Podcast
Questions and Answers
What marks the peak of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the menstrual cycle?
What marks the peak of luteinizing hormone (LH) in the menstrual cycle?
- Follicular phase
- Luteal phase
- Menstruation
- Ovulation (correct)
FSH and LH have no role in the development of ovarian follicles.
FSH and LH have no role in the development of ovarian follicles.
False (B)
What happens to the endometrial lining during menstruation?
What happens to the endometrial lining during menstruation?
It is shed.
Match the following hormones with their roles in the menstrual cycle:
Match the following hormones with their roles in the menstrual cycle:
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the negative feedback effect that regulates GnRH, FSH, and LH levels?
Which hormone is primarily responsible for the negative feedback effect that regulates GnRH, FSH, and LH levels?
Hormonal contraceptive pills act by increasing the levels of LH and FSH.
Hormonal contraceptive pills act by increasing the levels of LH and FSH.
What is the primary role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
What is the primary role of progesterone in the menstrual cycle?
What triggers the LH surge leading to ovulation?
What triggers the LH surge leading to ovulation?
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the __________.
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle transforms into the __________.
Match the hormone with its function in the menstrual cycle:
Match the hormone with its function in the menstrual cycle:
What happens to the corpus luteum if fertilization does not occur?
What happens to the corpus luteum if fertilization does not occur?
Estrogen only has positive feedback effects on the menstrual cycle.
Estrogen only has positive feedback effects on the menstrual cycle.
Study Notes
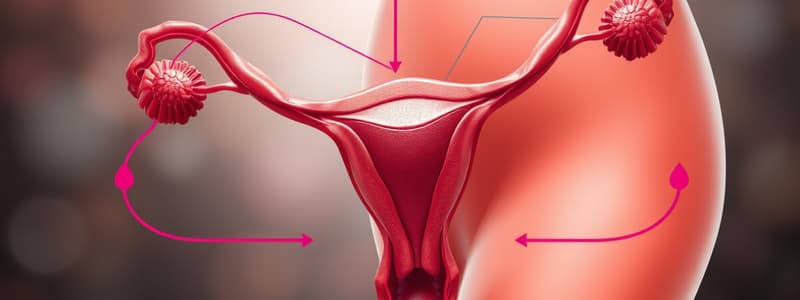
Menstrual Cycle Overview
- The menstrual cycle spans from menarche to menopause, marked by cyclic variations in estrogen and progesterone levels.
- Comprised of four key phases: follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation.
Hormonal Regulation
- Blood concentrations of FSH, LH, estrogen, and progesterone fluctuate during the cycle, with specific peaks critical for the MCAT.
- FSH is essential for ovum maturation, while the LH peak on day 14 leads to ovulation and oocyte release.
Follicular Phase
- Initiated by menstruation, whereby the previous cycle's uterine lining is expelled.
- Increased GnRH from the hypothalamus promotes FSH and LH release, which stimulate multiple ovarian follicles.
- Follicles produce estrogen, which exerts negative feedback on GnRH, LH, and FSH levels, stabilizing their concentrations.
- Estrogen plays a role in the regeneration of the endometrial lining through vascularization and glandularization.
Real World Implications of Hormones
- Oral contraceptives contain estrogen and progesterone, preventing pregnancy by inhibiting LH and FSH via negative feedback and suppressing ovulation.
- Placebo pills lead to withdrawal menstruation due to decreased estrogen and progesterone, despite absence of ovulated egg.
Ovulation Process
- Estrogen's dual feedback effects culminate in a positive feedback loop late in the follicular phase, leading to a spike in GnRH, LH, and FSH.
- The LH surge triggers ovulation, releasing the ovum into the peritoneal cavity.
Luteal Phase
- Post-ovulation, LH promotes the transformation of the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone.
- Progesterone maintains the uterine lining for potential implantation; estrogen levels remain elevated during this phase.
- High progesterone levels provide negative feedback on GnRH, FSH, and LH, preventing further ovulation.
Menstruation
- If fertilization does not occur, the corpus luteum degenerates, leading to decreased progesterone and estrogen levels.
- The drop in these hormone levels ends the inhibition on GnRH, marking the start of a new cycle as the uterine lining is shed.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.
Description
This quiz explores the hormonal dynamics involved in the menstrual cycle, particularly focusing on the roles of estrogen and progesterone. It examines how these hormones influence ovulation and the physiological processes behind withdrawal menstruation. Test your knowledge of reproductive biology and hormone feedback mechanisms.