secreted by the corpus luteum?
What is the primary hormone secreted by the corpus luteum?
During which phase does the endometrium mature in preparation for implantation?
During which phase does the endometrium mature in preparation for implantation?
What process refers to the embedding of a fertilized ovum in the uterus?
What process refers to the embedding of a fertilized ovum in the uterus?
What is the average time after fertilization that implantation occurs?
What is the average time after fertilization that implantation occurs?
What is gametosis in the context of conception?
What is gametosis in the context of conception?
What is the process of sperm formation called?
What is the process of sperm formation called?
What is the term for the expulsion of an egg from the ovary?
What is the term for the expulsion of an egg from the ovary?
What occurs during the premenstrual phase of the menstrual cycle?
What occurs during the premenstrual phase of the menstrual cycle?
What is the recommended drug of choice (DOC) for treating syphilis during pregnancy?
What is the recommended drug of choice (DOC) for treating syphilis during pregnancy?
At what point does the heart begin to beat during embryonic development?
At what point does the heart begin to beat during embryonic development?
Which of the following anomalies is characterized by the absence of the head or brain?
Which of the following anomalies is characterized by the absence of the head or brain?
What screening test should be conducted during the first prenatal visit to check for syphilis?
What screening test should be conducted during the first prenatal visit to check for syphilis?
What is a possible consequence of untreated syphilis in the fetus beyond the 18th week of pregnancy?
What is a possible consequence of untreated syphilis in the fetus beyond the 18th week of pregnancy?
What major development occurs by the end of the first lunar month (4th week)?
What major development occurs by the end of the first lunar month (4th week)?
At what age of gestation are the external genitalia distinct but not yet distinguishable by simple observation?
At what age of gestation are the external genitalia distinct but not yet distinguishable by simple observation?
What is one of the first significant physical developments observed in the fetus during the second month?
What is one of the first significant physical developments observed in the fetus during the second month?
Which treatment is recommended for women with genital lesions during pregnancy?
Which treatment is recommended for women with genital lesions during pregnancy?
At what week does the nervous system begin to appear during embryonic development?
At what week does the nervous system begin to appear during embryonic development?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Hormonal Feedback Mechanisms
- Negative feedback regulates blood glucose levels and osmoregulation.
- Positive feedback amplifies the body's response to stimuli, such as the stretching of the cervix during childbirth, leading to increased hormone secretion.
- Examples of positive feedback: uterine contractions during labor and the ripening of fruit.
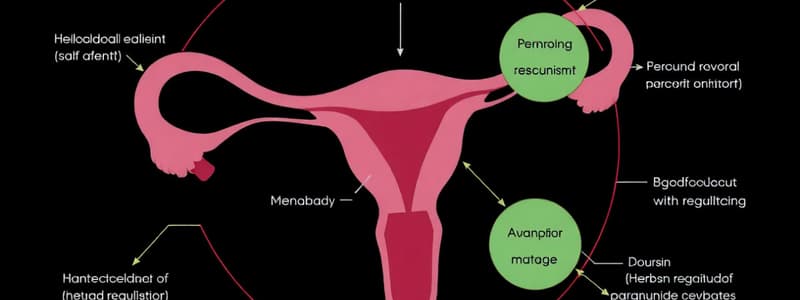
Endometrium Structure
- Composed of three layers:
- Basal layer: 1 mm thick, lowermost, above the myometrium, includes rudimentary structures for new endometrium development.
- Functional layer: 2-5 mm thick, middle layer containing tubular glands, varies under hormonal influence.
- Cuboidal ciliated epithelium: uppermost layer, covers the functional layer and lines the tubal glands.
Menstrual Cycle Phases
- Menstrual phase: lasts 3-5 days with vaginal bleeding as the endometrium sheds.
- Ovulation: release of a mature ovum from a Graafian follicle, usually occurs 13 to 15 days prior to menstruation.
- Luteal phase: 15 to 28 days, prompted by LH surge, leading to corpus luteum formation and secretion of progesterone and estrogen.
- If fertilization occurs, endometrium becomes thicker and more vascular to support implantation.
Conception Process
- Conception occurs when the fertilized ovum embeds in the uterus.
- Sequence includes: gametosis, ovulation, copulation, fertilization, development of fertilized ovum, and implantation.
- Egg expulsion from ovary signifies ovulation, followed by sperm transportation to the fallopian tube.
- Sperm encounter challenges in the vaginal acidic environment; only a few survive to fertilize the ovum.
Sperm Penetration and Fertilization
- Capacitance allows sperm to penetrate the outer barriers of the egg, with only one sperm fertilizing the ovum.
- After fertilization, the zygote undergoes cleavage, dividing into blastomeres.
- Early development includes stages of division leading to a multi-celled structure (16 to 32 cells).
Signs and Symptoms of Pregnancy
- Presumptive signs include subjective experiences, such as missed periods or nausea.
- First lunar month: heart forms and beats by the 14th day; limb buds and primary lung buds appear.
- Two lunar months: embryo begins to take human form; sex organs distinct but not identifiable.
- Six lunar months: surfactant production begins, and passive antibody transfer from mother starts.
- Ten lunar months (full-term): all newborn characteristics develop; average weight about 3200g, and length between 48-52 cm.
Key Pregnancy Milestones
- Fetal viability begins around the 24th week.
- Infants born around 28 weeks can survive with expert care, measuring 35-38 cm and weighing approximately 1,200 g.
- Meconium can be present in the rectum as early as 20 weeks.
Maternal Infections and Complications
- Syphilis, caused by Treponema pallidum, can lead to severe fetal outcomes if untreated.
- Infections may prompt recommendations for cesarean sections; acyclovir (Zovirax) is the drug of choice for genital lesions.
- Evidence suggests that timely treatment during the first trimester can prevent complications.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.