Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle originates from the medial epicondyle and crosses over the elbow joint?
Which muscle originates from the medial epicondyle and crosses over the elbow joint?
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Palmaris longus
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Pronator teres (correct)
Which of the following muscles is considered a guide to the ulnar artery and nerve?
Which of the following muscles is considered a guide to the ulnar artery and nerve?
- Pronator teres
- Flexor carpi ulnaris (correct)
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus
What is the correct order of the muscles from lateral to medial as they cross the elbow joint?
What is the correct order of the muscles from lateral to medial as they cross the elbow joint?
- Flexor carpi radialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi ulnaris, palmaris longus
- Pronator teres, palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, flexor carpi ulnaris
- Pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, flexor carpi ulnaris (correct)
- Palmaris longus, flexor carpi radialis, pronator teres, flexor carpi ulnaris
Which muscle listed has been indicated as 'Fail' regarding its function or status?
Which muscle listed has been indicated as 'Fail' regarding its function or status?
Which muscle is positioned medially to the flexor carpi radialis?
Which muscle is positioned medially to the flexor carpi radialis?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
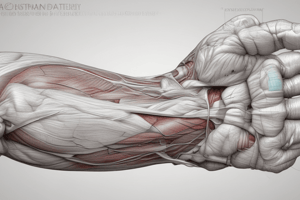
Superficial Group of Forearm Muscles
- Originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus.
- Comprises muscles that cross the elbow joint.
Muscle Organization from Lateral to Medial
- Pronator Teres
- Functions to pronate the forearm.
- Passes superficial to the flexor muscles.
- Flexor Carpi Radialis
- Acts on wrist flexion and radial deviation.
- Serves as a landmark for identifying the radial artery.
- Positionally fails to cross the elbow joint.
- Palmaris Longus
- Not universally present; absent in some individuals.
- Aids in wrist flexion, primarily passes through distal structures.
- Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
- Important for wrist flexion and ulnar deviation.
- Serves as a guide to the ulnar artery and nerve.
- Fails to cross the elbow joint.
Anterior View of the Forearm
- Illustrates the superficial muscles and their organization.
- Demonstrates the functional anatomy critical for forearm movements.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.