Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the name of the valve located between the right atrium and the right ventricle?
What is the name of the valve located between the right atrium and the right ventricle?
- Pulmonary valve
- Mitral valve
- Aortic valve
- Tricuspid valve (correct)
Which of the following valves is also known as the left atrioventricular valve?
Which of the following valves is also known as the left atrioventricular valve?
- Pulmonary valve
- Tricuspid valve
- Aortic valve
- Mitral valve (correct)
What is a common characteristic shared by all the valves mentioned in the text?
What is a common characteristic shared by all the valves mentioned in the text?
- They are all semi-lunar valves.
- They are all located on the right side of the heart.
- They all have two leaflets.
- They all have three leaflets.
- They have very little resistance to flow. (correct)
What is the name of the valve that connects the left ventricle to the aorta?
What is the name of the valve that connects the left ventricle to the aorta?
What is the alternative name for the mitral valve?
What is the alternative name for the mitral valve?
What is the name of the valve that connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery?
What is the name of the valve that connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery?
Which of the following valves is NOT a semi-lunar valve?
Which of the following valves is NOT a semi-lunar valve?
Why is the mitral valve also known as the bicuspid valve?
Why is the mitral valve also known as the bicuspid valve?
What is the primary function of the atrial kick during the cardiac cycle?
What is the primary function of the atrial kick during the cardiac cycle?
During diastole, which chamber experiences a higher pressure when the mitral valve opens?
During diastole, which chamber experiences a higher pressure when the mitral valve opens?
What is indicated by the presence of the P wave on the ECG during the cardiac cycle?
What is indicated by the presence of the P wave on the ECG during the cardiac cycle?
What happens to aortic pressure during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle?
What happens to aortic pressure during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle?
At which point in the cardiac cycle is the left ventricle nearly full of blood?
At which point in the cardiac cycle is the left ventricle nearly full of blood?
What happens to the left ventricular volume during the ejection phase?
What happens to the left ventricular volume during the ejection phase?
What phase of the cardiac cycle is characterized by contraction of the heart muscle?
What phase of the cardiac cycle is characterized by contraction of the heart muscle?
What triggers the opening of the aortic valve?
What triggers the opening of the aortic valve?
Why does blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle when the mitral valve opens?
Why does blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle when the mitral valve opens?
Which of the following accurately describes the phases of the cardiac cycle?
Which of the following accurately describes the phases of the cardiac cycle?
During isovolumic relaxation, which statement is true regarding the pressure in the left ventricle?
During isovolumic relaxation, which statement is true regarding the pressure in the left ventricle?
What is the stroke volume defined as?
What is the stroke volume defined as?
At what point does the left ventricular pressure reach its peak systolic maximum?
At what point does the left ventricular pressure reach its peak systolic maximum?
What is the typical diastolic blood pressure in the aorta?
What is the typical diastolic blood pressure in the aorta?
When does the left ventricle empty completely?
When does the left ventricle empty completely?
During the cardiac cycle, what measurement can be obtained by inserting a catheter into the left ventricle?
During the cardiac cycle, what measurement can be obtained by inserting a catheter into the left ventricle?
What determines the shape of the arterial pulse at different points in the vascular tree?
What determines the shape of the arterial pulse at different points in the vascular tree?
What is the term for the 'kick' that occurs when the forward pressure wave meets the reflected wave in the aorta?
What is the term for the 'kick' that occurs when the forward pressure wave meets the reflected wave in the aorta?
What is the cause of the two primary heart sounds, S1 and S2?
What is the cause of the two primary heart sounds, S1 and S2?
What is the term for the pattern of heart sounds known as 'Lup' 'Dub'?
What is the term for the pattern of heart sounds known as 'Lup' 'Dub'?
What is the name of the extra heart sounds that are not usually heard?
What is the name of the extra heart sounds that are not usually heard?
What is the term for the phenomenon where reflected waves can interfere with the forward compression wave, altering the pulse wave?
What is the term for the phenomenon where reflected waves can interfere with the forward compression wave, altering the pulse wave?
What is the term for the pattern of heart sounds shown in the slide?
What is the term for the pattern of heart sounds shown in the slide?
What is the term for the decrease in pulse pressure caused by out-of-phase reflected waves?
What is the term for the decrease in pulse pressure caused by out-of-phase reflected waves?
What is considered a normal ejection fraction range?
What is considered a normal ejection fraction range?
What happens when a patient has an ejection fraction of 35%?
What happens when a patient has an ejection fraction of 35%?
Which function measures how well the heart relaxes between beats?
Which function measures how well the heart relaxes between beats?
Which of the following describes ventricular compliance?
Which of the following describes ventricular compliance?
How much pressure does a 30 cm column of blood exert, relevant to the height of the brain above the heart?
How much pressure does a 30 cm column of blood exert, relevant to the height of the brain above the heart?
What affects blood pressure in the body due to gravity?
What affects blood pressure in the body due to gravity?
What does stroke work measure?
What does stroke work measure?
What is the approximate height of the brain above the heart that relates to hydrostatic pressure?
What is the approximate height of the brain above the heart that relates to hydrostatic pressure?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
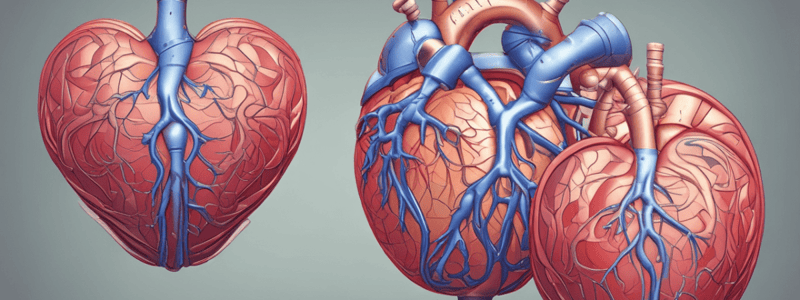
Heart Valves and Anatomy
- The heart has four primary valves: the mitral valve, tricuspid valve, aortic valve, and pulmonary valve.
- The mitral valve (bicuspid or left atrioventricular valve) separates the left atrium from the left ventricle and has two leaflets.
- The tricuspid valve separates the right atrium from the right ventricle, characterized by three leaflets.
- The aortic valve allows blood to flow from the left ventricle into the aorta, while the pulmonary valve directs blood from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery.
- Healthy valves offer minimal resistance to blood flow, promoting efficient ventricular filling during atrial contraction.
Cardiac Cycle Phases
- The cardiac cycle consists of two main phases: Diastole (relaxation) and Systole (contraction).
- During Diastole, aortic pressure decreases, and left atrial pressure temporarily exceeds left ventricular pressure, causing the mitral valve to open.
- This leads to an increase in left ventricular volume, peaking around 120 ml.
- At Point #1 in the ECG, the P wave indicates left atrial contraction, known as the atrial kick.
- Once left ventricular pressure surpasses 80 mmHg, the aortic valve opens and blood is ejected into systemic circulation, reducing ventricular volume to about 50 ml.
Pressure-Volume Loop
- The pressure-volume loop depicts the relationship between pressure and volume during the cardiac cycle.
- Systolic pressure in the aorta reaches approximately 120 mmHg during maximum ventricular contraction.
- The aortic valve closes when left ventricular pressure falls below aortic pressure, leading to isovolumic relaxation where pressure drops without a change in volume.
Measurement of Cardiac Function
- Stroke volume is calculated as the difference between end-diastolic volume and end-systolic volume.
- An ejection fraction of 55-75% is considered normal, while 35% indicates severe heart failure.
- Various metrics, including stroke work and contractility, can be measured to assess cardiac function.
- Compliance and stiffness of the ventricle are important in evaluating heart failure conditions.
Arterial and Venous Pulses
- Hydrostatic pressure changes with height; blood exerts 23.4 mmHg of pressure for every 30 cm, correlating with the height of the brain above the heart.
- The shape of arterial pressure pulses varies due to the compliance of the vascular system and reflected waves creating augmentation or damping effects.
- Pulse wave morphology differs across blood vessels, influenced by interference and resonance.
Heart Sounds
- Primary heart sounds, S1 and S2, indicate valve closures: S1 corresponds to atrioventricular valve closure at the onset of ventricular systole, while S2 marks semilunar valve closure.
- Additional heart sounds (S3 and S4) may arise but are typically not audible in a healthy heart.
- The "gallop rhythm" is characterized by unusual heart sounds, which may signal specific cardiac conditions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.