Podcast
Questions and Answers
What are the two sources from which the placenta develops?
What are the two sources from which the placenta develops?
- Fetal part and maternal part (correct)
- Amniotic fluid and umbilical cord
- Tissues and hormones
- Egg and sperm
The placenta functions only as a source of nutrients for the fetus.
The placenta functions only as a source of nutrients for the fetus.
False (B)
What role does amniotic fluid play during pregnancy?
What role does amniotic fluid play during pregnancy?
It provides protection, allows fetal movement, equalizes pressure, and maintains temperature.
The __________ connects the placenta to the fetus.
The __________ connects the placenta to the fetus.
What does the placenta dispose of from the fetus?
What does the placenta dispose of from the fetus?
Match the following functions of women and fetus with their corresponding roles:
Match the following functions of women and fetus with their corresponding roles:
Fetal movement is infrequent during weeks 13-16 of development.
Fetal movement is infrequent during weeks 13-16 of development.
What common substance accumulates in the intestines of the fetus by week 16?
What common substance accumulates in the intestines of the fetus by week 16?
What is the correct order of the prenatal development stages?
What is the correct order of the prenatal development stages?
The morula is a blastocyst that has formed after cleavage.
The morula is a blastocyst that has formed after cleavage.
What happens during cleavage division?
What happens during cleavage division?
The inner cell mass of the morula develops into the ______.
The inner cell mass of the morula develops into the ______.
What is the primary role of the decidua after implantation?
What is the primary role of the decidua after implantation?
Match the germ layers with what they develop into:
Match the germ layers with what they develop into:
What signifies the beginning of the embryonic period?
What signifies the beginning of the embryonic period?
The blastocyst implants into the endometrium around the 10th day after fertilization.
The blastocyst implants into the endometrium around the 10th day after fertilization.
Flashcards
Placenta: The Lifeline of Pregnancy
Placenta: The Lifeline of Pregnancy
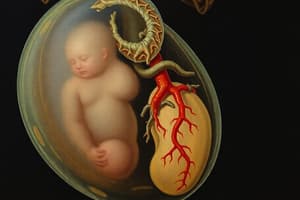
The placenta is a vital organ that connects the developing fetus to the mother's uterus. It plays a crucial role in delivering oxygen and nutrients to the fetus while removing waste products.
Placenta: Two Parts
Placenta: Two Parts
The placenta is composed of two parts: the fetal part, which originates from the embryo, and the maternal part, which originates from the uterus.
Placenta: Multi-Tasker
Placenta: Multi-Tasker
The placenta functions like a miniature kidney, lung, and digestive system for the fetus. It filters waste, provides oxygen, and delivers nutrients.
Amniotic Fluid
Amniotic Fluid
Signup and view all the flashcards
Functions of Amniotic Fluid: Protection and Movement
Functions of Amniotic Fluid: Protection and Movement
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Circulation
Fetal Circulation
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Development: Weeks 9-12
Fetal Development: Weeks 9-12
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Movement: Quickening
Fetal Movement: Quickening
Signup and view all the flashcards
Germinal Period
Germinal Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryonic Period
Embryonic Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Fetal Period
Fetal Period
Signup and view all the flashcards
Cleavage Division
Cleavage Division
Signup and view all the flashcards
Morula
Morula
Signup and view all the flashcards
Blastocyst
Blastocyst
Signup and view all the flashcards
Trophoblast
Trophoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Embryoblast
Embryoblast
Signup and view all the flashcards
Study Notes
Fetal Development Overview
- Life begins at fertilization of the ovum.
- A zygote forms, a single cell that develops into a fully formed adult.
- Prenatal development is the process of gestation from fertilization to birth.
Fertilization
- Also known as conception.
- Fusion of a sperm cell and a secondary oocyte to form a zygote.
- Typically takes about 24 hours.
- Usually occurs in the ampulla of the uterine tube.
Gestation Period
- Germinal period: Starts at fertilization, lasts until the third week.
- Embryonic period: From the 4th to the 8th week, marked by changes in shape and external appearance.
- Fetal period: From the 3rd month until termination of pregnancy.
Development of Supportive Structures & Major Events
- Fertilization: The union of sperm and egg.
- Cleavage Division: Repeated mitotic divisions increasing the number of cells (blastomeres).
Formation of Morula and Blastocyst
- Blastomeres form a compact ball called a morula.
- The center of the morula is the inner cell mass.
- The morula develops into a blastocyst, continuing to divide.
- The blastocyst includes a blastocele (fluid-filled cavity) and two cell layers: trophoblast (outer layer) and embryoblast (inner cell mass)
- The Zygote is called a blastocyst during this stage.
Implantation of Blastocyst
- The blastocyst attaches to the endometrium.
- Implantation occurs around 6-7 days after fertilization.
- The endometrium prepares to support the pregnancy, becoming the decidua.
The Decidua
- The corpus luteum continues producing progesterone.
- Progesterone stimulates the endometrial glands and increases the size of the blood supply.
- After implantation, the decidua is categorized into three specific sections:
- Basal decidua: Underneath the blastocyst.
- Capsular decidua: Thin superficial layer covering the ovum.
- Parietal decidua: The rest of the decidua lining the uterine cavity outside the implantation site.
Functions of Decidua
- Provides a bed for implantation.
- Provides nutrition for the early stages of the growing ovum.
Formation of Germ Layers
- First major event after implantation
- Three layers form:
- Ectoderm (forms skin and nervous system).
- Mesoderm (forms bone, muscle, heart, and blood vessels).
- Endoderm (forms mucus membranes and glands).
- These layers are collectively known as embryonic plates.
Development of Placenta
- Develops from two sources: the fetal and maternal parts.
Placenta
- Function: For nine months, the placenta nourishes the fetus and removes toxic waste.
- Similar to an artificial kidney, the placenta enables blood to exchange nutrients and oxygen between the mother and baby.
- Also acts as a lung, kidney, and digestive system for the fetus.
- Protects the developing fetus from possible infection.
Amniotic Fluid
- Clear, slightly yellowish liquid surrounding the fetus within the amniotic sac.
- Functions: Protects the embryo from shock, blows or pressure, allows the embryo to float, equalizes pressure, facilitates fetal movement, maintains a constant temperature, aids in cervical effacement and dilation of the uterine os, and provides nutrients.
Fetal Circulatory System
- Integrated with the placenta via the umbilical cord.
- Allows the fetus to receive oxygen and nutrients from the placenta.
Other Organ Systems (Weeks 9-12)
- Brain: Continues to expand.
- Body: Elongates.
- Ossification: Continues.
- Fetal Movement: Frequent throughout this period.
- Bone Marrow: Begins to take over erythrocyte production.
- Liver: Secretes bile.
- Amniotic Fluid Circulation: Fetus swallows amniotic fluid and produces urine.
- Eyes: Develop.
- Fingernails/Toenails: Begin to form.
- Fetus Size: Approximately 9cm by the end of week 12.
Other Organ Systems (Important developmental milestones)
- Weeks 13-16: Sensory organs develop, lips exhibit sucking motions, hair growth on scalp, meconium accumulation begins.
- Weeks 16-20: Fetus grows, limb movements become more powerful, quickening (mother feels fetal movement) can begin.
- Weeks 21-30: Rapid weight gain. Bone marrow takes over erythrocyte synthesis. Temperature regulation becomes important for the baby after birth. The skin develops a waxy, protective coating called vernix caseosa.
- 33 Weeks: Male testicles descend into the scrotum. Eyes are open
- Week 35-40: Fetus grows to approximately 40-46cm in length and weighs between 1800-1900 grams. Fetus is "full term" at 37 weeks.
- 40 Weeks: Much of vernix is gone. Lungs continue to develop, the fetus measures approximately 51cm and weighs around 3400 grams. Baby is ready to be born any time.
Studying That Suits You
Use AI to generate personalized quizzes and flashcards to suit your learning preferences.