Podcast
Questions and Answers
What is the main difference between omphalocele and gastroschisis?
What is the main difference between omphalocele and gastroschisis?
- The presence of a membrane containing abdominal organs
- The location of the abdominal wall disorder (correct)
- The surgical procedures used for correction
- The amount of intestinal contents herniating
What does gastroschisis mean in Greek?
What does gastroschisis mean in Greek?
- Stomach enclosure
- Stomach cleft (correct)
- Abdominal fissure
- Abdominal hernia
What is the cause of gastroschisis?
What is the cause of gastroschisis?
- Failure of abdominal wall closure (correct)
- Mesentery twisted as bowel reentered abdomen
- Incomplete canalization of intestine
- Mesentery fusion with the umbilical cord
What complication arises if there is twisting of the mesentery upon bowel reentering the abdomen?
What complication arises if there is twisting of the mesentery upon bowel reentering the abdomen?
How does the treatment differ for a ruptured sac in omphalocele compared to an unruptured sac?
How does the treatment differ for a ruptured sac in omphalocele compared to an unruptured sac?
What is a similarity between omphalocele and neural tube defects in terms of development?
What is a similarity between omphalocele and neural tube defects in terms of development?
What is a potential cause of intestinal obstruction in infants according to the text?
What is a potential cause of intestinal obstruction in infants according to the text?
How is an omphalocele or gastroschisis usually identified during pregnancy?
How is an omphalocele or gastroschisis usually identified during pregnancy?
What is the therapeutic management approach for gastrointestinal distention in neonates?
What is the therapeutic management approach for gastrointestinal distention in neonates?
What might be a sign of infant abdominal pain according to the text?
What might be a sign of infant abdominal pain according to the text?
What imaging technique would likely reveal no air below the level of intestine obstruction?
What imaging technique would likely reveal no air below the level of intestine obstruction?
When might an amniocentesis be performed during pregnancy according to the text?
When might an amniocentesis be performed during pregnancy according to the text?
What is the purpose of inserting a gastrostomy into the stomach?
What is the purpose of inserting a gastrostomy into the stomach?
What is the structure of an umbilical hernia typically like?
What is the structure of an umbilical hernia typically like?
When is surgical repair often not necessary for mild umbilical hernia cases?
When is surgical repair often not necessary for mild umbilical hernia cases?
What can be visible when a baby with an umbilical hernia cries?
What can be visible when a baby with an umbilical hernia cries?
What are IV medications given for in cases involving a gastrostomy?
What are IV medications given for in cases involving a gastrostomy?
In which group is umbilical hernia more common according to the text?
In which group is umbilical hernia more common according to the text?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
Surgical Approaches for Omphalocele
- Replace only a portion of the bowel at one time, with the remainder contained by a Silastic pouch (silo) suspended over the infant's bed
- Over the next 5-7 days, bowel is gradually returned to the abdomen by multiple surgical procedures
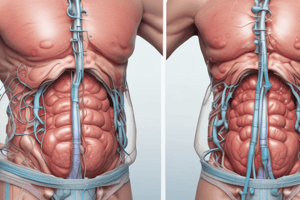
Omphalocele
- Abdominal wall disorder where the intestine or other organs protrude through the navel
- If ruptured sac: treated like gastroschisis due to infection potential
- If unruptured sac: external dressing with mild pressure is used to gradually compress abdominal contents, allowing skin to stretch between treatments
Gastroschisis
- Derived from Greek words for "stomach cleft" or "fissure"
- Abdominal wall disorder where organs spill freely from the abdominal wall, usually to the right of the umbilicus
- Incidence: 4-5 per 10,000 live births
- Children often have decreased bowel motility and difficulty absorbing nutrients and passing stool, even after surgical correction
Intestinal Obstructions
- Can be caused by a failure of canalization of the intestine in utero
- Atresia (complete closure) or stenosis (narrowing) of fetal bowel can develop
- Most common site: duodenum
- Twisting of the mesentery of the bowel can cause volvulus, a potential problem for the first 6 months
Abdominal Wall Defects
Umbilical Hernia
- Protrusion of a portion of intestine through the umbilical ring, muscle, and fascia surrounding the umbilical cord
- Incidence: more common in Black children, low-birth-weight infants, and girls
- Structure: 1-2 cm in diameter but may be as large as an orange when the child cries or strains
- Size of protruding mass is not as important as the size of the fascial ring through which the intestine protrudes
Diagnosis and Assessment
- Omphalocele and gastroschisis can be identified by an elevated maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MAFP) during pregnancy
- Prenatal sonogram can determine abdominal wall/spinal disorders
- Presence is obvious on inspection at birth if omphalocele or gastroschisis is identified in utero
- Cesarean birth may be prepared to protect exposed intestine
Therapeutic Management
- Insertion of an orogastric or nasogastric tube to prevent further gastrointestinal distension
- IV therapy to restore fluid and electrolyte balance
- Immediate surgery is scheduled to relieve the obstruction before pressure on the bowel causes death of the involved intestinal lining
- Obstruction repair usually involves laparoscopy, although full abdominal surgery may be necessary
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.