Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the primary purpose of Gram staining in microbiology?
What is the primary purpose of Gram staining in microbiology?
- To determine the age of bacterial cultures.
- To identify bacterial spores.
- To differentiate bacteria based on cell wall structure. (correct)
- To measure the metabolic activity of bacteria.
Which of the following reagents acts as a mordant in Gram staining?
Which of the following reagents acts as a mordant in Gram staining?
- Crystal violet
- Safranin
- Acetone
- Iodine (correct)
What color do Gram-positive bacteria appear after Gram staining, and why?
What color do Gram-positive bacteria appear after Gram staining, and why?
- Purple, due to retaining the crystal violet stain. (correct)
- Red, due to retaining the safranin counterstain.
- Pink, due to a thin peptidoglycan layer.
- Colorless, if the decolorization step is too short.
Which reagent is responsible for removing the primary stain from Gram-negative bacteria?
Which reagent is responsible for removing the primary stain from Gram-negative bacteria?
What is the function of the counterstain in the Gram staining procedure?
What is the function of the counterstain in the Gram staining procedure?
If a microbiologist forgets to apply iodine during a Gram staining procedure, what is the most likely outcome?
If a microbiologist forgets to apply iodine during a Gram staining procedure, what is the most likely outcome?
What would happen if the decolorization step was skipped during Gram staining?
What would happen if the decolorization step was skipped during Gram staining?
Why is it important to use a thin smear of bacteria when performing a Gram stain?
Why is it important to use a thin smear of bacteria when performing a Gram stain?
In Gram staining, what characteristic of bacterial cell walls determines their response to the staining procedure?
In Gram staining, what characteristic of bacterial cell walls determines their response to the staining procedure?
If you perform a Gram stain on a sample and all the bacteria appear pink/red, what is the most likely explanation?
If you perform a Gram stain on a sample and all the bacteria appear pink/red, what is the most likely explanation?
Which of the following dyes is NOT used as a counterstain in Gram staining?
Which of the following dyes is NOT used as a counterstain in Gram staining?
Which solvent is typically used as a decolorizing agent in the Gram staining procedure?
Which solvent is typically used as a decolorizing agent in the Gram staining procedure?
What is the role of crystal violet in Gram staining?
What is the role of crystal violet in Gram staining?
Ignoring the rinsing steps, what is the correct order of reagents used in the Gram staining procedure?
Ignoring the rinsing steps, what is the correct order of reagents used in the Gram staining procedure?
What could be concluded if Gram-stained bacteria appear as a mix of purple and pink cells?
What could be concluded if Gram-stained bacteria appear as a mix of purple and pink cells?
How does the thick peptidoglycan layer in Gram-positive bacteria contribute to their staining characteristics?
How does the thick peptidoglycan layer in Gram-positive bacteria contribute to their staining characteristics?
Why is timing critical during the decolorization step in Gram staining?
Why is timing critical during the decolorization step in Gram staining?
A microbiology student consistently observes distorted and inconsistent Gram stain results. What is the most probable cause?
A microbiology student consistently observes distorted and inconsistent Gram stain results. What is the most probable cause?
What is the immediate next step after applying the decolorizing agent such as acetone or alcohol in a Gram staining procedure?
What is the immediate next step after applying the decolorizing agent such as acetone or alcohol in a Gram staining procedure?
Which bacterial feature is LEAST relevant to the outcome of a Gram stain?
Which bacterial feature is LEAST relevant to the outcome of a Gram stain?
Flashcards
Gram Staining
Gram Staining
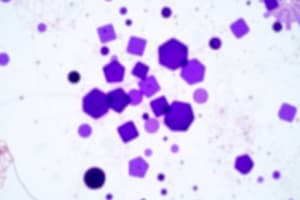
A staining technique used to differentiate bacteria based on their cell wall structure.
Gram Staining Reagents
Gram Staining Reagents
Crystal violet, iodine, decolorizing solvent (acetone/alcohol), and counterstain (safranin).
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Gram-Positive Bacteria
Bacteria that retain the primary stain (crystal violet) and appear purple/violet under the microscope.
Study Notes
- Gram staining identifies bacteria, demonstrates bacterial morphology, and differentiates between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- Christian Gram developed Gram staining in 1884 to stain bacteria in tissues.
Reagents
- Crystal violet, methyl violet, or gentian violet are examples of basic pararosaniline dyes.
- Iodine in an aqueous solution
- Acetone, alcohol, or aniline are examples of decolourising solvents.
- Basic fuchsin, neutral red, or safranin are examples of counterstains.
Gram-positive bacteria
- Gram-positive bacteria resist decolourisation.
- They retain the primary stain (methyl violet).
- They appear purple violet in colour.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.