Podcast
Questions and Answers
What role does GPR54 play in the context of the GnRH axis?
What role does GPR54 play in the context of the GnRH axis?
- It acts as a primary regulator of CNS pathways.
- It directly stimulates the release of kisspeptin-1.
- It is essential for the normal function of the GnRH axis. (correct)
- It inhibits the production of sex steroids.
How does kisspeptin-1 influence the GnRH axis?
How does kisspeptin-1 influence the GnRH axis?
- It directly inhibits the release of sex steroids.
- It does not influence the GnRH axis.
- It may function as a neurohormonal regulator of the GnRH axis. (correct)
- It downregulates the function of GPR54.
Which of the following is believed to inhibit the activity of the GnRH axis?
Which of the following is believed to inhibit the activity of the GnRH axis?
- Absence of GPR54
- Stimulation by kisspeptin-1
- Feedback inhibition by sex steroids (correct)
- Direct activation by CNS pathways
A researcher is investigating potential factors that influence the GnRH axis. Based on the information, which of the following is LEAST likely to directly impact the GnRH axis?
A researcher is investigating potential factors that influence the GnRH axis. Based on the information, which of the following is LEAST likely to directly impact the GnRH axis?
If GPR54 is non-functional from birth, what is the most likely outcome?
If GPR54 is non-functional from birth, what is the most likely outcome?
Which of the following hormonal effects primarily contributes to skeletal growth during puberty in both boys and girls?
Which of the following hormonal effects primarily contributes to skeletal growth during puberty in both boys and girls?
What triggers the completion of male puberty?
What triggers the completion of male puberty?
A positive feedback loop during male puberty directly involves which of the following?
A positive feedback loop during male puberty directly involves which of the following?
In females, what event signifies the end of puberty?
In females, what event signifies the end of puberty?
What is the role of testosterone during puberty in males??
What is the role of testosterone during puberty in males??
Which process describes the increase in production of adrenal androgens during puberty?
Which process describes the increase in production of adrenal androgens during puberty?
A 14-year-old boy is experiencing voice deepening, increased muscle mass, and growth of facial hair. Which hormone is MOST directly responsible for these changes?
A 14-year-old boy is experiencing voice deepening, increased muscle mass, and growth of facial hair. Which hormone is MOST directly responsible for these changes?
If a female experiences menarche but does not have an ovulatory cycle for another year, what does this indicate about her pubertal development?
If a female experiences menarche but does not have an ovulatory cycle for another year, what does this indicate about her pubertal development?
Which factor is most critical for the development of cervical dysplasia?
Which factor is most critical for the development of cervical dysplasia?
Why is early detection of cervical dysplasia so important?
Why is early detection of cervical dysplasia so important?
A 38-year-old woman with Ashkenazi Jewish heritage is concerned about her risk of breast cancer. Which additional factor would most significantly increase her risk, based on the information provided?
A 38-year-old woman with Ashkenazi Jewish heritage is concerned about her risk of breast cancer. Which additional factor would most significantly increase her risk, based on the information provided?
What is the primary function of the BRCA1 gene?
What is the primary function of the BRCA1 gene?
A woman discovers she carries a BRCA1 mutation. What does this primarily indicate regarding her health risks?
A woman discovers she carries a BRCA1 mutation. What does this primarily indicate regarding her health risks?
Which of the following factors is LEAST likely to be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in women younger than 45?
Which of the following factors is LEAST likely to be associated with an increased risk of breast cancer in women younger than 45?
A patient with a strong family history of both breast and ovarian cancer is tested and found to have a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene. Which gene is most likely to be affected?
A patient with a strong family history of both breast and ovarian cancer is tested and found to have a mutation in a tumor suppressor gene. Which gene is most likely to be affected?
Which statement best explains why risks for breast and ovarian cancers vary among BRCA1 mutation carriers?
Which statement best explains why risks for breast and ovarian cancers vary among BRCA1 mutation carriers?
Thelarche, a key indicator of puberty in girls, is directly caused by which hormonal action?
Thelarche, a key indicator of puberty in girls, is directly caused by which hormonal action?
How does the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) axis contribute to the onset of puberty?
How does the Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Gonadal (HPG) axis contribute to the onset of puberty?
Which of the following factors has the least influence on the timing of puberty?
Which of the following factors has the least influence on the timing of puberty?
What is the significance of increased nocturnal pulses of LH and FSH approximately one year before puberty in girls?
What is the significance of increased nocturnal pulses of LH and FSH approximately one year before puberty in girls?
How does estradiol secretion specifically contribute to the physical changes observed in girls during puberty?
How does estradiol secretion specifically contribute to the physical changes observed in girls during puberty?
Which of the following menstrual cycle patterns would be considered a risk factor for endometriosis?
Which of the following menstrual cycle patterns would be considered a risk factor for endometriosis?
Which of the following best describes the role of genetics in determining the onset of puberty?
Which of the following best describes the role of genetics in determining the onset of puberty?
A patient presents with severe dysmenorrhea and is considering surgical options. Which surgical treatment is MOST likely to be recommended specifically for pain relief associated with endometriosis?
A patient presents with severe dysmenorrhea and is considering surgical options. Which surgical treatment is MOST likely to be recommended specifically for pain relief associated with endometriosis?
In boys, the onset of puberty is closely associated with an increase in weight and body mass index (BMI). How might these factors influence the hormonal processes of puberty?
In boys, the onset of puberty is closely associated with an increase in weight and body mass index (BMI). How might these factors influence the hormonal processes of puberty?
A 30-year-old nulliparous woman is diagnosed with endometriosis. What does 'nulliparous' mean in this context?
A 30-year-old nulliparous woman is diagnosed with endometriosis. What does 'nulliparous' mean in this context?
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor related to the menstrual cycle that may increase the likelihood of developing endometriosis?
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor related to the menstrual cycle that may increase the likelihood of developing endometriosis?
How does the sequence of hormonal events during puberty ensure proper sexual maturation rather than just isolated development of certain traits?
How does the sequence of hormonal events during puberty ensure proper sexual maturation rather than just isolated development of certain traits?
What is the PRIMARY etiological agent implicated in the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer?
What is the PRIMARY etiological agent implicated in the development of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer?
Why is understanding the hormonal regulation of puberty critical for healthcare professionals?
Why is understanding the hormonal regulation of puberty critical for healthcare professionals?
Considering both genetic and environmental influences, how might a healthcare provider approach a case of delayed puberty in a young girl?
Considering both genetic and environmental influences, how might a healthcare provider approach a case of delayed puberty in a young girl?
A patient with endometriosis is undergoing laparoscopic removal of endometrial implants. What is the PRIMARY goal of this treatment?
A patient with endometriosis is undergoing laparoscopic removal of endometrial implants. What is the PRIMARY goal of this treatment?
A patient with a history of endometriosis is prescribed mifepristone. What is the MOST likely reason for using this medication in the management of endometriosis?
A patient with a history of endometriosis is prescribed mifepristone. What is the MOST likely reason for using this medication in the management of endometriosis?
A researcher is investigating the prevalence of endometriosis in women experiencing infertility. Based on the information provided, what percentage of women with infertility are likely to have endometriosis?
A researcher is investigating the prevalence of endometriosis in women experiencing infertility. Based on the information provided, what percentage of women with infertility are likely to have endometriosis?
Which of the following factors would MOST strongly suggest an increased risk of endometriosis in a young woman?
Which of the following factors would MOST strongly suggest an increased risk of endometriosis in a young woman?
Which condition is almost exclusively caused by HPV infection?
Which condition is almost exclusively caused by HPV infection?
A female patient with physiologic (constitutional) delay is considering treatment options. What is the primary goal of initiating hormone therapy in this scenario?
A female patient with physiologic (constitutional) delay is considering treatment options. What is the primary goal of initiating hormone therapy in this scenario?
A young male is diagnosed with physiologic (constitutional) delay. His parents are concerned about his final adult height. What factor provides the MOST reassurance regarding his growth potential?
A young male is diagnosed with physiologic (constitutional) delay. His parents are concerned about his final adult height. What factor provides the MOST reassurance regarding his growth potential?
What distinguishes physiologic (constitutional) delay from other causes of delayed puberty?
What distinguishes physiologic (constitutional) delay from other causes of delayed puberty?
Why might a lack of circulating estrogen during puberty increase the risk of inadequate bone density in adulthood?
Why might a lack of circulating estrogen during puberty increase the risk of inadequate bone density in adulthood?
A 14-year-old girl is diagnosed with physiologic delay of puberty. Her bone density is found to be below average for her age. Which intervention would be MOST appropriate?
A 14-year-old girl is diagnosed with physiologic delay of puberty. Her bone density is found to be below average for her age. Which intervention would be MOST appropriate?
A clinician is evaluating a 15-year-old male who has not shown signs of puberty. Which assessment would be MOST important in differentiating physiologic delay from hypogonadism?
A clinician is evaluating a 15-year-old male who has not shown signs of puberty. Which assessment would be MOST important in differentiating physiologic delay from hypogonadism?
A female patient with anorexia nervosa experiences delayed puberty. How does this etiology differ from physiologic delay?
A female patient with anorexia nervosa experiences delayed puberty. How does this etiology differ from physiologic delay?
If a patient with constitutional delay is treated with low-dose hormone therapy, what should the clinician monitor to ensure appropriate pubertal progression and minimize potential adverse effects?
If a patient with constitutional delay is treated with low-dose hormone therapy, what should the clinician monitor to ensure appropriate pubertal progression and minimize potential adverse effects?
Flashcards
Estrogen's role in skeletal growth
Estrogen's role in skeletal growth
Estrogen and growth factors stimulate rapid bone growth in both sexes during puberty.
Testosterone's effect on male anatomy
Testosterone's effect on male anatomy
Testosterone promotes the growth of the testes, scrotum, and penis during male puberty.
Pubertal positive feedback loop
Pubertal positive feedback loop
A positive feedback loop where gonadotropins stimulate the gonads to produce more sex hormones.
First ejaculation with mature sperm
First ejaculation with mature sperm
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ovaries role in female puberty
Ovaries role in female puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
First ovulatory menstrual period
First ovulatory menstrual period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Adrenarche
Adrenarche
Signup and view all the flashcards
Testes mature sperm production
Testes mature sperm production
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Thelarche?
What is Thelarche?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When does puberty typically begin in girls?
When does puberty typically begin in girls?
Signup and view all the flashcards
When does puberty typically begin in boys?
When does puberty typically begin in boys?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What influences the timing of puberty?
What influences the timing of puberty?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What does HPG axis stand for?
What does HPG axis stand for?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Besides the HPG axis, what other systems are involved in reproductive maturation?
Besides the HPG axis, what other systems are involved in reproductive maturation?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What promotes sexual maturation as puberty approaches?
What promotes sexual maturation as puberty approaches?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What happens about 1 year before puberty in girls?
What happens about 1 year before puberty in girls?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Stimulation of the gonads leads to what?
Stimulation of the gonads leads to what?
Signup and view all the flashcards
In girls, what does estradiol cause?
In girls, what does estradiol cause?
Signup and view all the flashcards
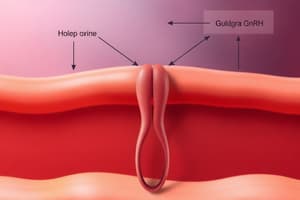
What is GPR54?
What is GPR54?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is Kisspeptin-1?
What is Kisspeptin-1?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the HPG axis?
What is the HPG axis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What inhibits Kisspeptin-1 and impacts the GnRH axis?
What inhibits Kisspeptin-1 and impacts the GnRH axis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is CNS feedback of the HPG Axis?
What is CNS feedback of the HPG Axis?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Estrogen's Role
Estrogen's Role
Signup and view all the flashcards
Physiologic (Constitutional) Delay
Physiologic (Constitutional) Delay
Signup and view all the flashcards
Constitutional Delay - Key Traits
Constitutional Delay - Key Traits
Signup and view all the flashcards
Retrospective Diagnosis
Retrospective Diagnosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Spontaneous Puberty Progression
Spontaneous Puberty Progression
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment for Constitutional Delay
Treatment for Constitutional Delay
Signup and view all the flashcards
Goals of Treatment
Goals of Treatment
Signup and view all the flashcards
Hormone therapy for delayed puberty
Hormone therapy for delayed puberty
Signup and view all the flashcards
Precancerous Dysplasia
Precancerous Dysplasia
Signup and view all the flashcards
HPV Infection
HPV Infection
Signup and view all the flashcards
BRCA1 Gene
BRCA1 Gene
Signup and view all the flashcards
Breast Cancer Risk Factor
Breast Cancer Risk Factor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Genetic Risk Factor
Genetic Risk Factor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ashkenazi Jewish Heritage
Ashkenazi Jewish Heritage
Signup and view all the flashcards
Radiation Exposure
Radiation Exposure
Signup and view all the flashcards
Family History
Family History
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Flow Interference
Menstrual Flow Interference
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometriosis & Infertility
Endometriosis & Infertility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Endometrial Implant Removal
Endometrial Implant Removal
Signup and view all the flashcards
Presacral Neurectomy
Presacral Neurectomy
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cervical Cancer Etiology
Cervical Cancer Etiology
Signup and view all the flashcards
Menstrual Cycle Abnormalities
Menstrual Cycle Abnormalities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Parity as Protective Factor
Parity as Protective Factor
Signup and view all the flashcards
Laparoscopic Techniques
Laparoscopic Techniques
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mifepristone
Mifepristone
Signup and view all the flashcards
Treatment Modalities
Treatment Modalities
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
- Chapter 25 discusses alterations of the female reproductive system, including uterine tumor types, puberty, amenorrhea, PCOS, endometriosis, and cervical cancer.
Uterine Tumor Types (Leiomyomas)
- Leiomyomas are benign smooth muscle tumors in the myometrium.
- They are the most common benign uterine tumors, affecting 70-80% of women.
- Most leiomyomas are small, asymptomatic, and clinically insignificant.
- Prevalence increases in women aged 30-50, then decreases with menopause.
- The cause is unknown, but size is related to estrogen, progesterone, growth factors, angiogenesis, and apoptosis.
- Can occur in the fundus of the uterus, in multiples, or singly.
- Classified as subserous, submucous, or intramural based on location in the uterine wall.
- Clinical manifestations include abnormal uterine bleeding, pain, and pressure.
- Can distort the uterine cavity and increase the uterine surface area, leading to increased bleeding.
- Evaluation includes bimanual examination, uterine enlargement, and pelvic sonography or MRI.
- Treatment depends on symptoms, tumor size, age, reproductive status, health, and patient preference.
Puberty in Girls and Boys
- Puberty is the onset of sexual maturation, different from adolescence which is the stage between childhood and adulthood.
- Girls typically begin puberty around 8-9 years with thelarche (breast development).
- Boys typically begin puberty around 11 years, with increased weight and BMI.
- Timing is influenced by genetics, environment, ethnicity, health, and nutrition.
- Reproductive maturation involves the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, CNS, and endocrine system.
- Hormonal events promote sexual maturation as puberty approaches.
- About a year before puberty in girls, there is an increase in the gonadotropin secretion (LH, FSH) and responsiveness to GnRH.
- Gonadarche stimulates estradiol secretion in girls and testosterone secretion in boys.
- Estradiol causes thelarche, maturation of reproductive organs, and fat deposit in hips.
- Estrogen and increased growth factor production cause rapid skeletal growth in boys and girls.
- Testosterone causes growth of testes, scrotum, and penis with gonadotropins stimulating the gonads.
- The testes produce mature sperm with the ovaries releasing mature ova.
- Male puberty completes with the first ejaculation while female puberty completes with the first ovulatory menstrual period.
- Adrenarche is increased production of adrenal androgens which occurs prior to puberty and results in axillary and pubic hair growth and odor.
- Puberty completes when a person can reproduce.
Delayed Puberty in Girls
- Defined as a lack of clinical signs of puberty by age 13.
- Clinical diagnosis is made without menarche age 15 or 16.
- Risks include psychosocial implications, skeletal development, and mineralization.
- Estrogen is important for bone density.
- Physiologic delay is when hormonal levels are normal, and the HPG axis is intact, but maturation is slow
- This type of delayed puberty tends to be familial.
- 30% of girls with delayed puberty later progressed through normal puberty.
- Treatment involves expectant management or hormone therapy to promote pubertal development and mineralization.
- Functional hypogonadotropic hypogonadism makes up 19% of delayed puberty cases.
- Functional hypogonadotropic hypogonadism is due to an underlying condition unrelated to gonadal function.
- Correction of the underlying issues is the treatment.
- Human gonadal function requires luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).
- Disruption in the HPG axis is caused when their releases are regulated by pulsatile secretion of GnRH.
- The GPR54 has been named the gatekeeper gene for activation of the GnRH axis and may require synthetic GnRH or hormone administration.
Delayed Puberty in Boys
- Defined as no clinical signs of puberty by age 14.
- Early diagnosis/treatment is recommended due to potential for sexual immaturity and self esteem issues.
- Physiologic delay is when hormonal levels are normal and the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis is intact, but maturation is happening slowly.
- Physiologic delay is difficult to distinguish from isolated gonadotropin deficiency, it is diagnosed retrospectively.
- Treatment is expectant management to promote pubertal development and mineralization.
- Treatment is correction of the underlying condition.
- Functional hypogonadotropic deficiency can be caused CNS defects, GPR54 mutations, hemochromatosis, hypopituitarism, and marijuana use.
- Chronic conditions cause disruption to the hpg axis.
- Evaluation should target delayed puberty causes that require lab work to measure thyroid function and serum levels.
Obesity and Early Puberty in Females
- Early puberty and obesity in girls could correlate due to higher estrogen levels which stimulate gonadotropin and estrogen secretion.
- Girls with too little body fat and intense exercise may have a delayed maturation while leptin plays an important role in puberty onset.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
- The most common cause of anovulation and ovulatory dysfunction and is associated with metabolic dysfunction and is defined by the presence of irregular ovulation and elevated androgen levels.
- A strong genetic link is suspected.
- Hyperandrogenic state is a cardinal feature.
- Clinical manifestations usually appear within 2 years of puberty with commonly known symptoms of obesity, hirsutism, menstrual disturbance, amenorrhea, hyperandrogenism, and infertility.
- Treatment involves reversing/stabilizing estrogen levels, androgen excess menstrual cycles and associated disturbance through combined oral contraceptives, Metformin, diet and exercise and lifestyle changes.
Endometriosis
- Endometriosis is the presence of functioning endometrial tissue outside the uterus.
- The cause is unknown, but the risk is greater for cancers especially in the ovarian area.
- Endometrial cells may implant during retrograde menstruation impaired immunity, and spread through the lymphatic or vascular systems.
- The ectopic endometrium proliferates similar to a normal menstrual cycle.
- Inflammation from cellular inflammatory mediators may lead to fibrosis, scarring, adhesions, and pain.
- Endometrial implants occur in the ovaries, uterine ligaments, and pelvic peritoneum.
- Family history, menstrual abnormalities, never giving birth raise concerns about endometriosis.
- Degree of invasiveness based on findings from different stages like minimal, mild, moderate from laparoscopic images.
- The goal of treatment involves the following: treating pain, stopping progression of symptoms, restoring fertility.
- Can be treated with suppression of ovulation or conservative surgical treatment.
Cervical Intraepithelial Carcinoma (CIN) and Cervical Cancer
- Cervical cancer is caused by cervical human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
- Precancerous dysplasia is called cervical intraepithelial carcinoma (CIN) and cervical carcinoma in situ (CIS).
- Cervical dysplasia can be identified through examination of cervical cells, and treatment is available to prevent the spread of cancer.
- Infection with high risk HPV is an important part of the development of cervical dysplasia.
BRCA1 Gene
- Most breast cancer occurs in women older than 55, however those younger than 45 may have a risk due to relatives with the sickness, Jewish heritage, radiation treatment, and breast health problems.
- BRCA1 is located on chromosome 17, is a tumor-suppressor gene therefore can be cause for uncontrolled cell growth.
- A family history of both breast cancer and ovarian cancer increases the risk that an individual with breast cancer carries a BRCA1 mutation.
- Carriers are at high risk for ovarian cancer.
- Risks are not equal in carrier.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.