Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is adipose tissue mainly composed of?
What is adipose tissue mainly composed of?
- Closely packed cells that store fat (correct)
- Bone cells
- Blood cells
- Elastic fibers
What type of connective tissue fills spaces between organs?
What type of connective tissue fills spaces between organs?
- Reticular Connective Tissue
- Areolar (loose) Connective Tissue (correct)
- Dense Regular Connective Tissue
- Adipose Tissue
What do reticulocytes produce?
What do reticulocytes produce?
Reticular fibers
What does dense regular connective tissue provide?
What does dense regular connective tissue provide?
Dense irregular connective tissue has a parallel arrangement of fibers.
Dense irregular connective tissue has a parallel arrangement of fibers.
What type of tissue provides flexibility to the walls of blood vessels?
What type of tissue provides flexibility to the walls of blood vessels?
Hyaline cartilage covers the ends of long bones to reduce __________.
Hyaline cartilage covers the ends of long bones to reduce __________.
What is the function of the collagen fibers in fibrocartilage?
What is the function of the collagen fibers in fibrocartilage?
Elastic cartilage provides flexibility to which structures?
Elastic cartilage provides flexibility to which structures?
What type of unit composes compact bone?
What type of unit composes compact bone?
What types of cells are predominantly found in blood?
What types of cells are predominantly found in blood?
Skeletal muscle fibers have nuclei located at the center of the fibers.
Skeletal muscle fibers have nuclei located at the center of the fibers.
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Adipose Tissue
- Composed of closely packed cells that store fat
- Slides show empty white spaces where fat was dissolved, known as "ghost cells"
Areolar (Loose) Connective Tissue
- Contains loosely organized thick collagen and thin elastic fibers that can stretch without damage
- Fills spaces between organs and separates skin from deeper structures
- Fibroblasts produce fibers; mast cells monitor for infections
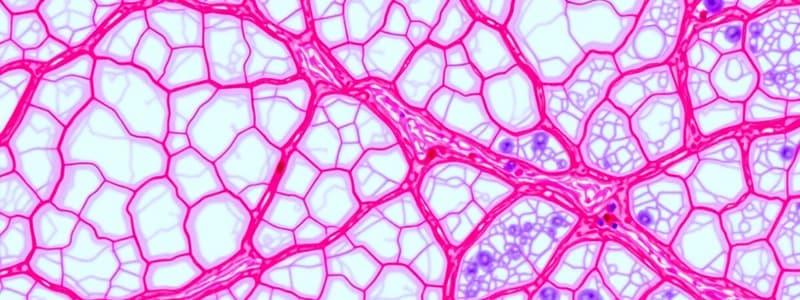
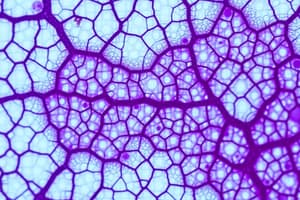
Reticular Connective Tissue
- Made up of reticulocytes producing short branched reticular fibers
- Forms a supportive framework for soft organs like liver, spleen, and lymph nodes
Dense (Fibrous) Regular Connective Tissue
- Characterized by thick parallel collagen fibers, providing strength and flexibility to tendons and ligaments
- Fibroblast nuclei are visible between the collagen fibers
Dense (Fibrous) Irregular Connective Tissue
- Found in the dermis layer of the skin, below the epidermis
- Collagen bundles are arranged in various directions, enhancing structural resilience
- Scattered fibroblast nuclei appear rounded rather than flattened
Elastic Connective Tissue
- Composed of fibroblasts producing wavy elastic fibers, enabling flexibility in stretchy structures
- Fibers are often parallel and exhibit a wrinkled appearance when relaxed
Hyaline Cartilage
- Smooth and slippery tissue that covers ends of long bones to minimize friction
- Chondrocytes are spaced apart, embedded in a colored matrix; each resides in a lacuna
- Nuclei of chondrocytes are clearly visible
Fibrocartilage
- Shown in intervertebral disks, aiding in shock absorption
- Collagen fibers form patterns that can be observed under different magnifications
Elastic Cartilage
- Contains closely packed chondrocytes surrounded by a network of short, wavy elastic fibers
- Provides stretch and flexibility, essential for structures like the outer ear and larynx
Bone
- Compact bone forms the outer layer of most bones, structured in units called osteons (bulls-eye appearance)
- Each osteon has a central canal surrounded by concentric lamellae; lacunae house osteocytes
- Canaliculi connect osteocytes, facilitating communication
Blood
- Composed of various cells suspended in a liquid matrix known as plasma
- Predominantly contains pinkish red blood cells which lack nuclei
- White blood cells possess nuclei of varying shapes; platelets play a role in clotting
Skeletal Muscle Tissue
- Features cylindrical parallel fibers made from fused cells during fetal development
- Muscle fibers are multinucleated, with nuclei positioned at the edges
- Alternating light and dark striations provide a distinct striped appearance
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.