Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which layer of smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract causes constriction of the lumen?
Which layer of smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal tract causes constriction of the lumen?
- Mucosal layer
- Thick inner circumferential layer (correct)
- Myenteric plexus
- Thin outer longitudinal layer
What is the primary role of the myenteric plexus in the gastrointestinal system?
What is the primary role of the myenteric plexus in the gastrointestinal system?
- Generating electrical impulses for voluntary muscle movement
- Secreting digestive juices
- Facilitating nutrient absorption
- Regulating gastrointestinal tract functions (correct)
Which muscle type in the gastrointestinal tract is under involuntary control?
Which muscle type in the gastrointestinal tract is under involuntary control?
- Both A and B
- Skeletal muscle
- Cardiac muscle
- Smooth muscle (correct)
What is the function of serosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the function of serosa in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which type of contraction is responsible for moving contents forward through the digestive tract?
Which type of contraction is responsible for moving contents forward through the digestive tract?
What process involves the chemical and mechanical breakdown of food into absorbable units?
What process involves the chemical and mechanical breakdown of food into absorbable units?
Which type of contraction facilitates both digestion and absorption by mixing food with digestive juices?
Which type of contraction facilitates both digestion and absorption by mixing food with digestive juices?
What is the term for the process of eating food?
What is the term for the process of eating food?
What is the primary enzyme involved in triglyceride digestion?
What is the primary enzyme involved in triglyceride digestion?
Which process primarily occurs in the small intestine?
Which process primarily occurs in the small intestine?
What role do bile salts play in fat digestion?
What role do bile salts play in fat digestion?
Which of the following is not a type of lipase involved in fat digestion?
Which of the following is not a type of lipase involved in fat digestion?
Defecation refers to which of the following processes?
Defecation refers to which of the following processes?
What is the primary function of trypsin and chymotrypsin in digestion?
What is the primary function of trypsin and chymotrypsin in digestion?
Which of the following statements about absorption is correct?
Which of the following statements about absorption is correct?
Which enzyme is known for specifically breaking down protein molecules?
Which enzyme is known for specifically breaking down protein molecules?
What is the primary function of the villi in the small intestine?
What is the primary function of the villi in the small intestine?
Which component of the gastrointestinal system is responsible for nutrient absorption?
Which component of the gastrointestinal system is responsible for nutrient absorption?
What role do the microvilli play in the small intestine?
What role do the microvilli play in the small intestine?
What function does the large intestine primarily serve?
What function does the large intestine primarily serve?
What is the main consequence of dysbiosis in individuals?
What is the main consequence of dysbiosis in individuals?
How often do the epithelial cells lining the villi renew themselves?
How often do the epithelial cells lining the villi renew themselves?
What is the primary composition of the submucosa layer of the gastrointestinal tract?
What is the primary composition of the submucosa layer of the gastrointestinal tract?
What beneficial substance does the bacteria in the large intestine help produce?
What beneficial substance does the bacteria in the large intestine help produce?
What is the primary role of saliva in the digestive process?
What is the primary role of saliva in the digestive process?
Which of the following glands secretes hydrochloric acid (HCl)?
Which of the following glands secretes hydrochloric acid (HCl)?
What component of gastric secretions combines with vitamin B12 to make it absorbable?
What component of gastric secretions combines with vitamin B12 to make it absorbable?
Which enzyme in saliva is responsible for starch digestion?
Which enzyme in saliva is responsible for starch digestion?
Which type of cell in the gastric glands secretes gastrin?
Which type of cell in the gastric glands secretes gastrin?
What is the main function of the mucous neck cells in the gastric glands?
What is the main function of the mucous neck cells in the gastric glands?
Which component of saliva helps to neutralize acids in food?
Which component of saliva helps to neutralize acids in food?
What is one of the primary functions of saliva aside from aiding digestion?
What is one of the primary functions of saliva aside from aiding digestion?
Which hormone is produced in the stomach and duodenum and stimulates acid secretion?
Which hormone is produced in the stomach and duodenum and stimulates acid secretion?
What action does Cholecystokinin primarily have?
What action does Cholecystokinin primarily have?
Which hormone is released in response to fats and proteins and inhibits food intake?
Which hormone is released in response to fats and proteins and inhibits food intake?
What stimulates the release of Secretin?
What stimulates the release of Secretin?
Which hormone is responsible for stimulating motility in the gastrointestinal tract?
Which hormone is responsible for stimulating motility in the gastrointestinal tract?
Where is Gastric inhibitory polypeptide produced?
Where is Gastric inhibitory polypeptide produced?
Which hormone is released primarily in response to acetylcholine?
Which hormone is released primarily in response to acetylcholine?
What effect does Secretin have on gastric secretion?
What effect does Secretin have on gastric secretion?
What role do bile salts and phospholipids play in fat digestion?
What role do bile salts and phospholipids play in fat digestion?
How do monoglycerides and fatty acids enter absorptive cells?
How do monoglycerides and fatty acids enter absorptive cells?
What happens to the sphincter of Oddi when fat is present in the duodenal lumen?
What happens to the sphincter of Oddi when fat is present in the duodenal lumen?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder regarding bile secretion?
What is the primary function of the gallbladder regarding bile secretion?
What type of digestion is primarily involved in breaking down food into absorbable units?
What type of digestion is primarily involved in breaking down food into absorbable units?
What does the secretion from the small intestine mainly consist of?
What does the secretion from the small intestine mainly consist of?
What is the role of mechanical digestion in the digestive system?
What is the role of mechanical digestion in the digestive system?
What triggers the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) in the digestive process?
What triggers the secretion of cholecystokinin (CCK) in the digestive process?
Flashcards
Mucosa
Mucosa
The innermost layer of the gastrointestinal tract (GIT). It's made of epithelial cells that line the inside of the GIT and have a protective role, secretion, and absorption.
Submucosa
Submucosa
The layer beneath the mucosa, containing loose connective tissue and the submucosal plexus. This plexus provides the GIT with distensibility and elasticity.
Villi
Villi
Small finger-like projections that extend into the lumen of the small intestine. They increase the surface area for absorption and digestion.
Microvilli
Microvilli
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enterocytes
Enterocytes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Crypts of Lieberkühn
Crypts of Lieberkühn
Signup and view all the flashcards
Large intestine
Large intestine
Signup and view all the flashcards
Dysbiosis
Dysbiosis
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract
Signup and view all the flashcards
Ingestion
Ingestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Digestion
Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Motility
Motility
Signup and view all the flashcards
Phasic Contraction
Phasic Contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Tonic Contraction
Tonic Contraction
Signup and view all the flashcards
Enteric Nervous System
Enteric Nervous System
Signup and view all the flashcards
Serosa
Serosa
Signup and view all the flashcards
What are digestive secretions?
What are digestive secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Name the main salivary glands.
Name the main salivary glands.
Signup and view all the flashcards
What type of saliva does the parotid gland produce?
What type of saliva does the parotid gland produce?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the purpose of HCl in gastric secretions?
What is the purpose of HCl in gastric secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of pepsinogen in gastric secretions?
What is the role of pepsinogen in gastric secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of mucus in gastric secretions?
What is the function of mucus in gastric secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the function of intrinsic factor in gastric secretions?
What is the function of intrinsic factor in gastric secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
What is the role of gastrin in gastric secretions?
What is the role of gastrin in gastric secretions?
Signup and view all the flashcards
Carbohydrate Digestion
Carbohydrate Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Protein Digestion
Protein Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fat Digestion
Fat Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Absorption
Absorption
Signup and view all the flashcards
Defecation
Defecation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Tract Functions
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Tract Functions
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidase
Trypsin, Chymotrypsin, Carboxypeptidase
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile Salts
Bile Salts
Signup and view all the flashcards
Emulsification of fats
Emulsification of fats
Signup and view all the flashcards
Bile
Bile
Signup and view all the flashcards
Sphincter of Oddi
Sphincter of Oddi
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Cholecystokinin (CCK)
Signup and view all the flashcards
Chemical Digestion
Chemical Digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Brush border enzymes
Brush border enzymes
Signup and view all the flashcards
Mechanical digestion
Mechanical digestion
Signup and view all the flashcards
Secretin
Secretin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastrin
Gastrin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cholecystokinin
Cholecystokinin
Signup and view all the flashcards
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide
Gastric Inhibitory Polypeptide
Signup and view all the flashcards
Intrinsic System of Regulation
Intrinsic System of Regulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
GIT Endocrine Hormones
GIT Endocrine Hormones
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Physiology (0603302)
- Course name: Physiology
- Chapter: Gastrointestinal system
- Semester: Summer 2023/2024
- Instructor: Dr. Mohammad A. Abedal-Majed
- Institution: The University of Jordan, School of Agriculture
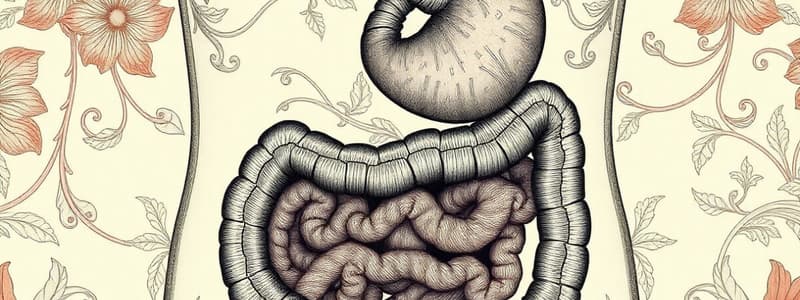
The Digestive System
- The gastrointestinal (GI) system is responsible for providing the body with nutrients and electrolytes from outside the body to maintain homeostasis.
Structure of the Gastrointestinal System
- The digestive system consists of two main parts:
- GI tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, and anus)
- Accessory glandular organs (salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, exocrine and endocrine glands)
Mouth
- Contains muscles for mechanical digestion
- Salivary glands secrete saliva for lubrication, food degradation, and carbohydrate digestion
- Carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth with salivary amylase.
- Food passes through the pharynx, a passageway for food and connecting the GI and respiratory system.
- The esophagus carries food rapidly.
- Minimal absorption occurs except for some drugs.
Stomach
- Contains a special lining that secretes digestive juices (pepsinogen and HCl acid) for protein digestion.
- Digestive enzymes originate within gastric pits.
- Gastric pits contain cells that secrete HCL and pepsinogen.
- Strong muscular walls mix food and digestive juices.
- Food moves from the stomach to the small intestine through the pylorus sphincter.
Small Intestine
- Contains enzymes from the pancreas and small intestine for further food digestion.
- Villi and microvilli increase surface area for absorption and digestion.
- Cells lining villi and microvilli (enterocytes) help with carbohydrate and protein digestion.
- Villi cells renew every 2-3 days from stem cells in the crypts.
- Microvilli (brush border) contain enzymes that aid in carbohydrate and protein digestion.
Large Intestine
- Absorbs a small amount of water and electrolytes.
- Contains beneficial bacteria for vitamin K production and lipid molecule processing.
- Patients with issues in beneficial bacteria may develop health problems like diabetes and obesity.
- Compacts and forms feces for elimination.
- Fiber in the diet aids in movement for constipation prevention.
Structure of the Gastrointestinal System (Layers)
- Mucosa: The innermost layer of the GI tract, composed of epithelial cells lining the tract, which plays a protective role, and is responsible for secretion and absorption.
- Submucosa: The layer below the mucosa, containing connective tissue and a network of neurons called the submucosal plexus, enabling the tract to expand and contract.
Muscle Layer
- Two perpendicular smooth muscle layers:
- Inner, thick circumferential layer for constricting and narrowing the lumen.
- Outer longitudinal layer for shortening the lumen.
- The GI tract is largely under involuntary control, but the mouth and end of the rectum are under voluntary control.
- The enteric nervous system (network of neurons) regulates the GI tract functions.
- Serosa: The outermost layer, a thin layer of connective tissue that lubricates and prevents friction with neighboring structures.
Processing of Food (General)
- Ingestion: The process of eating.
- Digestion: Chemical and mechanical breakdown of food.
- Motility: Muscular contractions in the digestive tract for mixing food and propelling it through the digestive tract (peristalsis.)
- Phasic contractions: Short, alternating contractions that propel food (e.g., peristalsis.)
- Segmental contractions: Move food back and forth for mixing with digestive juices.
- Tonic contractions: Long, sustained contractions found at sphincters.
Processing of Food and Secretion
- Secretion: Glands release substances like water, electrolytes, enzymes, bile salts, and mucus into the digestive tract.
- It's an energy-dependent process mediated by neural or hormonal stimulation.
- Specific examples of fluid and volume secretion include saliva, gastric, bile, and pancreatic secretions.
Gastric Gland Cells
- Exocrine cells
- Parietal cells secrete HCl acid and intrinsic factor.
- Chief cells secrete pepsinogen (converted to pepsin by HCl) for protein digestion.
- Mucous neck cells secrete mucus for protection.
- Pyloric gland contains G cells that secrete gastrin (stimulates parietal cell activity), and mucus.
- Cardiac glands secrete alkaline mucus.
- Endocrine cells include G and D cells.
Stomach Acid (HCl) Secretion
- Parietal cells actively transport H+ (hydrogen ions) into the gastric lumen.
- Cl- (chloride ions) are transported and actively join H+ in the lumen.
- Carbonic anhydrase regulates this process.
HCl Functions
- Activates digestive enzymes.
- Breaks down connective tissue.
- Denatures proteins.
- Kills ingested microorganisms.
Pepsinogen Secretion
- Present in chief cells, is released by regulated exocytosis.
- Pepsinogen is inactive; HCl converts it to the active pepsin enzyme used in protein digestion.
- Autocatalysis: Pepsin also cleaves pepsinogen, forming more active pepsin.
Intrinsic Factor
- Secreted by parietal cells.
- Forms a complex with vitamin B12, enabling its absorption in the intestines.
Gastric Mucosal Barrier
- Luminal membranes of gastric cells are impermeable to H+.
- Tight junctions prevent HCL from passing between cells.
- Mucus coating provides a physical barrier.
- HCO3- rich mucus serves as a chemical barrier by neutralizing acid near epithelial cells.
Pancreatic Secretion
- Endocrine part secretes insulin and glucagon (blood sugar control.)
- Exocrine part secretes digestive enzymes and bicarbonate.
- Secretion is stimulated and regulated by hormones like secretin and cholecystokinin.
Bile Secretion (Liver)
- Bile salts and phospholipids emulsify fats into smaller pieces, aiding in lipase access and digestion.
- Bile is produced by the liver and stored in the gallbladder.
- The Sphincter of Oddi controls bile entry into the duodenum.
- 95% of bile salts are recycled via enterohepatic circulation.
Small Intestine Secretion
- Aids in lubrication and facilitates enzymatic digestion.
- Doesn't secrete digestive enzymes, but the enterocytes (cells lining the villi and microvilli) contain digestive enzymes assisting with the absorption of digested nutrients from the lumen into the blood or lymphatic system.
Digestion (Overview
- Mechanical digestion: Chewing, mixing, churning in the stomach
- Chemical Digestion: Actions by enzymes in digestive juices.
Digestion: Overview (Table)
- Table summarizes the digestion processes for carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Carbohydrate Digestion
- Breaks down complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, and fructose) for absorption.
- Salivary amylase and pancreatic amylase are involved in the initial breakdown.
- Intestinal enzymes (sucrase, maltase, and lactase) further break down disaccharides to monosaccharides.
Protein Digestion
- Breaks down proteins into amino acids for absorption.
- Pepsin acts in the stomach, breaking down protein.
- Pancreatic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase) and intestinal aminopeptidases and carboxypeptidases continue the breakdown in the small intestines.
Fat Digestion
- Bile salts emulsify fat globules, increasing surface area for lipase action.
- Lipase breaks down triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides for absorption.
Absorption
- The passage of digested nutrients into the bloodstream (or lymph) for the body to use.
- Most occurs in the small intestine (specialized villi and crypts.)
Defecation
- Elimination of indigestible food substances.
Regulation of Gastrointestinal Tract Functions
- Intrinsic (intrinsic nervous system and endocrine cells in digestive tract walls) and extrinsic (nervous system and endocrine systems outside digestive tract) controls.
- Hormones like secretin and gastrin regulate various digestive functions.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.