Podcast
Questions and Answers
Which muscle is not supplied by the median nerve in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which muscle is not supplied by the median nerve in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
- Flexor digitorum profundus (medial half) (correct)
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Brachialis
- Flexor digitorum profundus (lateral half)
Which structure does the ulnar artery cross lateral to, as it enters the hand?
Which structure does the ulnar artery cross lateral to, as it enters the hand?
- Ulnar nerve and pisiform bone (correct)
- Brachial artery and bicipital aponeurosis
- Median nerve and flexor retinaculum
- Radial nerve and flexor carpi radialis
Which of the following veins forms a deep venous arch in the hand?
Which of the following veins forms a deep venous arch in the hand?
- Ulnar vein and radial vein (correct)
- Median vein and brachial vein
- Basilic vein and cephalic vein
- Vena comitantes and deep venous arch
In which part of the forearm is the radial artery medial to the brachioradialis muscle?
In which part of the forearm is the radial artery medial to the brachioradialis muscle?
Which branch of the ulnar artery supplies the wrist?
Which branch of the ulnar artery supplies the wrist?
Which of the following muscles is NOT associated with the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles is NOT associated with the anterior compartment of the forearm?
What is the primary function of the interosseous membrane in the forearm?
What is the primary function of the interosseous membrane in the forearm?
Which nerve is NOT found in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which nerve is NOT found in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
What is the lateral intermuscular septum responsible for in the forearm?
What is the lateral intermuscular septum responsible for in the forearm?
Which artery is NOT found in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which artery is NOT found in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the coronoid process of the ulna?
Which of the following muscles originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus and the coronoid process of the ulna?
Which nerve innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle?
Which nerve innervates the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle?
Which of the following muscles is located in the intermediate layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following muscles is located in the intermediate layer of the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which structure separates the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm?
Which structure separates the anterior and posterior compartments of the forearm?
Which of the following arteries is NOT located in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Which of the following arteries is NOT located in the anterior compartment of the forearm?
Flashcards are hidden until you start studying
Study Notes
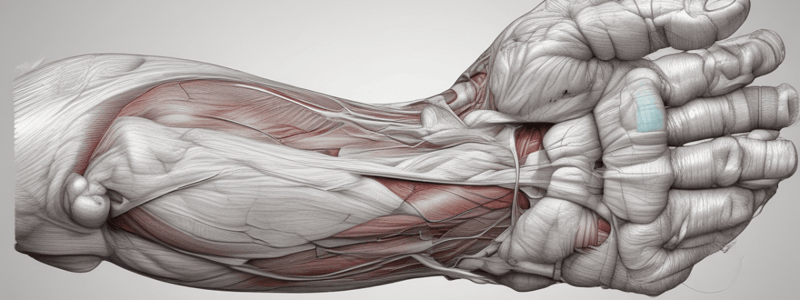
Muscles of the Forearm
Superficial Layer
- Consists of four muscles: pronator teres, flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor carpi ulnaris:
- Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus, olecranon, and posterior border of ulna
- Insertion: pisiform bone, hamate, and base of metacarpal V
- Innervation: ulnar nerve (C7, C8, T1)
- Action: flexes and adducts the wrist joint
- Palmaris longus:
- Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
- Insertion: palmar aponeurosis of hand
- Innervation: median nerve (C7, C8)
- Action: flexes the wrist joint
- Flexor carpi radialis:
- Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus
- Insertion: base of metacarpals II and III
- Innervation: median nerve (C6, C7)
- Action: flexes and pronates the wrist joint
- Pronator teres:
- Origin: medial epicondyle of humerus, medial margin of coronoid process, and adjacent supraepicondylar ridge
- Insertion: lateral surface of mid-shaft of radius
- Innervation: median nerve (C6, C7)
- Action: flexes and abducts the forearm
Intermediate Layer
- Consists of one muscle: flexor digitorum superficialis
- Flexor digitorum superficialis:
- Origin: humero-ulnar head, medial epicondyle of humerus, and adjacent margin of coronoid process
- Insertion: four tendons to the palmar surfaces of the middle phalanges of the index, middle, ring, and little fingers
- Innervation: median nerve (C8, T1)
- Action: flexes the proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and the wrist joint
Deep Layer
- Consists of three muscles: flexor digitorum profundus, flexor pollicis longus, and pronator quadratus
- Flexor digitorum profundus:
- Origin: anterior and medial surfaces of ulna and interosseous membrane
- Insertion: four tendons to the palmar surfaces of the distal phalanges of the fingers
- Innervation: lateral half by median nerve (C8, T1), medial half by ulnar nerve (C8, T1)
- Action: flexes the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and the wrist joint
- Flexor pollicis longus:
- Origin: anterior surface of radius and radial half of interosseous membrane
- Insertion: palmar surface of the base of the distal phalanx of the thumb
- Innervation: median nerve (C7, C8)
- Action: flexes the interphalangeal joint of the thumb
- Pronator quadratus:
- Origin: linear ridge on the distal anterior surface of ulna
- Insertion: distal anterior surface of radius
- Innervation: median nerve (C7, C8)
- Action: pronates the forearm
Blood Vessels
Arteries
- Ulnar artery:
- Origin: brachial artery
- Branches:
- Anterior and posterior ulnar recurrent arteries
- Common interosseous artery
- Cutaneous branches
- Muscular branches
- Dorsal carpal branch and palmar carpal branch
- Radial artery:
- Origin: brachial artery
- Branches:
- Radial recurrent artery
- Cutaneous branches
- Muscular branches
- Palmar carpal branch
- Superficial palmar branch
Veins
- Superficial veins:
- Basilic vein
- Cephalic vein
- Median vein
- Deep veins:
- Ulnar vein
- Radial vein
- Deep venous arch in the hand forming vena comitantes
Nerves
- Median nerve:
- Supplies all muscles except FCU and medial half of FDP
- Innervates the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
- Has a straight linear course in the fascia on the deep surface of the flexor digitorum superficialis muscle
Forearm
- Extends from the elbow to the wrist
- Contains two bones: radius and ulna, joined by an interosseous membrane
- Divided into anterior and posterior compartments by:
- Lateral intermuscular septum
- Interosseous membrane
- Attachment of deep fascia along the posterior border of the ulna
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.