Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which artery supplies the anterior two-thirds of the interventricular septum?
Which artery supplies the anterior two-thirds of the interventricular septum?
- Circumflex Branch
- Left Anterior Descending (LAD) (correct)
- Small Cardiac Vein
- Right Coronary Artery
What is the primary function of the coronary sinus?
What is the primary function of the coronary sinus?
- To connect the left and right atria
- To drain venous blood from the heart muscle (correct)
- To distribute blood to the coronary arteries
- To supply oxygenated blood to the heart
Which branch of the left coronary artery supplies the left atrium and ventricle?
Which branch of the left coronary artery supplies the left atrium and ventricle?
- Middle Cardiac Vein
- Circumflex Branch (correct)
- Right Marginal Branch
- Great Cardiac Vein
What vein ascends along the anterior interventricular groove?
What vein ascends along the anterior interventricular groove?
Which coronary artery arises from the aortic sinus?
Which coronary artery arises from the aortic sinus?
Which of the following structures is NOT involved in the venous drainage of the heart?
Which of the following structures is NOT involved in the venous drainage of the heart?
Where does the coronary sinus drain?
Where does the coronary sinus drain?
Which cardiac veins are responsible for draining the region of the heart supplied by the left coronary artery?
Which cardiac veins are responsible for draining the region of the heart supplied by the left coronary artery?
Which chamber of the heart primarily forms the anterior surface?
Which chamber of the heart primarily forms the anterior surface?
Which vessel drains well-oxygenated blood into the left atrium?
Which vessel drains well-oxygenated blood into the left atrium?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the atrioventricular valves open?
During which phase of the cardiac cycle do the atrioventricular valves open?
Where is the apex of the heart located relative to the mid-sternal line?
Where is the apex of the heart located relative to the mid-sternal line?
What forms the base of the heart?
What forms the base of the heart?
Which valves remain closed at the beginning of the systole phase?
Which valves remain closed at the beginning of the systole phase?
Which structure is responsible for the intrinsic conducting system of the heart?
Which structure is responsible for the intrinsic conducting system of the heart?
Which aspect of the heart primarily supports the diaphragm?
Which aspect of the heart primarily supports the diaphragm?
Which of the following structures has a double helical orientation in the myocardium of the heart?
Which of the following structures has a double helical orientation in the myocardium of the heart?
Which of the following would be least likely to be auscultated at the left fifth intercostal space?
Which of the following would be least likely to be auscultated at the left fifth intercostal space?
Which artery primarily supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node in the heart?
Which artery primarily supplies the sinoatrial (SA) node in the heart?
What structure in the heart prevents the prolapse of the tricuspid valve during ventricular contraction?
What structure in the heart prevents the prolapse of the tricuspid valve during ventricular contraction?
Where does the left coronary artery arise from?
Where does the left coronary artery arise from?
What is the role of the fossa ovalis within the heart?
What is the role of the fossa ovalis within the heart?
Which structure separates the smooth and rough portions of the right atrium?
Which structure separates the smooth and rough portions of the right atrium?
Which valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle?
Which valve is located between the left atrium and the left ventricle?
Which cardiac structure is primarily involved in the conduction pathway and supplies the right ventricle?
Which cardiac structure is primarily involved in the conduction pathway and supplies the right ventricle?
What is the primary drainage route for the cardiac veins?
What is the primary drainage route for the cardiac veins?
Which of the following valves is a semilunar valve?
Which of the following valves is a semilunar valve?
What role do the papillary muscles play during diastole?
What role do the papillary muscles play during diastole?
What is the primary function of the pulmonary valve?
What is the primary function of the pulmonary valve?
Which part of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?
Which part of the heart has the thickest muscular wall?
Which auscultation site corresponds to the location of the left atrioventricular valve?
Which auscultation site corresponds to the location of the left atrioventricular valve?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Heart Anatomy
- The coronary sinus separates the atria from the ventricles
- The right atrium receives venous blood from the superior vena cava (SVC) and inferior vena cava (IVC)
- The right atrium has a right auricle, a muscular pouch that:
- Is an extension of the right atrium
- Overlies the ascending aorta
- Releases atrial natriuretic factor
- The interior of the right atrium is divided into:
- Sinus venarum: smooth posterior portion where the SVC and IVC open
- Pectinate muscle: rough anterior portion
- Right atrioventricular (AV) orifice
- The smooth and rough portions of the right atrium are separated by the crista terminalis
- The right atrium also contains the opening for the coronary sinus and fossa ovalis
Ligamentum Arteriosum and Fossa Ovalis
- Ligamentum arteriosum is a remnant of the ductus arteriosus
- Fossa ovalis is a remnant of the foramen ovale
Right Ventricle
- The right ventricle interior is composed of muscular elevations called trabeculae carneae
- The superior portion of the right ventricle tapers into an arterial cone called the conus arteriosus which leads to the pulmonary trunk
- The right ventricle also contains a supraventricular ridge
Right Atrioventricular Valve (Tricuspid)
- The tricuspid valve guards the right AV orifice
- The base of the cusp of the tricuspid valve attaches to the fibrous ring
- Papillary muscles with their chordae tendineae attach the free edge of the cusp, preventing prolapse of the cusp into the ventricle
Interventricular Septum (IVS)
- The IVS is composed of a membranous portion, fibrous portion, and a muscular portion
Septomarginal Trabecula
- The septomarginal trabecula (moderator band) is a muscular bundle that runs from the inferior part of the IVS to the base of the anterior papillary muscle
- The right AV bundle branch is within the septomarginal trabecula
Pulmonary Valve
- The pulmonary valve is a semilunar valve with three cusps
Left Atrium
- The left atrium receives oxygenated blood from four pulmonary veins:
- Left superior and inferior pulmonary veins
- Right superior and inferior pulmonary veins
- The Left Auricle overlaps the root of the pulmonary trunk
- The left auricle contains pectinate muscle
- The left atrium contains an AV orifice
Left Ventricle
- The left ventricle has a thick muscular wall
- The left ventricle contains trabeculae carneae and a double-leaflet mitral valve
- The mitral valve guards the AV orifice
- The left ventricle also contains an aortic orifice
Left Atrioventricular Valve (Bicuspid, Mitral)
- The mitral valve has anterior and posterior cusps, and anterior and posterior papillary muscles with chordae tendineae
Mitral Valve Function
- During diastole, the left ventricle relaxes and the papillary muscles relax, allowing the mitral valve to open
- During systole, the left ventricle contracts and the papillary muscles contract, resisting the pressure developed in the left ventricle and preventing the cusp from prolapsing into the left atrium
Aortic Valve
- The aortic valve is a semilunar valve with three cusps
Semilunar Valves
- The pulmonary and aortic valves are semilunar valves
- During diastole, the three concaved cusps catch reverse blood flow
- During systole, the cusps are forced open
- Aortic and pulmonary sinuses are dilations in the wall of the vessel at the attachment of the cusp
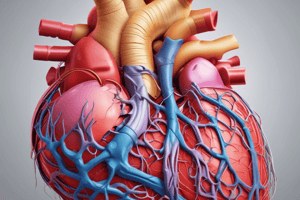
Coronary Arteries
- The coronary arteries are the first branches off the aorta
- There are two main coronary arteries:
- Right coronary artery:
- Arises from the aortic sinus
- Passes between the pulmonary trunk and right auricle
- Gives off the following branches:
- Sinoatrial branch: supplies the SA node in 60% of the population
- Right marginal branch: supplies the right atrium and ventricle
- Posterior interventricular branch:
- Descends in the posterior interventricular groove
- Supplies the right ventricle and part of the left ventricle
- Supplies the posterior third of the interventricular septum
- Supplies the AV node in 80% of the population
- Left ventricular branch: terminal branch
- Left coronary artery:
- Arises from the aortic sinus
- Passes between the pulmonary trunk and left auricle
- Divides into two branches:
- Anterior interventricular branch:
- Runs in the anterior IV groove
- Gives off a lateral (diagonal) branch
- Supplies adjacent parts of both ventricles
- Supplies the anterior two-thirds of the interventricular septum (including the AV bundle)
- Circumflex branch:
- Runs in the coronary groove to the posterior
- Gives off a left marginal branch which supplies the left atrium and ventricle
- Terminates in the coronary groove on the posterior of the heart
- Anterior interventricular branch:
- Right coronary artery:
Venous Drainage of the Heart
- Most cardiac veins empty into the coronary sinus
- The coronary sinus runs in the coronary groove
- The coronary sinus drains into the right atrium
- The coronary sinus receives:
- Great cardiac vein: ascends in the anterior IVG, runs in the coronary groove, drains the area supplied by the LCA
- Middle cardiac vein: ascends in the posterior IVG
- Small cardiac vein: ascends on the right margin
Cardiac Cycle
- The cardiac cycle is divided into diastole and systole
- Diastole:
- Starts with the closure of the pulmonary and aortic valves
- Opening of the atrioventricular valves
- Atrial contraction
- Ventricular filling
- Systole:
- Starts with the closure of the atrioventricular valves
- Opening of the aortic and pulmonary valves
- Ventricular contraction
Myocardial Orientation
- The myocardium of the heart has a double helical orientation
- When the ventricles contract, they wring themselves out instead of just collapsing inward
Heart Structure and Location
- The heart is a hollow muscular organ composed of four chambers:
- Right atrium
- Right ventricle
- Left atrium
- Left ventricle
- The heart and pericardium are situated obliquely:
- 2/3 left of the mid-sternal line
- 1/3 right of the mid-sternal line
Heart Surfaces
- Surfaces of the human heart:
- Anterior (sternocostal) surface: formed mainly by the right ventricle
- Right pulmonary surface: formed mainly by the right atrium
- Left pulmonary surface: formed mainly by the left ventricle
- Inferior (diaphragmatic) surface: formed mainly by the left ventricle
Heart Apex
- The apex of the heart is the inferior lateral part of the left ventricle
- The apex of the heart lies posterior to the 5th intercostal space, 9cm left of the mid-sternal line
Heart Base
- The base of the heart is the posterior aspect of the heart
- Formed by the left atrium and part of the right atrium
- Extends from the pulmonary trunk superiorly to the coronary groove inferiorly
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.