Podcast
Questions and Answers
Connective tissues form the majority of the body's composition.
Connective tissues form the majority of the body's composition.
True (A)
In histological slides, connective tissues are typically found beneath the epithelium.
In histological slides, connective tissues are typically found beneath the epithelium.
False (B)
The extracellular matrix of connective tissues contains only cells.
The extracellular matrix of connective tissues contains only cells.
False (B)
Tendons contain loosely arranged fibers and a large amount of ground substance in their extracellular matrix.
Tendons contain loosely arranged fibers and a large amount of ground substance in their extracellular matrix.
Connective tissues do not play a role in supporting organs.
Connective tissues do not play a role in supporting organs.
Collagen fibers found in tendons provide resistance to longitudinal stretching in all directions.
Collagen fibers found in tendons provide resistance to longitudinal stretching in all directions.
Elastic fibers are made of elastin and fibrinogen proteins.
Elastic fibers are made of elastin and fibrinogen proteins.
Ground substance in connective tissues determines the color of the tissue.
Ground substance in connective tissues determines the color of the tissue.
Reticular fibers form a net-like structure called the reticulum that wraps around organs to protect their integrity.
Reticular fibers form a net-like structure called the reticulum that wraps around organs to protect their integrity.
Chondrocytes are undifferentiated cells that build new cartilage within developing fetuses.
Chondrocytes are undifferentiated cells that build new cartilage within developing fetuses.
Flashcards
Connective Tissue
Connective Tissue
A type of tissue that provides support, structure, and function to organs and tissues. They also fill the spaces between other tissues.
Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular Matrix
The non-cellular component of connective tissue, composed of ground substance and fibers.
Ground Substance
Ground Substance
The gel-like material in the extracellular matrix, containing glycoproteins and other molecules.
Collagen Fibers
Collagen Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Elastic Fibers
Elastic Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Reticular Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fibroblasts
Fibroblasts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Loose Connective Tissue
Loose Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dense Connective Tissue
Dense Connective Tissue
Signup and view all the flashcards
Specialized Connective Tissues
Specialized Connective Tissues
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
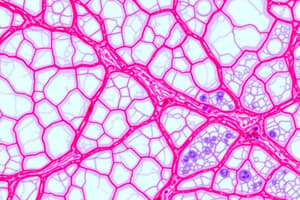
Connective Tissues
- Connective tissues make up a large part of the body and provide support, structure, and function to organs and tissues.
- Connective tissues fill the spaces between other tissues and form organs.
Characteristics of Connective Tissues
- Connective tissues have relatively few cells that are not necessarily connected.
- Connective tissues are immersed in a considerable quantity of extracellular matrix.
- Extracellular matrix is a composite of "filler material" (ground substance) and varying quantities of fibers.
Functions of Connective Tissues
- Form the bulk of organs.
- Fill the spaces between other tissues and bind organs together.
- Support organs by forming fascia and sheaths, ligaments, and tendons.
- Form support structures in the joints, such as joint capsules, synovial membranes, and tendon sheaths.
- Store calcium, fat, immune cells, water, and many bodily chemicals, such as growth factors and hormones.
- Insulate (mostly due to stored fat, but also by forming the dermis of the skin).
- Transport substances through the body via blood.
Types of Connective Tissues
- Ordinary connective tissues:
- Loose connective tissue (areolar, reticular, adipose)
- Dense connective tissue (regular)
- Specialized connective tissues:
- Cartilage (hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic)
- Bone (compact, irregular, spongy)
- Blood and blood-forming tissues
Ground Substance
- A gel-like material that fills the spaces between connective tissue cells.
- A mixture of glycoproteins, glycoaminoglycans (such as hyaluronic acid), and proteoglycans.
- Can be very fluid (e.g., vitreous humor in the posterior cavity of the eye) or calcified (e.g., bone).
- Determines the permeability of a connective tissue and its ability to store water.
Fibers in Connective Tissues
- Three types of fibers:
- Collagen fibers (found in tendons, provide tensile strength and resistance to longitudinal stretching)
- Elastic fibers (stretchy in all directions, help tissues return to their previous shapes after extension)
- Reticular fibers (very fine collagen fibers, form a net-like structure, wrap around organs and protect their integrity)
Production and Maintenance of Connective Tissues
- Formed by undifferentiated cells (whose names end in "-blast") that create new ground substance and connective tissue fibers.
- When these "-blast" cells become surrounded by the ground substance they are producing, they are considered mature and are referred to by names that end in "-cyte".
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.