Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which of the following muscle actions contributes to mouth opening?
Which of the following muscle actions contributes to mouth opening?
- External pterygoid (correct)
- Internal pterygoid
- Masseter
- Temporalis (anterior fibers)
A patient presents with limited mouth opening and pain, but no swelling, and deviation to the contralateral side during mouth opening. Which condition is most likely?
A patient presents with limited mouth opening and pain, but no swelling, and deviation to the contralateral side during mouth opening. Which condition is most likely?
- TMJ synovitis
- TMJ capsulitis (correct)
- TMJ hypermobility
- TMJ disc displacement
What is the primary movement occurring in the superior joint of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
What is the primary movement occurring in the superior joint of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)?
- Hinge movement
- Compression
- Rotation
- Translation (correct)
Which of the following best describes the 'open packed position' of the TMJ?
Which of the following best describes the 'open packed position' of the TMJ?
A patient reports a clicking sound when closing their mouth. Based on the text, which TMJ condition is most likely indicated by this symptom?
A patient reports a clicking sound when closing their mouth. Based on the text, which TMJ condition is most likely indicated by this symptom?
Which layer of the scalp contains valveless emissary veins, making it a potential route for infection to spread intracranially?
Which layer of the scalp contains valveless emissary veins, making it a potential route for infection to spread intracranially?
The Galea aponeurotica connects which two muscles of the scalp?
The Galea aponeurotica connects which two muscles of the scalp?
What type of joint is described as a 'Synarthrodial joint'?
What type of joint is described as a 'Synarthrodial joint'?
At what age does the anterior fontanelle typically close in infants?
At what age does the anterior fontanelle typically close in infants?
Which of the following skull bones is a single (unpaired) bone?
Which of the following skull bones is a single (unpaired) bone?
The squamosal suture connects which two bones of the skull?
The squamosal suture connects which two bones of the skull?
What is another name for the periosteum, the innermost layer of the scalp?
What is another name for the periosteum, the innermost layer of the scalp?
At which anatomical point do the coronal and sagittal sutures intersect?
At which anatomical point do the coronal and sagittal sutures intersect?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for adducting the eyeball?
Which of the following muscles is responsible for adducting the eyeball?
Which of the following describes the bilateral action of the Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle?
Which of the following describes the bilateral action of the Sternocleidomastoid (SCM) muscle?
The submandibular triangle is bordered by which of the following structures?
The submandibular triangle is bordered by which of the following structures?
The digastric muscle is innervated by which of the following cranial nerves?
The digastric muscle is innervated by which of the following cranial nerves?
What is the primary function of the suprahyoid muscles as a group?
What is the primary function of the suprahyoid muscles as a group?
Which of the following muscles listed is NOT an infrahyoid muscle?
Which of the following muscles listed is NOT an infrahyoid muscle?
What two muscles form the borders of the Occipital triangle?
What two muscles form the borders of the Occipital triangle?
What bony landmark does the stylohyoid ligament connect to the hyoid bone?
What bony landmark does the stylohyoid ligament connect to the hyoid bone?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for depressing the angle of the mouth, often associated with expressions of displeasure?
Which muscle is primarily responsible for depressing the angle of the mouth, often associated with expressions of displeasure?
A patient exhibits difficulty looking upwards and inwards with their right eye. Which extraocular muscle is MOST likely affected?
A patient exhibits difficulty looking upwards and inwards with their right eye. Which extraocular muscle is MOST likely affected?
Damage to which cranial nerve would MOST directly impair the ability to close the eyelids?
Damage to which cranial nerve would MOST directly impair the ability to close the eyelids?
A patient presents with ptosis (drooping eyelid) following damage to the Oculomotor nerve (CN III). What percentage of eye opening function has been lost, approximately?
A patient presents with ptosis (drooping eyelid) following damage to the Oculomotor nerve (CN III). What percentage of eye opening function has been lost, approximately?
After a traumatic injury, a patient is diagnosed with a Jefferson fracture. Which cervical vertebra is affected by this type of fracture?
After a traumatic injury, a patient is diagnosed with a Jefferson fracture. Which cervical vertebra is affected by this type of fracture?
Which feature is unique to cervical vertebrae, distinguishing them from thoracic or lumbar vertebrae?
Which feature is unique to cervical vertebrae, distinguishing them from thoracic or lumbar vertebrae?
Vertical diplopia (double vision) is MOST likely associated with dysfunction of which extraocular muscle?
Vertical diplopia (double vision) is MOST likely associated with dysfunction of which extraocular muscle?
What is the main function of the levator labii superioris muscle?
What is the main function of the levator labii superioris muscle?
Damage to the pterion is extremely dangerous because of its proximity to which major vessel?
Damage to the pterion is extremely dangerous because of its proximity to which major vessel?
Which facial muscle is primarily responsible for the physical act of smiling?
Which facial muscle is primarily responsible for the physical act of smiling?
If a neurologist elicits a positive glabellar tap reflex on a patient, what might this indicate?
If a neurologist elicits a positive glabellar tap reflex on a patient, what might this indicate?
A stroke patient struggles to wrinkle their forehead to show surprise. Which muscle is likely affected?
A stroke patient struggles to wrinkle their forehead to show surprise. Which muscle is likely affected?
Which of the following best describes the location of the nasion?
Which of the following best describes the location of the nasion?
In which facial expression would the corrugator supercilii most likely be actively involved?
In which facial expression would the corrugator supercilii most likely be actively involved?
A musician who plays the trumpet relies heavily on a specific facial muscle. Which of the following is most likely the muscle they utilize the most?
A musician who plays the trumpet relies heavily on a specific facial muscle. Which of the following is most likely the muscle they utilize the most?
What is a key difference between the risorius and zygomaticus major muscles?
What is a key difference between the risorius and zygomaticus major muscles?
What is the nasion?
What is the nasion?
What is the anatomical significance of the inion?
What is the anatomical significance of the inion?
What is the primary muscle responsible for smiling?
What is the primary muscle responsible for smiling?
What is the primary function of the risorius muscle?
What is the primary function of the risorius muscle?
What is the primary action of the Levator Palpebrae Superioris muscle?
What is the primary action of the Levator Palpebrae Superioris muscle?
What is the primary function of Mueller's muscle?
What is the primary function of Mueller's muscle?
What condition is associated with the weakness of cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve)?
What condition is associated with the weakness of cranial nerve VI (abducens nerve)?
What is the primary action of the superior rectus muscle in the eye?
What is the primary action of the superior rectus muscle in the eye?
What is the primary function of the lateral rectus muscle?
What is the primary function of the lateral rectus muscle?
What is the primary function of the medial rectus muscle?
What is the primary function of the medial rectus muscle?
Which of the following structures is located in the Submandibular/Digastric?
Which of the following structures is located in the Submandibular/Digastric?
Which structures are referred to as supraclavicular or jugular?
Which structures are referred to as supraclavicular or jugular?
Flashcards
Nasion
Nasion
The bony depression between the eyes formed by frontal and nasal bones.
Glabella
Glabella
The area of skin between the eyebrows and above the nose.
Nasolabial Folds
Nasolabial Folds
Creases extending from the sides of the nose to the corners of the mouth, known as smile lines.
Philtrum
Philtrum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Pterion
Pterion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygomaticus Major
Zygomaticus Major
Signup and view all the flashcards
Zygomaticus Minor
Zygomaticus Minor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orbicularis Oris
Orbicularis Oris
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Joint Type
TMJ Joint Type
Signup and view all the flashcards
Open Packed Position
Open Packed Position
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Hypomobility
TMJ Hypomobility
Signup and view all the flashcards
TMJ Disc Displacement
TMJ Disc Displacement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Muscles of Mastication
Muscles of Mastication
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levator anguli oris
Levator anguli oris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mentalis
Mentalis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Platysma
Platysma
Signup and view all the flashcards
Levator palpebrae superioris
Levator palpebrae superioris
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mueller's muscle
Mueller's muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Orbicularis oculi
Orbicularis oculi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior oblique muscle
Superior oblique muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior oblique muscle
Inferior oblique muscle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Superior Rectus
Superior Rectus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Inferior Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Lateral Rectus
Lateral Rectus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Medial Rectus
Medial Rectus
Signup and view all the flashcards
SCM (Sternocleidomastoid)
SCM (Sternocleidomastoid)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Suprahyoid Muscles
Suprahyoid Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Infrahyoid Muscles
Infrahyoid Muscles
Signup and view all the flashcards
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Maxillae
Maxillae
Signup and view all the flashcards
Layers of the scalp
Layers of the scalp
Signup and view all the flashcards
Aponeurosis
Aponeurosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Periosteum
Periosteum
Signup and view all the flashcards
Anterior fontanelle
Anterior fontanelle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Posterior fontanelle
Posterior fontanelle
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sutures
Sutures
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cranial bones
Cranial bones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
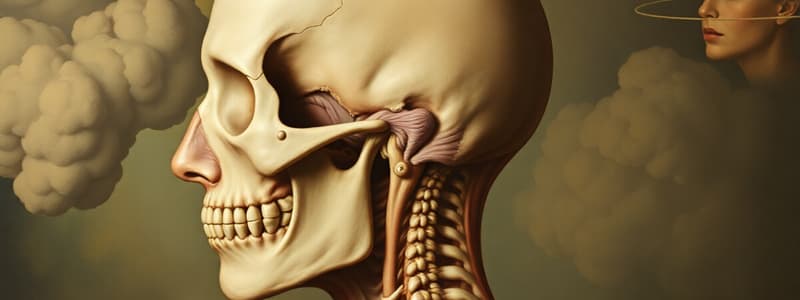
Head, Neck, and TMJ Anatomy and Conditions
- Scalp: Soft tissue covering and protecting the cranial vault
- Scalp Layers:
- Skin: Outermost layer, with sebaceous glands and hair follicles
- Connective tissue: Contains major arteries and veins
- Aponeurosis (Galea aponeurotica): Connects occipitalis and frontalis muscles
- Loose areolar tissue: Contains emissary veins ("dangerous layer")
- Periosteum (Pericranium): Innermost layer, providing nutrition to the scalp
- Cranial Bones:
- Frontal bone: 1
- Parietal bones: 2
- Occipital bone: 1
- Temporal bones: 2
- Sphenoid bone: 1
- Ethmoid bone: 1
- Facial Bones:
- Zygomatic bones: 2
- Sutures (Synarthrodial joints):
- Joints joining cranial bones
- Important sutures include coronal, sagittal, and lambdoid sutures.
- Temporal bone joins with the parietal bone at the squamosal suture
- Fontanelles:
- Spaces between cranial bones in infants
- Anterior fontanelle closes between 18-24 months
- Bregma is the point where coronal and sagittal sutures meet
- Posterior fontanelle closes between 9-12 months
- Lambda is the point where sagittal and lambdoid sutures meet
Landmarks of the Skull
- Nasion: Midline bony depression between the eyes; where frontal and nasal bones meet
- Glabella: Area between eyebrows and above the nose
- Nasolabial folds: Creases from nose to mouth corners
- Philtrum: Vertical groove between nose base and upper lip
- Pterion: Thinnest portion of the lateral skull; middle meningeal artery location
- Inion: Most prominent point on the external occipital protuberance; landmark for head circumference
Facial Muscles
- Occipitofrontalis: Elevates eyebrows
- Corrugator supercilii: Pulls eyebrows together
- Procerus: Wrinkles bridge of nose
- Zygomaticus major: Primary muscle for smiling
- Zygomaticus minor: Secondary muscle for smiling
- Risorius: Muscle for a grimace or fake smile
- Orbicularis oris: Closes lips
- Buccinator: Pouts cheeks
- Levator anguli oris: Elevates angle of mouth
- Mentalis: Raises and wrinkles chin
- Platysma: Depresses mandible angle
Eye Muscles
- Levator palpebrae superioris: Responsible for 80% of eye opening
- Müller's muscle: Responsible for 20% of eye opening
- Orbicularis oculi: Closes eyelids
Extraocular Muscles
- Superior rectus: Upward and outward movement
- Inferior rectus: Downward and outward movement
- Lateral rectus: Abduction (lateral movement) of eye
- Medial rectus: Adduction (medial movement) of eye
- Superior oblique: Downward and inward movement
- Inferior oblique: Upward and inward movement
Neck Region
- Cervical Vertebrae: Small, triangular shaped bodies
- Atlas (C1): No body and no spinous process
- Axis (C2): Odontoid process
- Hyoid Bone: Located in the neck, not directly articulated with other bones; connected by ligaments
Neck Triangles
- Anterior triangles: Submental, submandibular/digastric, carotid
- Posterior triangles: Occipital, supraclavicular/jugular
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
- Articulation between mandibular condyle and mandibular fossa, modified hinge joint.
- Superior joint: Translation
- Inferior joint: Rotation
- Open packed position: Mouth slightly open, lips together
- Closed packed position: Tightly clenched teeth.
Muscles of Mastication
- Temporalis: Muscle for closing the mouth
- Internal pterygoid: Muscle for protrusion
- Masseter: Muscle for protrusion
- External pterygoid: Muscle for opening the mouth
TMJ Conditions
- TMJ Disc Displacement: Clicking during mouth opening or closing
- TMJ Displacement: Clicking during mouth opening or closing.
- TMJ Capsulitis: Pain during mouth opening
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.