Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary role of the gut, according to the information presented?
What is the primary role of the gut, according to the information presented?
- Digesting food and absorbing nutrients.
- Controlling hormone production exclusively.
- Serving as the largest sensory organ and gathering immune system information. (correct)
- Filtering toxins from the bloodstream.
How do gut bacteria contribute to human health?
How do gut bacteria contribute to human health?
- By synthesizing vitamins and minerals for absorption.
- By directly influencing muscle strength and physical endurance.
- By producing hormones that regulate mood.
- By breaking down indigestible food and supporting the immune system. (correct)
What is the potential impact of early childhood antibiotic use on the gut microbiome?
What is the potential impact of early childhood antibiotic use on the gut microbiome?
- Improved nutrient absorption and digestion.
- Profound alterations, potentially leading to obesity and other health issues. (correct)
- Enhanced immune response to common allergens.
- Increased microbial diversity, leading to better disease resistance.
What is the human microbiome comprised of?
What is the human microbiome comprised of?
How does a high-fiber diet affect the gut microbiome?
How does a high-fiber diet affect the gut microbiome?
What is the focus of Health Psychologists?
What is the focus of Health Psychologists?
According to the WHO definition, what does health encompass?
According to the WHO definition, what does health encompass?
What are the roles of a Health Psychologist?
What are the roles of a Health Psychologist?
How does health psychology view the relationship between the mind and body?
How does health psychology view the relationship between the mind and body?
How would you describe one of the early views of Mind-Body Relationship around disease?
How would you describe one of the early views of Mind-Body Relationship around disease?
What characterizes the biopsychosocial model of health?
What characterizes the biopsychosocial model of health?
What are the benefits of the biopsychosocial model?
What are the benefits of the biopsychosocial model?
What is the correct order of steps for a Biopsychosocial Model?
What is the correct order of steps for a Biopsychosocial Model?
What is the relationship between acute and chronic disorders?
What is the relationship between acute and chronic disorders?
How has the prevalence of chronic illnesses influenced the field of health psychology?
How has the prevalence of chronic illnesses influenced the field of health psychology?
What are the benefits of understanding health and illness?
What are the benefits of understanding health and illness?
What is something that is NOT considered a determinant of health?
What is something that is NOT considered a determinant of health?
What is the main purpose for health psychology training?
What is the main purpose for health psychology training?
Which statement best describes the function of the nervous system?
Which statement best describes the function of the nervous system?
What is the role of neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
What is the role of neurotransmitters in the nervous system?
Which bodily function is primarily regulated by the parasympathetic nervous system?
Which bodily function is primarily regulated by the parasympathetic nervous system?
What is Epilepsy?
What is Epilepsy?
How does multiple sclerosis affect the nervous system?
How does multiple sclerosis affect the nervous system?
What is the hypothalamus?
What is the hypothalamus?
Which hormone controls contractions during labor and lactation?
Which hormone controls contractions during labor and lactation?
In the context of the adrenal glands, what is the role of cortisol?
In the context of the adrenal glands, what is the role of cortisol?
What is the first step that happens during times of high stress?
What is the first step that happens during times of high stress?
What is the function of glucorticoids?
What is the function of glucorticoids?
Which condition results from insufficient thyroid hormones, leading to low activity levels and weight gain?
Which condition results from insufficient thyroid hormones, leading to low activity levels and weight gain?
What is the pancreas and how does it function?
What is the pancreas and how does it function?
What happens in the respiratory system?
What happens in the respiratory system?
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
What is the difference between arteries and veins?
During the cardiac cycle, what is the distinction between diastole and systole?
During the cardiac cycle, what is the distinction between diastole and systole?
Which factor does not decrease BP?
Which factor does not decrease BP?
What happens to the arteries related to Atherosclerosis?
What happens to the arteries related to Atherosclerosis?
Flashcards
Inner sphincter muscle
Inner sphincter muscle
Muscle that allows food to move through to allow some food to move through.
Gut's sensory role
Gut's sensory role
The gut is the largest sensory organ, collecting information about the immune system and hormones.
Good and bad Bacteria
Good and bad Bacteria
Needed to help clean, also for the immune system to recognize bad bacteria.
Bacterial composition
Bacterial composition
Signup and view all the flashcards
Natural birth benefits
Natural birth benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Antibiotics effect on children
Antibiotics effect on children
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microbial Diversity Impact
Microbial Diversity Impact
Signup and view all the flashcards
Early Childhood Antibiotics
Early Childhood Antibiotics
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fecal transplants
Fecal transplants
Signup and view all the flashcards
Human microbiome
Human microbiome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Microbiome
Microbiome
Signup and view all the flashcards
Our microbiota
Our microbiota
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bacteria in the gut
Bacteria in the gut
Signup and view all the flashcards
Short chain fatty acids
Short chain fatty acids
Signup and view all the flashcards
High fiber diet benefits
High fiber diet benefits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Polyphenol-rich Foods
Polyphenol-rich Foods
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health Psychology
Health Psychology
Signup and view all the flashcards
WHO defines health
WHO defines health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Health Psychologists focus
Health Psychologists focus
Signup and view all the flashcards
Etiology
Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mind-Body relationship
Mind-Body relationship
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epidemiology in health psychology
Epidemiology in health psychology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morbidity
Morbidity
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mortality
Mortality
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biopsychosocial model of health
Biopsychosocial model of health
Signup and view all the flashcards
Biopsychosocial health says
Biopsychosocial health says
Signup and view all the flashcards
Nervous System
Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cell body
Cell body
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dendrites
Dendrites
Signup and view all the flashcards
Axon
Axon
Signup and view all the flashcards
Synaptic knobs
Synaptic knobs
Signup and view all the flashcards
Message
Message
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
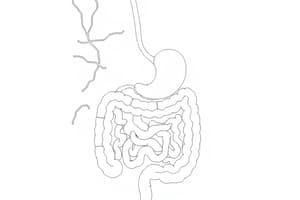
The Gut & Microbiome
- The inner sphincter muscle delivers leftover food to the inner part of the body.
- Sensory cells analyze the delivered material to determine if it is gaseous or solid.
- The brain is alerted when the need to use the bathroom arises and coordinates with the outer sphincter through nervous cells.
- The small intestine cleans up during digestion, causing stomach growls.
- During stress, the digestive system, at times, conserves energy by reducing its own resource consumption.
- 90% of information is channeled from the gut to the brain
- The gut functions as the largest sensory organ, collecting data on the immune system and hormones, and sends signals to areas of the brain involving morality and fear.
- The brain sympathizes with gut issues.
- Many bacteria are beneficial and aid in cleaning, necessitating a balance of good and bad bacteria for the immune system to recognize harmful ones.
- Bacteria types vary in different body regions, with each area having unique microbes.
- Bacterial composition exceeds the body's in terms of cells and DNA.
- The baby obtains beneficial microbes during natural birth through exposure to vaginal microbes.
- C-section babies are mostly exposed to skin microbes.
- Early antibiotic use in children can affect gut microbial community.
- Microbial diversity impacts digestion and disease resistance.
- Early childhood antibiotics can alter gut microbes, leading to obesity and health issues.
- Fecal transplants from donors show therapeutic potential for C.diff patients.
Human Microbiome Definition
- The human microbiota comprises bacteria, viruses, and microscopic organisms, with 95% residing in the gastrointestinal tract.
- The microbiome includes microbes, their genes, their environment, and their metabolic products.
- The human microbiome is linked to conditions, such as obesity, asthma, allergies, anxiety, depression, and autoimmune diseases like Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA).
- Microbiota assists in discerning between beneficial and harmful pathogens.
- Humans and microbiota share a symbiotic connection.
Gut Health & Diet
- Gut bacteria aids in breaking down indigestible food.
- Protects against harmful bacteria which supports the immune system.
- High-fiber foods, including nuts, fruits, and legumes, positively affect gut bacteria.
- The production of short-chain fatty acids is facilitated, which nurtures the gut barrier, bolsters immune function, and reduces inflammation.
- A research study involving diet swapping Western versus African diets, demonstrated inflammation in the colon when consuming a Western diet.
- Low fiber results in less fuel = bacterial diminishment resulting in low diversity.
- Sauteed, raw, or steamed vegetables are preferable to fried, and probiotics benefit the stomach.
Fiber, Microbiomes & Fermented Foods
- A high-fiber diet reduces colon inflammation and cancer risk.
- Polyphenol-rich foods like fruits, teas, and vegetables enhance gut bacterial diversity.
- Fermented foods with probiotics, including kimchi and yogurt, support gut microbiome diversity and traditional diets.
Health Psychology Definition & Scope
- Health psychology is a new field focused on understanding psychological influences on the maintenance of health, onset of illness, and response to illness.
- Considers the origins and implications of health policy and interventions.
- Health psychology researchers study habits, such as smoking, in order to inform smoking cessation intervention strategies.
- WHO defines health as a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being.
- Wellness relies on balancing physical, mental, and social health.
- Health promotion, developing good health habits, promoting regular exercise, and implementing effective media campaigns to improve diets are areas in which health psychologists focus.
- The mental facets regarding the prevention and treatment of illness are areas of interest.
- Successfully managing stress can be taught by Health psychologists.
- Etiology/ HP interests involve the causes of illness through behavioral factors.
- High blood pressure is an example of an objective sign that the body is not functioning properly.
- Pain and nausea are subjective symptoms of disease or injury.
Health & Disease
- Health status is impacted by medical care (10%), behaviors (40%), and genetics (20%).
- Promoting mental and physical Health is the concern.
- Prevention and treatment of illness is a focus of health psychologists.
- HP covers etiology and correlates of health, illness and dysfunction.
- Studying the impact of behavior from health institutions/ professionals.
- The educational scientific and professional benefits.
- Prevention of illness through understanding the causes and correlates of health and illness are key roles.
Health Psychology & Views of the Mind
- Philosophical positioning regards mind and body connection and how they operate, either as separate or indistinguishable systems.
- Guiding principle of health psychology = interconnectedness.
- Some previously held viewpoints included disease seen as - God's punishment, evil spirits, or imbalances of bodily fluids.
- Supernatural Belief results stemming from- sorcery, social taboos, object intrusion, supernatural possession, losing one's soul
- Treatments included confession, appeasing of gods, magical sucking, animal excrement and torture, and trephination.
- Diseases have historically been viewed as natural processes.
- The humoral theory suggests disease comes from imbalanced body fluids: black bile, blood and phlegm.
- Specific personality types may also be associated with bodily fluids impacting risk.
- Disease localization (anatomical pathology), tissue-specific disease (tissue pathology), and cell-specific conditions (cellular pathology) are beliefs.
- Infections are caused by unseen particles in the air (germ theory)
- Magic bullet = cure can be found.
- Health is impacted from interaction with mind, body, and environment(biopsychosocial model).
Psychoanalytic & Somatic Contributions
- Early work by Freud focused on conversion hysteria.
- Unconscious conflicts produced physical disturbances = repressed issues.
- Patients became free of anxiety through nervous system improvements.
- Profiles of psychosomatic disorders, like anxiety and stress-induced ulcers, were researched.
- Bodily issues may occur do to emotional conflicts.
- Psychosomatic medicine is related to health psychology.
- Examines psychological and somatic origins.
- Behavioral medicine includes body and mind interventions.
- Integrative approach involving biological science.
- Treatment impacted by patient-practitioner relationships.
- Good health is greatly based on good habits, culture and social support, and health resources.
Biopsychosocial Model & Health
- Physical and psychological well-being.
- Health issues interplay and impact from biological, social and psychological origins.
- All are involved in overall health and wellness.
- Aberrant somatic ( bodily) processes explains every illness which negates relevance of some psychological processes.
- Illness relies on somatic processes.
Disease & The Biological and Psychosocial models
- The biopsychosocial model of disease states that psychological components are related to all other origins.
- Biopsychosocial model of disease includes influences within physical/ physiological, intellectual, and spiritual influences along side emotional and cognitive interactions.
- The biopsychosocial model takes into account both micro and macro levels of wellness.
- Clinical Implications includes a variety of biological, physical, intellectual, social, and spiritual needs.
Early Heart Attack & Illness Models
- The treatment approach needs to be examined and tailored based on individual conditions.
- Family history of heart can lead to a medical approach relying administrative drugs.
- A biopsychosocial approach evaluates community integration and behavioral factors.
- Focuses on connecting socially with others.
- Rehabilitation goals include maintaining a healthy balance in order to decrease personal constraints.
- The acute disorders came into form in the early 20th century.
- The chronic disease impacts all the main contributions to disability and death that result to irreversibility, but is treatable with medication and management.
Health Psychology's Role
- Health Psychologists make an impact from many origins, based on the knowledge of technology and research.
- The amount that disease impacts wellness relies on the ability of technology, medicine, and physical support.
- Preventative medicine relies on providing wellness tools to help with overall health.
Body Systems
- Consists of the nervous system, The endocrine system, The cardiovascular system, and The immune system impacts the way the human responds with external factors.
- The function provides bodily needs and correlate with health and or the dysfunction.
- NS transmits message from rest of the body and sends messages from dendrites cells, axons and synaptic knobs, creating a electrical response.
- Promotes sympathetic NS by releasing catecholamines, epinephrine, and norepinephrine during high stimuli.
- Sympathetic responses are: Heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, pupils dilate, sweat, and vasconstriction.
- Spinal cord is where all the nerves exist and have their bodily functions.
- Efferent nerves are away from the brain and afferent nerves are toward.
- Autonomic actions are uncontrollable, and are conveyed from the spine from muscles.
- Sympathetic responses call response or mobilize emergency.
- Sympathetic or parasympathetic system maintains and monitors equilibrium.
Body Systems & Disease
- Parkinson's disease is an autoimmune condition that impact the ability function bodily movement while the nervous system creates disturbances to the movement.
- NS disorders impact several canadians and their daily conditions.
- Huntington's disease and paraplegia are conditions that impact the way movement happens.
- The endocrine function releases secretion which creates regulation that interact with functionality in the brain.
- Hypothalamus provides messages to bodily and the pituitary gland, providing and receiving signals that have impacts.
- Sympathetic energy gets released which causes hormone creation, and increased activity for both, bodily needs.
Medulla & Brain Functions
- The medulla releases sensory data for the brain, which results in breathing responses.
- There is the process of diencephalon and the cerebral cortex and the integration of their nervous system. Cerebral includes higher function and has emotional responses based in the system.
Understanding & Assessing Stress
- Stress is associated with - negative stimuli whether that's intellectual, mental to social and physiological.
- Response to a personal environment.
- The reactions to stress have physical side effects - blood pressure and hormone changes and can result in external changes - alcohol, dietary, sleeping change.
- Individual assessment determines ability to respond with stress.
- Organisms respond to stress with phases of- mobilization phase, resistance phase, and a potential for exhaustion.
- Selye believed the response was uniform to the conditions.
- People are seen and believed to have a response, but based on many conditions that have genetic and emotional responses.
- "befriending and tending" - social interaction provide self control and awareness.
- Personal assessment is also a factor which could lead internal or external, resulting in positive and or negative impacts in many ways.
- The factors associated with events include- external and or external, which effects future stress.
- Personal effects on intellectual thoughts.
- Physiological states last from the impacts of many reasons.
- High cholesterol can impact bodily results.
- Stress suppresses immune system.
- The way to relieve and manage stress is through social interaction, mindfulness.
- Reactivitiy relies on genetics and the predisposition in order to react during intense experiences.
- The reasons to develop and implement new ways to help the many reasons of stress is based on all of the combined factors.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.